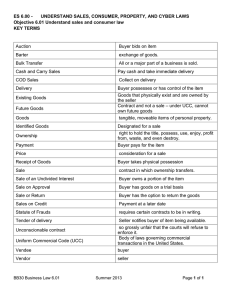
PowerPoint Slides to Accompany
CONTEMPORARY BUSINESS AND
ONLINE COMMERCE LAW
6th Edition
by Henry R. Cheeseman
Chapter 17
Performance of Sales, Leases,
and E-Contracts
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Introduction
Article 2 of the UCC establishes precise
rules for determining the passage of title
in sales contracts. [UCC 2-401]
Article 2 adopts concise rules for risk of
loss that are not tied to title.
Parties to the sales contract have the right
to insure the goods against loss if they
have an “insurable interest” in the goods.
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 2
Identification of Goods
Distinguishing the goods named in the
contract from the seller’s or lessor’s other
goods.
Identification of goods can be made at any
time and in any manner explicitly agreed
to by the parties to the contract.
In the absence of such an agreement, the
UCC mandates when identification
occurs. [UCC 2-501(1), 2A-217]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 3
Passage of Title (1 of 2)
Once the goods exist and have been
identified, title to the goods may be
transferred from the seller to the buyer.
Article 2 of the UCC establishes precise
rules for determining the passage of title
in sales contracts.
Lessees do not acquire title to the goods
they lease.
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 4
Passage of Title (2 of 2)
Under UCC 2-401(1), title to goods
passes from seller to the buyer in any
manner and on any conditions explicitly
agreed upon by the parties:
Shipment contracts [UCC 2-401(2)(a)]
Destination contracts [UCC 2-401(2)(b)]
Document of title [UCC 2-401(3)(a)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 5
Carrier Cases: Movement of Goods
Generally, goods shipped via carrier are considered
to be sent pursuant to a shipment contract or a
destination contract.
Shipment contract – the buyer bears the risk of loss
during transportation. [UCC 2-509(1)(a)]
Destination contract – requires the seller to deliver
conforming goods to a specific destination. [UCC 2509(1)(b)]
The seller bears the risk of loss during transportation
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 6
Shipping Terms
Sales contracts often contain the following terms:
F.O.B. (free on board) point of shipment
F.A.S. (free alongside) or F.A.S. (vessel) port of
shipment
C.I.F. (cost, insurance, and freight) and C. & F.
(cost and freight)
F.O.B. place of destination
Ex-ship (from the carrying vessel)
No arrival, no sale contract
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 7
Noncarrier Cases: No Movement
of Goods (1 of 3)
A sales contract may stipulate that the
buyer is to pick up the goods, either at the
seller’s place of business or another
specified location.
Who bears the risk of loss if the goods are
destroyed or stolen after the contract date
and before the buyer picks the goods up
from the seller?
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 8
Noncarrier Cases: No Movement
of Goods (2 of 3)
Merchant-Seller Rule: If the seller is a
merchant, the risk of loss does not pass to
the buyer until the goods are received.
Nonmerchant-Seller Rule:
Nonmerchant-sellers pass the risk of loss
to the buyer upon “tender of delivery” of
the goods.
[UCC 2-509(3)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 9
Noncarrier Cases: No Movement
of Goods (3 of 3)
Goods in the Possession of a Bailee
(i.e., a warehouse) – goods sold by a
seller to a buyer are sometimes in the
possession of a bailee.
If such goods are delivered to the buyer
without moving them, the risk of loss passes
to the buyer. [UCC 2-509(2)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 10
Risk of Loss: Conditional Sales (1 of
3)
Sale on Approval
There is no actual sale unless and until the
buyer accepts the goods.
In a sale on approval the risk of loss and title
remain with the seller.
They do not pass to the buyer until
acceptance.
[UCC 2-327(1)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 11
Risk of Loss: Conditional Sales (2 of
3)
Sale or Return Contract
The seller delivers goods to a buyer with the
understanding that the buyer may return
them if they are not used or resold within a
stated or reasonable period of time.
The risk of loss and title transfer to the buyer
when he or she takes possession of the
goods.
[UCC 2-327(2)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 12
Risk of Loss: Conditional Sales (3 of
3)
Consignment
A seller (the consignor) delivers goods to a
buyer (the consignee) for sale.
