Protein Synthesis Lab
advertisement

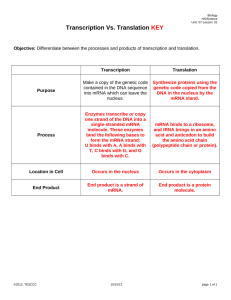
Protein Synthesis Lab Click Here to Begin Your Lab Background • Welcome to the CELL. Many process occur regularly that keep the CELL alive. Of these processes, one of the most important is a process called “Protein Synthesis.” It is this process that uses the information stored in DNA to create the CELL’S proteins. Click here to continue Warm-up Directions: On your sheet of paper, match each definition to the correct term 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. DNA mRNA codon tRNA Ribosome - Brings the amino acids to the ribosome - Assembles the protein by combining amino acids - Stores the information on how to make the various proteins of the body. - Is a copy of a gene that can leave the nucleus later to be read by a ribosome. - Equals 3 bases, also equals 1 amino acid Click here to continue The first step of Protein synthesis is called Transcription. Click on the organelle where transcription takes place in eukaryotic cells Mitochondria Rough E.R. Golgi Apparatus Smooth E.R. Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosomes Step 1: Transcription • Transcription is the first step of protein synthesis. This step takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Segments of DNA called genes store the information on the proper order of amino acids to construct the cells proteins. Click on one of the chromosomes to see what genes they contain. Once you have finished with all 3 chromosomes, click here to answer the final lab questions. Chromosome 1 Chromosome 2 Chromosome 3 Chromosome 1 • DNA is too valuable to allow it to leave the nucleus, so the cell copies it into the form of mRNA. Messenger RNA can then take this information out of the nucleus to the ribosomes to make the proteins. • Directions: You need to transcribe the DNA message below into the form of mRNA on your paper. Also write down what Chromosome you are working on. (Click here to review Base Pairing Rules) GCGCGCGTACAGGAAAGCCACAAGTTGTGATAGCGGGCGCATATTATCCTGCATCCGGTTTC Once you are done with transcription Click here to move to translation Chromosome 2 • DNA is too valuable to allow it to leave the nucleus, so the cell copies it into the form of mRNA. Messenger RNA can then take this information out of the nucleus to the ribosomes to make the proteins. • Directions: You need to transcribe the DNA message below into the form of mRNA on your paper. Also write down what Chromosome you are working on. (Click here to review Base Pairing Rules) CCGGAATCTACTAGTATTTCTAGGGTCTTACGAAACTCCGTCCCGTCATTCGTGCTATCCGA Once you are done with transcription Click here to move to translation Chromosome 3 • DNA is too valuable to allow it to leave the nucleus, so the cell copies it into the form of mRNA. Messenger RNA can then take this information out of the nucleus to the ribosomes to make the proteins. • Directions: You need to transcribe the DNA message below into the form of mRNA on your paper. Also write down what Chromosome you are working on. (Click here to review Base Pairing Rules) CTGCGCAACCTACCCTAAACTCGACTTTCATAGGAAAGACTTTCACATCGCCAGCATCC Once you are done with transcription Click here to move to translation Step 2: Translation • Translation is the second step in protein synthesis. Here, the mRNA is read by the ribosome by matching up codons to amino acids. • Directions: Use your mRNA and click on the codons to see what the amino acids are. Write down the amino acids on your paper. Click here to begin Translation Messenger RNA now leaves the nucleus. To begin translation click on the organelle that reads the mRNA and makes the protein. Mitochondria Rough E.R. Golgi Apparatus Smooth E.R. Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosomes Directions: Below are mRNA codons. Using your transcribed gene from the first part of the lab, click on the various codons to see what the amino acids are for each. Write the amino acids down in the proper order until you come to the stop codon. The amino acids in this lab are represented by words and linked together to make sentences (proteins). (Note: some codons may be used more than once). Once you have finished putting your protein together, click here. GUC UGG GAA AAU GAG AGG AGU GAU CCC GGA AGC GAC AUA CAG GGG GGC CCA UGC UCA CUG UUA UUC ACG CAA CUA AAG ACC GUA CCU UCU GCC CCG AUC UCG GCU UUU GUU AGA CAU GCG ACA GUG CGG AUG GCA ACU UCC UAG AAA UGU UGA CGU CGC AUU CAC CGA UAC UAU CUC AAC CUU GGU UUG UAA YOU WHAT FIND DO NOT BECOME EVEN I ACT COME FORWARD BUT STOP CODON THIS IS THE END OF YOUR PROTEIN (SENTENCE) SHINE STARS ON TO THEIR LET WHEN HAPPINESS SINGULAR MORE COURAGE HABIT IN PREPARE YOUR THEM STOP This is NOT a stop codon. This is a word in the sentence. THE EXCELLENCE ARE START CODON THIS IS THE BEGINNING OF YOUR PROTEIN (SENTENCE) OVER WE FIND REMEMBER CAN FACE OF SOMETHING LUCKIER ABSENCE DOING AS IS FROM NIGHTS BRIGHTEST ABILITY MOVING A THAT CANNOT FEARS REPEATEDLY FALL AN LIVES DARKEST OUR STILL IT NOPE Click Here to Try Again NO!!! Click Here to Try Again What are you thinking?!! Click Here to Try Again Are you guessing now? Click Here to Try Again Yes!! Transcription occurs in the Nucleus of Eukaryotic cells. Genes found in the DNA are copied into the form of mRNA. Once it is made, mRNA leaves the nucleus to begin step 2 of protein synthesis (translation) Click Here to Continue NOPE Click Here to Try Again NO!!! Click Here to Try Again What are you thinking?!! Click Here to Try Again Are you guessing now? Click Here to Try Again Yes!! Translation of mRNA to make a protein happens at the ribosomes. In Eukaryotic cells some ribosomes are found floating in the cytoplasm, while some ribosomes are attached to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. Click Here to Continue Base Pairing Rules for Transcription • Transcription makes mRNA using a DNA gene as a template. As such, transcription follows basic base pairing rules. Those rules are listed below and must be memorized for your test. T in DNA bonds with A in RNA G in DNA bonds with C in RNA C in DNA bonds with G in RNA A in DNA bonds with U in RNA Return to Chromosome 1 Return to Chromosome 2 Return to Chromosome 3 Lab Questions Directions: On your lab paper, answer the following questions using complete sentences. 1. What are the 2 steps of Protein Synthesis? 2. What do we call three mRNA bases that code for an amino acid? 3. Where does transcription and translation occur? 4. What are the base pairing rules for transcription? Click here once you have finished Congratulations!! You have completed your Virtual Protein Synthesis Lab. Don’t forget to turn your paper in for credit