The Development of the Atomic Theory
advertisement

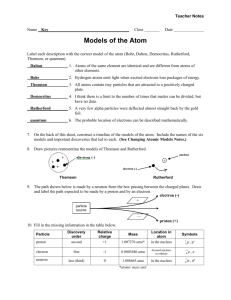
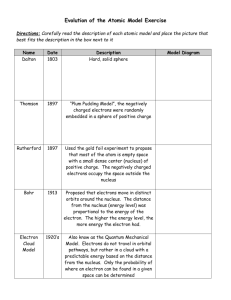
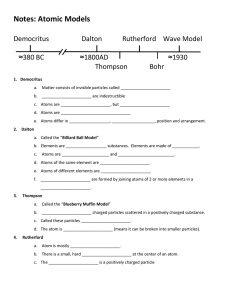
A Brief History of Atomic Theory This Section will focus on Scientists who have had an impact on the study of the atom. Ready To Meet Them? Democritus 470-380 B.C. Democritus proposed that matter cannot be broken down indefinitely. At some point you end up with a piece that can’t be divided. That smallest piece he called an atom, from the Greek word atomos, which means “indivisible”. Next Slide Democritus’ Model “Atomos” ATOMOS was the word Democritus used the point, or stage where matter cannot be broken down any further. ATOMOS literally means “indivisible” John Dalton John Dalton was a British chemist.He was the first modern scientist to propose the existence of atoms.He described an atom as an invisible indestructible, solid sphere, like a billiard ball. 1766 - 1844 Dalton’s Model The “Indivisible Sphere” Sir Joseph “J.J.” Thomson 1856 - 1940 J.J. Thomson was a British physicist who was the first scientist to propose the plum pudding model. He was also the first to propose the theory of the negatively charged electron. He was credited for the discovery. He also proposed the isotope. Thomson “plum pudding” model + - Ernest Rutherford 1871- 1937 Ernest Rutherford experiments proved that atoms are mostly empty space Discovered the nuclear, which contains positively charged particles .Was the first to suggest that electrons circle the dense nucleus. Rutherford’s Model Nucleus It has a + charge Electron Negative charge Niels Bohr Niels Bohr stated that electrons move in different orbits, or energy levels, around the nucleus like planets orbit the sun. Each energy level is located a specific 1885 - 1962 distance from the nucleus and contains a certain number of electrons. Next Slide Bohr Model Nucleus Energy levels Electronnegative charge Current Model This model is based upon Bohr’s model, except that electrons orbit the nucleus in random patterns. The region where these particles are found is referred to as the electron cloud. Electron Clouds Nucleus Next Slide