TOPIC: Cells AIM: What are the parts of a cell?
advertisement

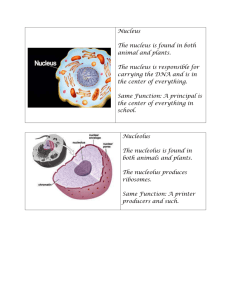
TOPIC: Cells AIM: Describe the different cell organelles and their functions. Do Now: Explain what all living cells are made up of. HW: Read p. 39. Write a paragraph describing the two types of cells that exist. Cell Membrane “SECURITY GUARD” Cell membranes are like gates. •Plasma Membrane •Surrounds the cell • Semi-permeable or Selectively permeable: controls what enters & leaves the cell • Made of a bilayer of lipids with proteins Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the gelatin-like material that is found inside the cell membrane. • Jellylike material • Holds cell organelles Nucleus “BRAIN” of the cell (Control center of the cell) • Controls all cell activities • Stores hereditary information (DNA) • Nucleolus: produces ribosomes • Surrounded by the nuclear membrane Nucleus of a Mouse Spleen Cell Onion Cells Cheek Cell Ribosomes •Produce proteins • Found –Floating free in cytoplasm –on Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Nucleus “HIGHWAY OF THE CELL” • Channels in the cytoplasm • Used to TRANSPORT materials • 2 types of ER: 1.Rough ER: ribosomes on surface 2.Smooth ER: no ribosomes on surface Rough ER Smooth ER TOPIC: Cells AIM: Describe the different cell organelles and their functions. Do Now: Take out your notes packet. You will be using the space under the Endoplasmic reticulum box. Write out numbers 1 – 10. HW: Work on your science fair project! Identify the cell organelle described: 1. Controls all cell activities. 2. Made up of a bilayer of lipids and proteins. 3. Produces proteins. 4. Is selectively permeable. 5. Transports substances around the cell. 6. Produces ribosomes. 7. Has ribosomes on its surface. 8. Holds all cell organelles. 9. Contains DNA. 10. Controls what enters and leaves the cell. Mitochondria “POWERHOUSE” of the cell Mighty Mitochondria • Where ENERGY is produced (cell respiration) ATP Vacuoles • Stores materials (food, water, wastes…) • Animal = many small • Plant = few large Golgi Bodies When a protein is made in the ER, something called a vesicle is made. This vesicle or sac floats through the cytoplasm to the Golgi apparatus and is absorbed. After the Golgi does its work on the molecules inside the sac, a secretory vesicle is created and released into the cytoplasm. From there, the vesicle moves to the cell membrane and the molecules are released out of the cell. “UPS / POST OFFICE” • Collects, packages, and sends materials out of the cell Lysosome • Contain digestive enzymes that: 1. digest food 2. break down old organelles & bacteria Organelles found only in Animal Cells • Centrioles: used for cell division Organelles found only in Plant Cells CELL WALL Cell Membrane 1.Cell Wall: • Outer wall of plant cell • Gives cell shape and support • RIGID 2. Chloroplasts: • Carry out photosynthesis • Contain green pigment called chlorophyll Let’s Label!!! L. mitochondria M. Centrioles K. Golgi Bodies J. Nucleolus I. Nuclear Mem. H. chromosomes G. nucleus A. Cell membrane B. Ribosome F. lysosome E. ER C. cytoplasm D. vacuole 3 7 4 8 2 5 6 1 8 7 A. Cell Wall B. Cell Membrane H. Ribosome I. Chloroplast C. Nucleus D. Nuclear Mem J. Cytoplasm E. Chromosomes K. Golgi Bodies F. Nucleolus L. Mitochondria G. ER M. Vacuole E Review: 1. Which structure composed mainly of proteins and lipids, aids in maintaining homeostasis in the cell? (1.) chromosome (2.) nucleolus (3.) cell membrane (4.) cell wall 2. In which organelle would water and dissolved minerals be stored? (1.) vacuole (2.) lysosome (3.) nucleus (4.) ribosome 3. The rigidity (support) of a plant cell is due primarily to the presence of the (1.) DNA (2.) cell membrane (3.) cell wall (4.) lysosomes 4. The structure most closely associated with the destruction of worn out cell organelles is the (1.) lysosome (2.) vacuole (3.) golgi apparatus (4.) chromosome 5. Which structure is found ONLY in animal cells? (1.) cell wall (2.) vacuoles (3.) centrioles (4.) ribosomes 6. The organelle most closely associated with the manufacture of proteins within the cell is the (1.) ribosome (2.) lysosome (3.) nucleolus (4.) cell membrane 7. Which structure chiefly functions in intracellular transport? (1.) vacuole (2.) mitochondrion (3.) golgi apparatus (4.) endoplasmic reticulum 8. The cell wall is (1.) selectively permeable (2.) rigid (3.) living (4.) a hardened cell membrane 9. Cyanide, a metabolic poison, interferes with the production of energy. Which cell organelle does cyanide most directly influence first in this situation? (1.) nucleus (2.) lysosome (3.) mitochondria (4.) ribosomes 10. The structure that is known as the control center of the cell is the (1.) vacuole (2.) cell membrane (3.) lysosome (4.) nucleus http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/cell/cell.html http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/health/anatom y/cell/cell_quiz.htm http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/health/anatom y/cell/plant_cell_game.htm