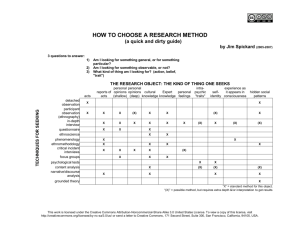
Evaluating an Emerging Technology
advertisement

Mediascapes: Collaborative work Environments Ashley Sherman ITEC 7445 Summer 2015 What is a Mediascape? This is a collaborative area that allows many users to use devices at one time, and some areas even allow multiple devices to be connected at once. There are typically one or multiple screens for easy viewing and multiple connections for a variety of devices. What does a Mediascape look like? Below is an example from The University of Washington Libraries (n.d.): Vision A mediascape in our learning commons will support the Cobb County Technology Plan (2011) and vision by ensuring that “ students will use technology to connect and collaborate with classmates, educators, and experts around the world” (p.3). With the purchase of a mediascape and appropriate sitting, entire classes could make use of the technology to videoconference or connect with other classes in Cobb county and around the world. Vision cont’d The addition of a mediascape will also support the Frey Elementary Strategic Plan (2014) by helping to “develop, implement, and support new plans and/or programs that focus on student-centered learning, higherorder thinking, and problem solving in the classroom.” Students will have the opportunity to work through authentic issues and situations collaboratively to promote higher-order thinking skills and promote problem solving. Planning and Diffusion The first mediascape would be in the newly renovated learning commons in classroom area/teaching area two. The mediascape can be requested for classroom teacher use as well as media specialist use for instruction on the learning commons sign-up. When not in use by whole-class instruction, students can use the area for small group work, collaboration, or presentations. The use of the mediascape will be documented in the monthly usage data for the learning commons. Planning and Diffusion cont’d All students will receive appropriate training and work time with the mediascape space during learning commons orientation. Teachers will also receive training in addition to the area TTIS and local tech. Funding Frey Elementary’s Foundation supports the STEM program as well as the addition and maintenance of other school technology. The foundation would be the first source of funding. Media center funds can also be used to purchase the technology as well as other equipment as needed (VGA cables, AC adapters, etc.) because these items would remain in the media center/learning commons area. A certain percentage of the media center budget can also purchase flexible seating as needed. Funding cont’d For the mediascape screens and installation, the school instructional funds could be used for this purchase in addition to any local funds the school may have, such as money from book fairs. Content Standards Based on the new Georgia Standards of Excellence (2015), the mediascape would support the following content standards by allowing students locate and work collaborate with digital resources. ELAGSEW6: With guidance and support from adults, use a variety of tools to produce and publish writing, including digital tools in collaboration with peers. ELAGSEW8: Recall information from experience or gather information from print or digital resources; take notes, categorize information, and provide a list of sources. Technology Standards The possibilities for the use of the mediascape in the learning commons are limitless, but the focus would be on the possibility of forms of collaboration. The ISTE (2014) standard for communication and collaboration states: Students use digital media and environments to communicate and work collaboratively, including at a distance, to support individual learning and contribute to the learning of others. Learner-Centered Strategies Strategies for using the mediascape in classroom and media center instruction are limitless. However, the technology and it’s uses allow for the highest level of small and whole group instruction and collaboration for students. According to Coastal Carolina University (2015), “ the technology [mediascape] that enables interactivity also allows users to seamlessly switch between feeds, taking away many of the barriers to collaborative work.” Learner-Centered Strategies cont’d Specific include: examples of collaboration Blogs (creation, responses, or global responses) Website/wiki creation by multiple users Collaborative multi-genre research projects Audio and video elements to projects completed simultaneously Authentic Learning The use of the mediascape allows for students and teachers to use the area to best meet their needs and for truly authentic learning experiences. Specific examples may include: If students are working as small group and are created a webpage, wiki, or blog, they can all work on a device at the same time and see edits on the larger screen of what classmates are doing. If being used by a whole class and the teacher uses lync or skype or talk with a class in another state or country, the students can view the feed and have other questions posted to another screen for discussion later. Higher Order Thinking Skills By using the mediascape and collaborative resources, students will be achieving the highest level of Bloom’s Taxonomy by analyzing, evaluating, and creating products. Examples of students demonstrating higher order thinking skills in the mediascape environment could include: Presenting opposing sides of an argument simultaneously for a comparison/contrast discussion Identifying alternative endings for a text that allow for discussion and questioning Differentiation In addition to collaboration, the mediascape allows students the opportunity to have access to resources and devices that appropriate for their specific learning needs. This technology and working space allows for differentiation, whether it be through using different resources to complete one culminating project or access to different interactive tools, and aligns with Frey’s (2014) goal to “differentiate resources for students based on needs.” Instructional Design Frey Elementary serves students in grade K-5 All classes and grades have access to the laptops, computer labs, and ipad carts as well as the media center/learning commons technology. All students would receive orientation on the mediascape and it’s uses during their learning commons orientation. Instructional Design cont’d While the primary grades (K-2) may not be using the mediascape for small group work, teachers can demonstrate and use the area for instructional purposes (presentations, video conferencing, etc.), and primary students would see the area in use. Upper grade students (3-5) would use the area for both whole group instruction and small group work and collaboration. Collaborative Learning Again, the mediascape allows for varied opportunities for student and even teacher collaboration. This space and technology would even allow for the opportunity for students to collaborate across disciplines and content while still meeting the technology standards. According to Educause (2011), this “will promote greater levels of collaboration in the learning commons. New services will emerge, expanding the opportunities for new, highly effective learning