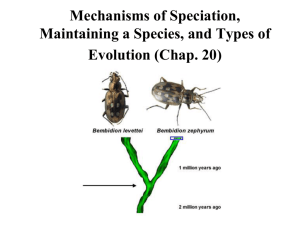
Chapter 22
advertisement
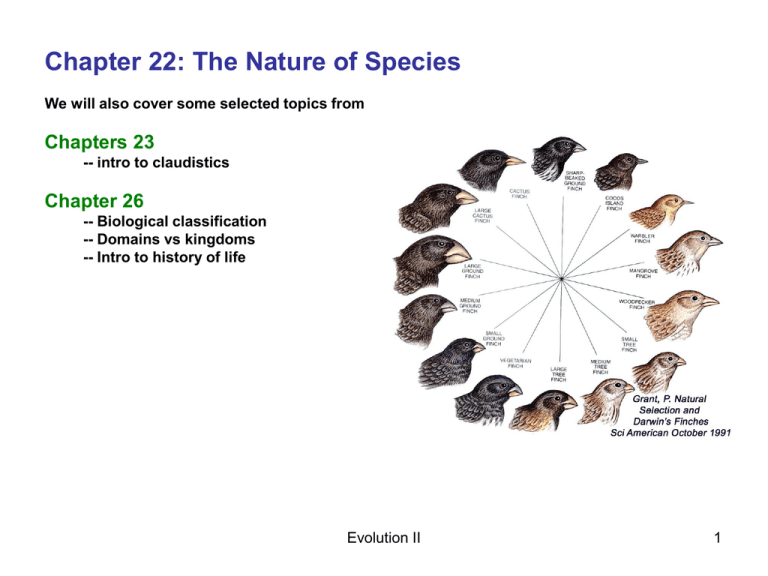
Chapter 22: The Nature of Species We will also cover some selected topics from Chapters 23 -- intro to claudistics Chapter 26 -- Biological classification -- Domains vs kingdoms -- Intro to history of life Evolution II 1 What is a species? Scientific naming of species Scientific binomial – Carolus Linnaeus Genus + Species Homo sapiens vs “humans” Acer rubrum “red maple” vs Biological classification system: Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Writing Conventions Question Definition “A group of interbreeding organisms that are reproductively isolated” What is ‘reproductive isolation’? Which of these is Acer rubrum? Evolution II 2 What are some mechanisms of reproductive isolation? Pre-zygotic Ecological (habitat) e.g., mountain ranges Mechanical e.g. reproductive anatomy Temporal e.g. mating seasons Behavioral e.g., mating rituals Gametic gametes incompatible (many plants) e.g., frogs of Sierra Nevada foothills e.g., bowerbirds of Australia Evolution II 3 Mechanisms of reproductive isolation, con’t. Post-zygotic Hybrid inviability -- embryo / fetus does not develop e.g., cattle and water buffalo Hybrid infertility -- offspring is infertile e.g., colored and pied flycatchers Question Evolution II Meet and hybridize in central and northern Europe 4 The biological species concept has limitations If two species can hybridize, are they separate species? -- plants -- animals Native: California Tiger Salamander Invasive: Adult Barred Tiger Salamander Hybrid: Appears to be more fit then native Should all dogs be classified in the same species? http://sciencemode.co m/2007/09/20/californ ia-barred-tigersalamandersinterbreed-producehybrids/ Evolution II 5 How does geographic distribution relate to speciation? Allopatric speciation: geographic isolation mountains, rivers, islands What evolutionary mechanisms can operate? Can Sympatric speciation occur? e.g., “blackbellied seedcracker” Less fit hybrids -‘reinforcement’ Reinforcement among European flycatchers Question Evolution II 6 How can we explain the origin of the apple maggot? Apple Maggot Hawthorn Apple Visit Martin G. Kelly’s site at http://www.sciencecases.org/maggot_fly/maggot_fly.asp Evolution II 7 Under what conditions does ‘Adaptive Radiation’ occur? -A special case of disruptive evolution Darwin’s Finches -- classic example Can occur regionally or globally -- rise of mammals Adaptations reinforced by “Character Displacement’ Question Evolution II 8 Plotting macroevolution What are some characteristics of evolution that can be diagrammed? Gradualism vs ‘punctuated equilibrium’ Stephen J Gould & Niles Eldredge What are possible mechanisms of rapid speciation? -- polyploidy -- mutations to developmental genes -- geologic time vs ‘human’ time Evolution II 9 Plotting evolutionary relationships (from Chapter 23) The traditional “evolutionary tree” vs Claudistics Clade= all organisms with “Shared derived characteristics” Evolution II 10 Revisiting Classification… (from Chapter 26) Domains and Kingdoms Biological classification system: Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Question Evolution II 11 Highlights of the History of Life (from Chapter 26) Advanced life forms have appeared Late in earth’s geologic history Origin of life ~ 3.8 bya Eukaryotic cells ~ 1.7 bya Multicellular organisms ~ 1.2 bya Origin of life Multicellular organisms Humans only ~ 1 mya Evolution II 12 The origin of major groups of animals The ‘eras’ The Cambrian explosion Vertebrates Invertebrates Age of reptiles Age of mammals Insects most successful of them all Evolution II 13 There have been many mass extinctions! Some small, Some BIG! Question Evolution II 14