Measurement of Bioreactor KLa
advertisement

Measurement of Bioreactor
KL a
Motivations
1.
Biotech/pharmaceutical
industry employing more
Chemical Engineers
• Process
Engineering
• Validation
• Management
• Pilot testing
• Scale-up
2.
Good example of
mass transfer at gasliquid interface
3.
Experience modeling
in both semiempirical and
factorial methods
Types of Products
• Natural Products
– Drugs
•
•
•
•
Penicillin is early example
Taxol
Mupricin
Cyclosporin A, etc.
– Foods
• Fermented beverages
• Fermented dairy products
Types of Products
• Transgenic Products
– Gene for a therapeutic protein inserted in
foreign expression system
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Factor IX
a-1-antitrypsin
EPO
Antibodies
antithrombin III
tissue plasminogen activator (TPA)
Interferons, etc.
Expression Systems
•
•
•
•
•
Bacterial Cells
Fungal Cells
Plant Cells
Insect Cells
Mammalian Cells
Types of Bioreactors (fermenter)
(often depends on shear sensitivity)
• Stirred tank
– Aerobic or Anaerobic (air-sparged if aerobic)
– Most common for bacterial cells
• Bubble or airlift column
– Good for shear-sensitive cells
• Fixed bed systems
– Trickle beds, hollow membrane fiber
(mammalian cells), etc.
Industrial Stirred Fermenter
Experimental Apparatus
Transport in Bioprocess Systems
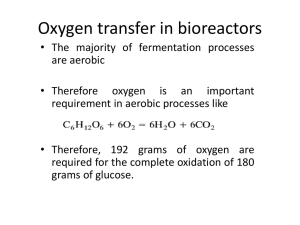
Why is KLa Important?
• Dissolved oxygen is an important
substrate in aerobic fermentations. Since
oxygen is sparingly soluble in water, it may
be the growth-limiting substrate in these
fermentations. For bacteria and yeast
cultures, the critical oxygen concentration
is about 10% to 50% of the saturated DO
(dissolved oxygen concentration).
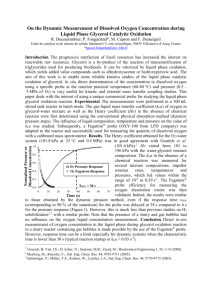
Equation for Transport
Oxygen transfer is usually limited by the liquid film surrounding the
gas bubbles:
mO2 kL a C* CL
where mO2 is the rate of oxygen transfer per volume of bioreactor (mass
O2/ L3 t), kL is the oxygen transport coefficient, [=]L/t, a is the gas-liquid
interfacial area per volume of reactor [=] L2/L3, kLa is the volumetric
oxygen transfer coefficient [=]1/t, C* is saturated DO (dissolved oxygen)
concentration [=] m/L3 (approx. 7 mg/l at 25 deg. C and 1 atm.), CL is the
actual DO concentration in the liquid [=] m/L3
Terms affecting rate
• KLa
– What we are trying to determine and correlate
with mixing speed and aeration rate
– Two quantities multiplied together
• Liquid side (essentially overall mass transfer
coefficient)
• Total area of bubbles in bioreactor
• Can’t be separated
Some Interactions Affecting Oxygen Transport in Aerobic Systems
Terms affecting rate
• C* (saturation oxygen concentration; max
solubility of the gas in liquid)
- Constant at a given T and P
- Available in tables (see on-line lab manual)
• CL (C(t)) the oxygen concentration at a
given time during the run; what we
measure
- {C*- CL} = “driving force”
Terms affecting rate
• KL -mass transfer coefficient
• a- interfacial area for mass transfer
Probe response rate needed to get
“real” CL(t) value
1. Gaseous oxygen dissolves in water at
bubble interface and disperses in the
bioreactor
2. Dissolved O2 crosses probe membrane
at tip.
3. O2 in probe is sensed and sent to meter
1
Time constant =1/kLa
2
Time constant =1/kp
3
Fast
Some Interactions Affecting Oxygen Transport in Aerobic Systems
Data Acquisition