The consignee is paid a fee if he or she sells
the goods on behalf of the consignor.
A consignment is treated as a sale or return
under the UCC.
[UCC 2-326(3)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 13
Risk of Loss: Breach of a Sales
Contract
Seller in Breach
A seller breaches a sales
Buyer in Breach
Buyers breach a sales
contract if he or she
tenders or delivers
nonconforming goods to
the buyer [UCC 2-510]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
contract if they:
Refuse to take delivery of
conforming goods,
Repudiate the contract, or
Otherwise breach the
contract [UCC 2-510]
17 - 14
Risk of Loss: Lease Contracts
If the parties to a lease contract do not
agree as to who will bear the risk of loss
of the goods if they are lost or destroyed,
the UCC supplies risk of loss rules:
Ordinary Lease – risk of loss is retained by the lessor.
Finance Lease – risk of loss passes to the lessee.
Tender of delivery of goods fails to conform to the lease
contract – the risk of loss remains with the lessor or
supplier until cure or acceptance.
[UCC 2A-219, 2A-220(1)(a)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 15
Insuring Goods Against Loss
or Damage
Determine the value of goods subject to the sales
or lease contract.
Purchase insurance from a reputable insurance
company covering the goods subject to the
contract.
Maintain the insurance by paying the premiums
when they are due.
Immediately file the proper claim and supporting
documentation with an insurance company if the
goods are damaged, destroyed, lost, or stolen.
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 16
Sales by Nonowners (1 of 2)
Void Title and Lease: Stolen Goods
A thief acquires no title to the goods he or she
steals. [UCC 2-403(1)]
Voidable Title
Title that a purchase has if the goods were
obtained by:
Fraud
A check that is later dishonored
Impersonating another person
[UCC 2-201(1), 1-201(44)(d), UCC 2-403(1)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 17
Sales by Nonowners (2 of 2)
Good Faith Purchaser
for Value
A person to whom good
title can be transferred
from a person with
voidable title.
The real owner cannot
reclaim goods from a good
faith purchaser for value.
Good Faith Subsequent
Lessee
A person to whom a lease
interest can be transferred
from a person with
voidable title.
The real owner cannot
reclaim the goods from the
subsequent lessee until
the lease expires.
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 18
Entrustment Rule: Buyer in the
Ordinary Course of Business
A person who in good faith and without knowledge
that the sale violates the ownership or security
interests of a third party buys the goods in the
ordinary course of business from a person in the
business of selling goods of that kind.
A buyer in the ordinary course of business takes
the goods free of any third-party security interest in
the goods. [UCC 2-403(2)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 19
Entrustment Rule (continued)
The entrustment rule also applies to leases.
If a lessor entrusts the possession of his or her
goods to a lessee who is a merchant who deals in
goods of that kind, the merchant-lessee has the
power to transfer all the lessor’s and lessee’s rights
in the goods to a buyer or sublessee in the ordinary
course of business. [UCC 2A-305(2)]
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 20
Summary: Passage of Title in Sales by
Nonowner Third Parties and Sales of Goods
Subject to Security Agreements (1 of 2)
Type of
Transaction
Title Possessed
by Seller
Innocent
Purchaser
Purchaser
Acquires Title to
Goods
Goods acquired
by theft are
resold.
Void title.
Good faith
purchaser for
value.
No. Original
owner may
reclaim the
goods.
Good faith
purchaser for
value.
Yes. Purchaser
takes free of claim
of original owner.
Goods acquired
Voidable title.
by fraud or
dishonored check
are resold.
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 21
Summary: Passage of Title in Sales by
Nonowner Third Parties and Sales of Goods
Subject to Security Agreements (2 of 2)
Type of
Transaction
Title Possessed
by Seller
Innocent
Purchaser
Purchaser
Acquires Title to
Goods
Goods entrusted
by owner to
merchant who
deals in that type
of good are
resold.
No title.
Buyer in ordinary
course of
business.
Yes. Purchaser
takes free of claim
of original owner.
Buyer in ordinary
course of
business.
Yes. Purchaser
takes free of
creditor’s security
interest.
Creditor possess Good title.
security interest in
goods that are
sold.
Copyright © 2009 by Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
17 - 22