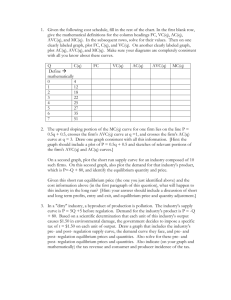
Document
advertisement

Competitive Markets
Structure
• Fragmented
• Undifferentiated Products :
Homogeneous
• Perfect Information about Price
• Equal Access to Resources
Three Implication
• Price Takers
• Law of one Price
• Free Entry & Free Exit
Profit Maximization
(q) TR(q) TC (q)
Max (q) Max{TR(q) TC (q)}
Profit Maximization Condition
d (q )
0
dq
d
dTR(q) dTC (q)
0
dq
dq
dq
dTR(q)
MR
dq
dTC (q)
MC
dq
MR MC
Slope(TR) Slope(TC )
TR
TR,TC
TC
Profit
0
Q
MC
MR = P
0
Q
MC > MR
MC < MR
MC = MR
MC > MR
Price
Firm
Price
Industry
AR = P = MR
D
Q
Q
Price
MC
AC
A
P1
MR = P
Excess Profit
AVC
C
B
0
Q
Q
Price
AC
MC
P1
A
AVC
C
0
MR = P
Q
Q
Price
MC
B
AC
AVC
C
Loss
P1
0
A
MR = P
Q
Q
Price
MC
AC
B
C
AVC
Loss
A
MR = P
P1
0
Q
Q
Price
MC
AC
B
C
AVC
Loss
MR = P
P1
A
0
Q
Q
Price
MC
AC
P1
AVC
P2
P3
P4
Shut Down Point
0
Q
Price
Firm’s Supply
MC
AC
P1
AVC
P2
P3
P4
Shut Down Point
0
Q
Example
The Firm’s short run total cost curve is
STC = 100 +20Q + Q2.
The short run Marginal cost curve is
SMC = 20 + 2Q
If SFC = 100, while SVC = 20Q + Q2
Find AVC , Minimum level of average
variable cost, supply curve
Fixed Cost + Sunk Cost
TFC = SFC + NSFC
NSFC
ANSC=AVC+
Q
Price
MC
AC
ANSC
AVC
B
C
P1
Minimum ANSC = P
A
0
Q
Q
Example
The Firm’s short run total cost curve is
STC = 100 +20Q + Q2.
The short run Marginal cost curve is
SMC = 20 + 2Q
If SFC = 36, while NSFC = 64
Find ANSC , Minimum level of average non sunk
cost, supply curve
Firm Supply and Market Supply
Firms
P
Market
P
p
Q1
Q2
Q
Q1+Q2
Q
Short Run perfectly Competitive
equilibrium
S1 ( P ) S2 ( P ) .... Sn ( P ) D( P )
*
*
*
P
*
P
S
SAC
P*
D
Q*
Q
D(P*)
Q
The Market consists of 300 identical firms, and the
market demand curve is given by
D(P) = 60 – P.
Each firm has a short run cost curve
STC = 0.1 + 150Q2 , all fixed cost are sunk.
The corresponding short run marginal cost curve
SMC = 300Q.
The corresponding average variable cost curve is
AVC = 150Q.
You should verify that the minimum level of AVC is
0. Thus, a firm will continue to produce as large as
price is positive
Find Short run equilibrium in market, at equilibrium,
do the firm make positive profit?
Comparative Statics in short run
Increase in the number of firm
P
P
S
SAC
S’
P1
P2
D
Q2f Q1f
Q
Q1 Q2
Q
Long Run – Plant Adjustment
Price
MC2
MC1
SAC2
LMC
P1
SAC1
LAC
Quantity
Q1
Q2
Long Run Supply Curve
Price
LMC
LAC
P1
P2
P*
Quantity
Q*
Q2
Q1
Long Run Supply Curve
Price
LMC
LAC
P1
P2
P*
Quantity
Q*
Q2
Q1
Free Entry and Long Run
1. Long Run Profit is maximized with respect to
output and plant size.
P* = MC ( Q* )
2. Economic profit is Zero.
P* = AC ( Q* )
Free Entry and Long Run
3. Demand equals Supply.
D( P* ) = n Q*
P
SMC
LAC
P
LMC
S
SAC
P*
D
Q*
Q
D(P*) = n*Q*
Q
In this market, each firm and potential entrant has
a long – run average cost
AC( Q ) = 40 – Q – 0.01Q2.
And a corresponding long run marginal cost curve
MC( Q ) = 40 – 2Q + 0.03Q2.
Where Q is thousand units per year. The Market
demand curve is
D( P ) = 25,000 – 1,000P,
Where D(P) is also measured in thousand units.
Find the long run equilibrium price, quantity per
firm, and number of firms.
Long Run Market Supply Curve
P
P
LMC
S
LAC
P2
S’
SAC
A
B
P1
D’
D
Q1f Q2f
Q
Q1
Q2
Q
Industry Long Run Supply Curve
Constant Cost
P
P
LMC
S
S’
LAC
P2
A
SL
B
P1
D’
D
Q1f Q2f
Q
Q1
Q2
Q
Industry Long Run Supply Curve
Increasing Cost
P
P
LMC2
LAC2
S
LMC1
S’
LAC1
P2
P3
SL
P1
D’
D
Q1f Q2f
Q
Q1
Q2
Q
Problem 1
The bolt industry currently consists of 20 producers,
all of whom operate with identical short run total
cost function
STC ( Q ) = 16 + Q2
Where Q is the annual output. The corresponding
short run marginal cost curve is
SMC ( Q ) = 2Q
The market demand for the bolts is
D ( P ) = 110 – P
Where P is the market price
a ) Assuming that all of the firm fixed cost is sunk,
what is the firm’s short run supply curve?
b ) What is the short run market supply curve?
c ) Determine the short run equilibrium price and
quantity in the industry.
Problem 2
Propylene is used to make plastic. The propylene
industry is perfectly competitive, and each producer
has a long run marginal cost function given by
MC ( Q ) = 40 – 12Q + Q2
The corresponding long run average cost function
is
AC ( Q ) = 40 – 6Q + (1/3)Q2
The market demand curve for propylene is
D ( P ) = 2200 – 100P
a ) What is long run equilibrium price in the industry?
b ) At this price, how much would an individual firm
produce?
c ) How many firms are in the propylene market in
long run competitive equilibrium.
d ) Suppose the demand curve shifted so that it is
now D ( P ) = A – 100P. How large would A have to
be so that in the new long run competitive
equilibrium, the number of propylene firms was
twice what it was in the initial long run equilibrium?.
Problem 3
The long run total cost function for producers of
mineral water is
TC ( Q ) = cQ
Where Q is the output of individual firm expressed
as thousand liters per year. The market demand
curve is
D ( P ) = a – bP
Find the long run equilibrium price and quantity in
term of a, b, c, . Can you determine the equilibrium
number of firms? If so, what is it? Why not?