Climate Zones
advertisement

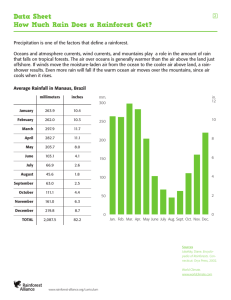
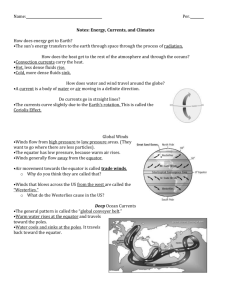
view the power point. -Record all notes and com in your notebook. - If a page doesn’t have a like this, just get the notes Climate Lesson What factors contribute to a region’s climate? Weather vs Climate? • Weather: Atmospheric conditions (temperature, rainfall, etc…) at a specific point in time • Climate: Atmospheric conditions (temperature, rainfall, etc…) of a region over a long period of time Houston • Weather - Climate Notes Template • Use this template to create your own notes from the Power point. Zones of Latitude Factors that affect climate Zones of Latitude - A region’s latitude (distance from the equator) can impact its climate. - Sketch the diagram below. Polar Temperate Tropical Tropical Temperate Polar Zones of Latitude • Tropical Zones: Warm weather year round. Area between the Tropic of Cancer (23 ½ º N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23 ½ º S). • Temperate Zones: Warm summers and cold winters (four seasons). Areas between Tropic of Cancer (23 ½ º N) and Arctic Circle (66 ½ º N) and Tropic of Capricorn (23 ½ º S) and the Antarctic Circle (66 ½ º S). • Polar Zones: Cold year round. Areas north of the Arctic Circle and south of the Antarctic Circle. 1. High Latitude = ______________ zone, _____ ° N _____ ° S, where is it? 2. Middle Latitude = _______________ zone, _____ ° N _____ ° S, where is it? 3. Low Latitude = _________________ zone, _____ ° N _____ ° S, where is it? POLAR 60°N 60°N TEMPERATE 30°N 30°N TROPICAL 30°S 30°S TEMPERATE 60°S 60°S POLAR 1. Which cities will have a temperate climate? 2. Which cities are warm year-round? What is this zone of latitude called? 3. Which cities are in the polar zone? Notes Template • Use this template to create your own notes from the Power point. Rain Shadows Zones of Latitude Topograph y Factors that affect climate Topography - Elevation • Elevation is the height above sea level • The higher the elevation of a region the cooler the temperature becomes. 19,341ft. Cooler Temperatures Warmer Temperatures Mt. Kilimanjaro Topography – Rain Shadows • Mountains can create orographic rainfall. • The windward side of the mountain is rainy while the leeward side is very dry. • Rain Shadows are desert regions created on the leeward side of the mountain Which side is the leeward side, the right or the left? Windward Which side is the windward side, the right or the left? 1. Which gets more more rain point A or point B. 2. What causes the difference in rainfall amounts between point A and point B? Hint: Rain comes from here 1. Which gets more more rain point A or point B. 2. What causes the difference in rainfall amounts between point A and point B? Hint: Rain comes from here If you said Point A gets more rain because the Himalayas act as a rain shadow you are correct. Desert – arid region with very little rainfall Humid Subtropical – warm temperatures, lots of rainfall Notes Template • Use this template to create your own notes from the Power point. Elevation Rain Shadows Zones of Latitude Topograph y Factors that affect climate Wind Currents Wind Currents • Wind currents help distribute the sun’s heat from one part of the world to another. • Warmer air has lower pressure than cooler air. The cooler air rushes into the low pressure areas causing wind. • Warm air currents make areas warmer than normal. Cold air currents make areas cooler than normal High Pressure Air Low Pressure Air Wind blows from areas of High Pressure to Low Pressure Jet stream – wind currents on land that impact weather and climate. 1. How does the jet stream affect the climate of the NE? Notes Template • Use this template to create your own notes from the Power point. Elevation Rain Shadows Zones of Latitude Topograph y Wind Currents Factors that affect climate Warm Currents Ocean Current s Cold Currents Ocean Currents • Ocean current move in large circular systems • Ocean currents affect temperature and precipitation of an area. • Warm ocean currents make surrounding areas warmer and rainy. • Cool ocean currents make surrounding areas cooler and drier Warmer and Rainy Cool Ocean Current Cooler and Drier Warm Ocean Current Ocean Currents Notes Template • Use this template to create your own notes from the Power point. Elevation Rain Shadows Zones of Latitude Topograph y Climate Changes El Niño Wind Currents Factors that affect climate Warm Currents Ocean Current s Global Warmin g Cold Currents Global Warming • Global Warming is the build up of carbon dioxide (greenhouse gases) in the atmosphere trapping heat and causing increase temperature and shifting weather patterns. • Global Warming is being caused by both the human release of greenhouse gases from the burning of fossil fuels (oil, coal) and a natural warming cycle the Earth is going through • As the global temperature begins to rise many changes will occur to climates around the world • Complete the global warming simulation on the class webpage. – What are the effects of global warming? El Niño • The natural warming of waters off the west coast of South America about every 2 – 7 years due to a reversal of wind direction. • El Nino causes floods and mudslides in the Americas. • El Nino causes droughts in Australia and Asia. Climographs • Climographs are a combination of a line graph, measuring average temperature, and a bar graph, measuring average rainfall, for each month. Temperature Rainfall Notes Template • Use this template to create your own notes from the Power point. Elevation Rain Shadows Zones of Latitude Topograph y Climate Changes El Niño Wind Currents Factors that affect climate Warm Currents Ocean Current s Global Warmin g Cold Currents Major Climate Regions • Tropical Wet: Always hot and rain falls almost daily (Amazon Rainforest) • Desert: Receives less than 10 inches of rain per year (Phoenix, AZ) • Semiarid: Receives between 10 and 16 inches of rain per year (West Texas) • Mediterranean: Dry and hot summers, cool and rainy winters (Los Angeles, CA) • Humid Subtropical: Hot and humid summers, mild to cool winters (Houston, Tx) • Marine West Coast: Located close to warm ocean currents. Moderate temperatures and constant rainfall (Seattle, WA). • Humid Continental: Hot summers and Cold winters. Located in the interior, far away from oceans. Have four distinct seasons (St. Louis, MO). • Tundra: Always cold. Flat, treeless lands around the Arctic Ocean. Very little rain. Land has permafrost. (Greenland) Map Questions • Use the map of the world’s climates and the slide following to answer the questions below. 1. What is the climate of Houston? 2. Which types of climate are present in the tropical zone of latitude? •http://www.mcwdn.org/MAPS&GLOBES/C limate.html