Paleolithic and Neolithic
advertisement

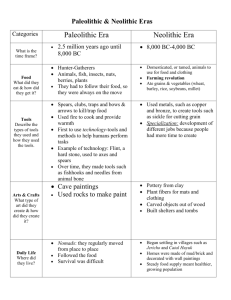
Paleolithic and Neolithic Unit 1 Bellringer • Practice walking in, picking up papers by the door and placing your homework in the in box before the bell rings. ALL CELL PHONE SHOULD BE TURNED OFF! Review Procedures • Entering class – Take today’s papers – Sharpen pencils, etc. – Start the Bellringer • “On time” means in your seat working when the bell rings Procedures • Leaving the room – Bathroom/water/nurse ask before leaving. • Wait till all instructions have been given. • Interrupt class for emergencies – End of class: clean up supplies, move desks to where they belong, wait for teacher to dismiss you Agenda Day 2 1. Bellringer 2. Stations – – – – Station 1: Time and Timelines Station 2: Charts and Graphs Station 3: Textbook scavenger hunt Station 4: Vocabulary Words m(1-18)/ Maps 3. Review 4. Begin on Homework Skills Objectives Students will be able to… 1. Identify and locate key features of the S textbook. 2. Take effective notes from textbook S readings. Textbooks • • • • You break it (or lose it), you bought it! Make sure your name is in it Make sure my name is in it Make sure the Textbook List is filled out completely and legibly Stations Directions • You will have 15 minutes at each station • Complete packet located in each folder • You may work in pairs within your group NO MORE than 3 per group • When time is up pass folder to the next group Stations Review • • • • Station 1: Time and Timelines Station 2: Charts and Graphs Station 3: Textbook scavenger hunt Station 4: Vocabulary Words/ Maps VOCABULARY WORDS Prehistory Objective #1 • Prehistory – the time in human history before What this? This help you the invention of writing identify which objective this slide is related to! • What sources can we use to understand the “prehistoric” world? VOCABULARY word! With definition! Unwritten History 1. Oral histories 2. Drawings 3. Stuff they left behind Oral Histories • Storytellers prized in many cultures, and stories are passed down for generations • Problems: – “Whisper down the lane” effect – Dead people don’t tell stories Drawings • Mostly, cave paintings – Famous pictures from Lascaux (France) Cave Paintings • Art is in the eye of the beholder – Stories? – Actual events? – Religious beliefs? – Nice pictures? – Textbooks? Artifacts • Something made by people VOCABULARY word! Fossils • Solidified remains of living things Using Artifacts • Some assembly required – Like a giant puzzle with no idea what the picture will be • What if we use things for different purposes? • If we know what, do we know when? • Some things get lost Objective #2 Studying the Past • Archeology • Anthropology Archeology • The study of the human past by examining artifacts and remains – Excavation – Hoping to find ancient settlements, burial sites, tools, etc. Carbon Dating • A scientific test used to analyze the age of artifacts and fossils • (based on the half-life decay of Carbon-14… ask a science teacher) • Pretty accurate for the last 40,000 years or so Anthropology • Study of human origins, relationships, and cultures – Try to determine how humans evolved (physically and culturally) – Archeology is a subfield of anthropology • What is culture? Culture Objective #3 • Culture is a system of beliefs, values, and assumptions about life that guide behavior and are shared by a group of people • Everyone has culture • What does culture include? Homework • Buy a notebook. Bring by next class • Read: Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic Societies – Read Directions carefully! Bellringer • Pull out the following items – Syllabus – Your homework – Vocabulary words • Grab the following (will need to share!) – Glue – Scissors Agenda • Bellringer: Setting up interactive notebook • Preview (aka: Bellringer) • Notes – Working with book – Working independently – Discussion • Process • Homework Objectives • 1: Identify the characteristics of Prehistoric man, and their migration patterns throughout the prehistoric world • 2: List the major advances early humans made during the Paleolithic Era. • 3: Describe hunter-gatherer life. Interactive notebook • Why: – To help student to be organized – Allow student to become more active with their learning • Expectations – Placing all required work in notebook – Leaving notebook in class room – Will use a folder to carry homework in Notebook Set up • On the back of the front cover: – Syllabus • First page – Front: table of contents (pg1) – Back: level of questioning (pg2) • 2nd Page – Front Ms. Heath’s Rule of World History (pg3) – Back: Page one of Vocabulary words (pg 4) • 3rd page – Front: page two of vocabulary words (pg 5) – Back: Preview activity (pg6) Notebook Set up • Glue the notes and Process on the next pages Any Questions??? • From now on when you walk – – – – Collect your notebook Glue homework in Cut and glue in Preview I will give you directions on the notes and process • Either in the powerpoint or after I get class started Objective #2 Early Humans Early Humans • Start our story at the dawn of the Paleolithic Era, about 2.5 million years ago – the Old Stone Age – Humans created the first tools made out of stone Better than Monkeys • Early humans developed 1. Simple stone tools 2. Control of fire 3. Oral language • All keys to cooperating in hunts, which bring food and resources Wise Man • Smarter, larger-brained humans known as homo sapiens (Latin for “wise man”) – Developed technology • Clothing • Shelter • Art • Homo sapiens are modern humans Out of Africa • Homo sapiens arose in Africa about 200,000 years ago • Migration to all continents (except Antarctica) beginning around 100,000 years ago Objective #3 Hunter-gatherer Life People Profiles Source of Food • Hunting – Main source, whatever they could catch, kill, and cook! • Gathering – Wild fruits, vegetables, nuts, grains, etc. • Get it? Hunter-gatherers! Size of Groups • Small groups – Clans: 60-100 people, one or a few extended families • Why? Permanent Settlements • No! They were nomads • Why move? – Follow herds – No food left – Seasons change • Too cold or hot • No water left Location Factors • Mainly, Paleolithic (and prehistoric) people followed their food – Animals migrate, so did the people • Overpopulation (of people) • Overconsumption (of resources in one spot) Getting Along • • • • • Cooperation was necessary for survival Knew everyone in their clan – all relatives No private property – no where to put it No fighting other groups – no one around Finding food…just not that hard Bellringer – Have completed 10minutes after the bell – Collect your notebook – Cut and glue all items into notebook – Finish Process from last class and begin working on Preview for lesson 2 – REMEMBER the order! • • • • Preview (can begin once completed) Notes Process homework from last night Agenda • • • • • Preview: Discussion Activity Lecture Reading Process Homework • Study for Test • Will be allowed to take home your notebook DO NOT LOSE IT! Neolithic Age • Neolithic Age means: – New Stone Age • How did Neolithic Age differ from Paleolithic Age? – Learnt to polish tools – Make pottery – Grow crops and domesticated animals Neolithic Revolution • Shift from hunting and gathering to farming Neolithic Revolution Cont. • Provided a steady source of food and extra – Causing • Need to store food – Causing • Permanent Settlement – Causing • Population growth – Causing • Specialization and Organization Early Farming Methods Crops • Slash and burn faming • Cut tree or grass and burnt them to clear a field • Ashes fertilized the soil Animals • Domestication taming of animals • Happened slowly • Human being to control some animals lives Where did it happen? • First seen in the fertile crescent • Later in river valleys Example of Neolithic Activity • Stonehenge – Started during the Neolithic Age and completed during the bronze Age • Aleppo – Ancient City which was a regional trading post Homework • Study Guide