4.09 Presentation Notes
advertisement

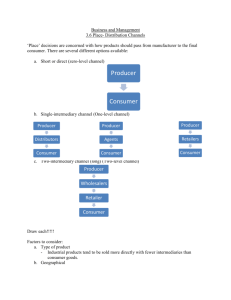
Objective 4.09 Channel of Distribution Identify factors that affect the choice of channel of distribution • • • • 1. Nature of market- there are many aspects of market which determine the choice of channel of distribution The most important consideration in choosing a distribution channel is that market segment the producer wants to reach. Changes in consumer buying behavior may influence a channel decision. 2. Nature of product -considerably affects the choice of channel of distribution. 3. Nature of the company – a firm having enough financial resources can afford to its own a distribution force and retail outlet, or both. 4. Middlemen consideration -if the right kind of middlemen having the necessary experience, contacts, financial strength and integrity are available, their use is preferred as they can ensure success of newly introduced products. Describe how the following factors affect selection of distribution channels • • • • • Nature of product 1. industrial/consumer production – when the product being manufactured and sold is industrial in nature, direct channel is useful because of the relatively small number of customers need for personalized attention, customer training requirements and after sale servicing 2. perishable nature – when products are perishable nature, like milk, dairy products bread and meat, etc., it is useful to opt for direct channel 3. seasonality – when product sale is subject to seasonal variations like woolen textile in India. In such cases intermediaries are seldom prepared undertake the function of inventory carrying and as consequence manufacturer build up indirect distribution channels 4. technicality – when product is very technical and complex like computers business machines etc. the direct channel is relatively more useful 1. consumer-the number of consumers, their geographic location and purchase pattern considerable affect the choice of a channel • Describe how the following factors affect selection of distribution channels • • 2. intermediaries -the relative strengths & weaknesses of intermediaries and the differences in the types o unctions performed and facilities and privileges desired by them often determine the choice o channel 3. competitors – the distribution channel used by competitors also • Access to channel members Describe how the following factors affect selection of distribution channels • • • • 1. middlemen/agents-engaged in the process of transfer of title of goods 2. marketing intermediaries, operating between the producer and the consumer or industrial purchaser 3. wholesaling intermediaries, selling primarily to retailers, other wholesalers, r industrial users 4. retailers, selling goods and services to individuals for their own use rather Explain procedures for selecting channels of distribution • Steps for selecting distribution include: 1. Identify how competitors' products are sold. • 2. Analyze strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for your business. • 3. Examine costs of channels and sales force options. • 4. Determine which distribution options match your overall marketing strategy. • 5. Prioritize your distribution choices. • Demonstrate procedures for selecting channels of distribution. • The selection of a distribution channel depends on several factors: the market, the product, the producer, and the competition. • • • 1. “Market factor -The most important consideration in choosing a distribution channel is that market segment the producer wants to reach. Changes in consumer buying behavior may influence a channel decision. 2. Product factors - Products that are complex, expensive, custommade, and perishable move through shorter distribution channels. Inexpensive and standardized products are typically sold through longer channels. 3. Producer factors - Producers that offer a broad product line and have the financial and marketing resources to distribute and promote their products are more likely to use a shorter channel of distribution.” http://faculty.piercecollege.edu/rskidmore/Ghost/library/Chapters/CHPT15-04.pdf • Types ofAchannels for consumer goods and services Channel There are five ways in which direct distribution is used for consumer goods: • 1. selling products at the production site • 2. having a sales force call on consumers at home • 3. using catalogs or ads to generate sales • 4. having a sales representative call a consume on the telephone (telemarketing) • • 5. using the internet to make online sales • Channel B most commonly used for merchandise that dates Types of channels for consumer goods and services • Channel C • Channel D the most common distribution method for staple goods, which are items that are always carried in stock and whose styles do not change frequently – distribution of goods and services goes from manufacturers/producers to wholesalers to retailers to consumers this channel is for manufacturers who wish to concentrate on production and leave sales and distribution to others – distribution of goods and services goes from manufacturers/producers to agents to wholesalers to retailers to consumers Types of channels for consumer goods and services • Channel E This channel is chosen by manufacturers who do not want to handle their own sales to retailers – distribution of goods and services goes from manufacturers/producers to agents to retailers to consumers • Channel A Types of channels for industrial products goods and services • Channel B most common method of distribution for major equipment used in manufacturing and other businesses – goods/services goes directly from manufacturer/producer to industrial user used most often from small standardized parts and operational supplies needed to run a business – • Channel C • Channel D Types of channels for industrial products goods and services small manufacturers who do not have the time or money to invest in a direct sales – goods/services goes from manufacturer/producer to agents to industrial distributors to industrial users used when a manufacturer does not want to hire its own sales once – goods/services goes from manufacturer/producer to agents to Demonstrate procedures for selecting channels of distribution • 4. “Competitive factors - Producers consider how well an intermediary performs marketing functions. A producer may become less competitive when an intermediary fails to adequately promote the firm's products.” http://faculty.piercecollege.edu/rskidmore/Ghost/library/Chapters/CHPT15-04.pdf • • Selective distribution means that you Distributions only distribute to a small number of customers based on 1. Type of store, e.g., boutique or specialty • 2. Geographic location • 3. Minimum order, and • 4. The image of the store • Exclusive distribution strategies are • • Limited distribution can create exclusivity.Distributions Exclusivity can also be created by limiting the quantity of goods available, such as limited editions. For example, some private label or store brands, such as Nordstrom's and Saks Fifth Avenue, are available only at those stores Mass distribution is an alternative distribution strategy. You will use this strategy if you want to sell to as many http://www.scribd.com/doc/22784449/307/FACTORS-AFFECTING-THE-CHOICE-OF-DISTRIBUTION-CHANNEL RESOURCES • • • • Allen, K.R. & Meyer, E.C. (2006). Entrepreneurship and small business management (pp. 210-213). Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Farese, L.S.; Kimbrell, G.; & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (pp. 375-379). Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. http://faculty.piercecollege.edu/rskidmore/Ghost/library/Chapters/CHPT15-04.pdf http://www.scribd.com/doc/22784449/307/FACTORS-AFFECTING-THECHOICE-OF-DISTRIBUTION-CHANNEL