activities”(p. 2). Equipment/Software The equipment needed for a fully functioning mediascape is below along with vendors. No software is needed as a connection would be established through a wire or adapter. Mediascape screens X 2 (Steelcase) and installation VGA cables X 2 (amazon) Apple VGA adapter X 2 (amazon) Headphones (Supplied by media center as needed) Flexible/mobile sitting: optional 2 puzzle tables (steelcase) 8-10 chairs (steelcase) Technical Support The technology for the mediascape space would be purchased from the Cobb county approved bid list, and these vendors provide technical support and tutorials. The local tech, area TTIS and media specialist would be responsible for overseeing installation, receiving initial training, and providing teachers and students with tutorials and continued technical support. Limitations The specific area envisioned for a mediascape would make it a stationary technology that could only be used in one area of the learning commons. A mobile device where teachers could use it in their classrooms would be ideal. Frey isn’t a 1:1 device school, so students and teachers would be responsible for having a device from the school in order use the mediascape. All students may not have their own device to connect to the mediascape. Limitations cont’d Because of the cost of this technology, multiple mediascape areas may not be a viable option. All teachers may not have equitable access to the area because of the limited number of instructional slots per week the area could accommodate. Cost Costs below with vendors are approximate estimates: Mediascape screens X 2 (Steelcase) and installation, $8,099.00 VGA cables X 2 (amazon), $15.95 Apple VGA adapter X 2 (amazon), $29.00 Headphones (Supplied by media center as needed-already in media center inventory) Research The mediascape area in the learning commons provides a flexible space for learning where students can interact in small and whole groups settings. According to Partnership for 21st Century Skills (n.d.), “the flexible spaces that enable productive learning and shared work/play opportunities, the creative uses of time that promote continuous learning, the extensible technologies that support collaboration among the school community and the outside world—all these systems are valuable…” The mediascape technology is the model for flexible, innovative, and global learning. Communication The communication possibilities using the mediascape technology can address communication forms with multiple stakeholders (examples below): Student to student/peers: blog/edmodo responses, presentations Student to parents: creation of digital products and presentations accessible through various platforms at school and home, posting of digitally created materials to class blog or school website Student to larger community: video conferencing capabilities, debates or discussions across classrooms Safe, Healthy, Legal, and Ethical Issues All Cobb county students/parents must sign an Internet user agreement in addition to a video/photo release agreement. (All forms and agreements are signed at the beginning of the year or when the student registers, and they can be found on the CCSD website as well). This would allow students to use the mediascape for videoconferencing in a whole class setting and use internet-based digital tools as needed. Safe, Healthy, Legal, and Ethical Issues cont’d All students receive a lesson on Internet safety from the media specialist or the technology teacher, and Cobb county schools also has Internet filters in place as well as blocks inappropriate websites. Students in grade 2-5 also receive a media center lesson on copyright and plagiarism in order to understand how to put ideas into your own words or give the author credit of their ideas. Diversity The diverse needs of students will be met through the addition of a mediaspace area because this technology allows for individual, small group, and whole group instruction. Additionally, students will have access to the devices provided through the school, included headphones, laptop, and ipads, in order to use the mediaspace to best meet their needs. Professional Learning The local tech, area TTIS, and media specialist will train teachers about how to best use the mediascape for whole class instruction, and how to ask students to use it for small group work and collaboration. On-going professional development can be conducted by the media specialist as needed in order for teachers to integrate best practices with the mediascape. These professional development sessions can be a session at the monthly teacher professional development training as needed. Teachers can also use the mediascape when PD sessions are held in the learning commons to develop their mediascape knowledge. Continuous Learning While a mediascape in an elementary media center/learning commons environment is a fairly new concept, the options and possibilities are continuing to grow. The mediascape takes student assignments, presentations, debates, and discussions to another level because of the collaborative, interactive possibilities. Technology and applications to consider in conjunction with a mediascape or in the future would be Apple TV and Periscope for instructional uses. These resources could even jumpstart other possibilities for the mediascape work area and technology. Reflection cont’d Additionally, this space and technology can allow students to truly see collaboration and interaction on a school-wide, county, and possibly global level. Also, the mediascape promotes learning and inspires creativty, which aligns with Frey Elementary’s mission statement. Reflection While researching information about mediascapes and flexible learning environments for media centers/learning commons, I realized how vital these areas are for student engagement during instruction with the media specialist and classroom teachers. A flexible environment that can be altered to meet the student needs on an individual, small group, and whole class level is very important for meeting the diverse needs of a 21st century learner. References Coastal Carolina Univerisity. (2015). Technology in the Library and Commons. Retrieved from www.coastal.edu/library/commons/tools.html Cobb County School District. (2011). Three Year Technology Plan. Retrieved from http://www.cobbk12.org/centraloffice/Instruction alTechnology/TechPlan/2012_2015_CCSD_District_ Technology_Plan.pdf. Educause. (2011). 7 Things You Should Know About...The Modern Learning Commons. Retrieved from https://net.educause.edu/ir/librarypdf/ELI7071.pdf Frey Elementary School. (2014). School Strategic Plan-Elementary. Retrieved from from http://www.cobbk12.org/frey/SSP2014.pdf References cont’d Georgia Department of Education. (2015). Georgia Standards of Excellence. Retrieved from https://www.georgiastandards.org/GeorgiaStandards/Documents/ELA-Standards-Grades-K-5.pdf ISTE. (2014). ISTE Standards: Students. Retrieved from https://www.iste.org/docs/pdfs/20-14_ISTE_StandardsS_PDF.pdf. Partnership for 21st Century Skills. (n.d.). @1st Century Learning Environments. Retrieved from www.p21.org/storage/documents/le_white_paper-1.pdf University of Washington. (n.d.). Media Scape image. Retrieved http://commons.lib.washington.edu/resources/mediascape.