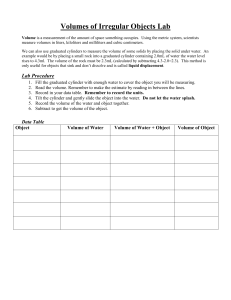
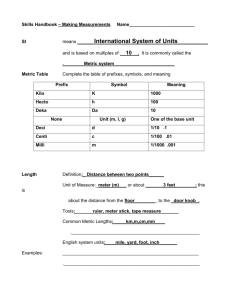
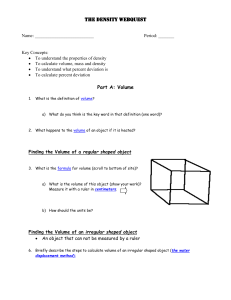
Metric-Measurement
advertisement

Metric Measurement The measurement system used in science and in most countries of the world. Where? • The Metric system is used in all but three nations in the entire world. Can you name the three that don’t? Most countries have adopted the metric system as their official system of measurement. There are only three countries in the world that do not use the metric system for official measurement. The United States, Burma (Myanmar) and Liberia all depend on older systems of measurements. Within these countries, however, the metric system is often used, especially in scientific and international contexts. Source www.ehow/about.com Why? It is a better system because it is easier to use. It is based on multiples of 10, which is easy to multiply and divide by. Example: if a table is 354 centimeters long that would be equal to 3.54 meters. You just divide by 100 (or move the decimal point two places to the left). If a table is 354 inches long you would divide by 36 which would be 9.83. Distance • Distance (also called length, width, height, depth & thickness) is measured in one direction, point A to point B. Distance continued… • The tools used include meter sticks, metric rulers, and odometers. This is a meter stick… …it is a stick and it is a meter long Distance continued… The units used are based on the meter. The common units that we use are the • meter (m) • centimeter (cm) • millimeter (mm) • kilometer (km) They are all parts of a meter or are made up of meters How big are they? Centi means (1/100) so… … a centimeter (cm) is 1/100th of a meter Milli means (1/1000) so… … a millimeter (mm) is 1/1000th of a meter Kilo means 1000 so… ,,, a kilometer (km) is 1000 meters Area • Area (or surface area) is measured in two directions. • It is the measure of how many square units it takes to cover a surface. Area continued… • The tools used include meter sticks and metric rulers. Area continued… • The area measurement process involves measuring the surface in two directions and then multiplying these dimensions (L x W). Area continued… • The common units that we use are the square centimeter (cm2), square meter (m2) and the square kilometer (km2). Volume Volume is the measure of how much space is taken up by matter in three dimensions. Volume continued… There are three different types of volume measurement depending on what it is you are measuring. • • • Volume of regular shaped solids Volume of liquids Volume of irregular shaped solids Volume continued… Volume of regular shaped solids… …is used when you are measuring solid objects that have regular / consistent characteristics such as flat sides and right angles. There are different formulas used depending on which geometric shape you are measuring. The most common is for the rectangular prism (L x W x H) 4cm x 3cm x 5cm = 60cm3 Volume continued… Volume of regular shaped solids The tools used include meter sticks and metric rulers. The common units used when measuring the volume of solids are the cubic centimeter (cm3), and the cubic meter (m3). Volume of liquids This process involves the use of a graduated cylinder. The liquid is simply poured into the graduated cylinder and you read the graduated lines on the side to determine the Meniscus – curved volume. surface of the liquid Volume continued… Volume of liquids The tools used include graduated cylinder. The common units used when measuring the volume of liquids are the milliliter (mL) and the Liter (L). It is important to understand that 1mL is equal to 1cm3. e 1mL used for liquids = 1cm3 used for solids Volume of irregular shaped solids This is used for solid objects that do not have a regular (measurable) shape. The objects are submerged in water and the amount of water that is displaced is measured. Volume continued… Volume of irregular shaped solids. The common measurement tool used is the graduated cylinder. Even though graduated cylinders measure in milliliters, since a solid is being measured the units used are cm3. Lets get organized with a chart Tools Regular Shaped solids Liquids Irregular shaped Solids Units Tools Regular Shaped solids Liquids Irregular shaped Solids Meter Stick Units Tools Regular Shaped solids Liquids Irregular shaped Solids Meter Stick Units cm3 Tools Regular Shaped solids Meter Stick Liquids Graduated Cylinder Irregular shaped Solids Units cm3 Tools Regular Shaped solids Liquids Irregular shaped Solids Units Meter Stick cm3 Graduated Cylinder mL Tools Regular Shaped solids Liquids Irregular shaped Solids Units Meter Stick cm3 Graduated Cylinder mL Graduated Cylinder Tools Regular Shaped solids Liquids Irregular shaped Solids Units Meter Stick cm3 Graduated Cylinder mL Graduated Cylinder cm3 Mass • Our book defines mass as the amount of matter in an object. • It is similar to weight and the two are often confused. Mass continued… To measure mass, a balance is used. The objects mass is compared to objects whose mass is known. Mass continued… The base unit is the gram. The common mass units are the milligram (mg), the gram (g) and the kilogram (kg). Metric Units Metric Units 1 kilogram (kg) = 1000 grams (g) 1 gram (g) = 1000 milligrams (mg) Click the image to watch a short video about mass. Which is larger? A. 1 kilogram or 1500 grams C. 12 milligrams or 12 kilograms B. 1200 milligrams or 1 gram D. 4 kilograms or 4500 grams Kilogram Prototype Image - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kilogram Measuring Mass We will be using triple-beam balances to find the mass of various objects. The objects are placed on the balance and then you move the weights on the beams until you get the lines on the right-side of the balance to match up. Once you have balanced the scale, you add up the amounts on each beam to find the total mass. What would be the mass of the object measured in the picture? _______ + ______ + _______ = ________ g Top Image: http://www.southwestscales.com/Ohaus_Triple_Beam_750-SO.jpg Bottom Image: http://www.regentsprep.org/Regents/biology/units/laboratory/graphics/triplebeambalance.jpg Measuring Mass – Triple-Beam Balance 1st – Place the film canister on the scale. 2nd – Slide the large weight to the right until the arm drops below the line. Move the rider back one groove. Make sure it “locks” into place. 3rd – Repeat this process with the top weight. When the arm moves below the line, back it up one groove. 4th – Slide the small weight on the front beam until the lines match up. 5th – Add the amounts on each beam to find the total mass to the nearest tenth of a gram. Click here to try an online activity. Mass - vs. - Weight Weight is similar to mass… … but they are not the same thing. Weight is the measure of how much gravity is pulling on an object. If the amount of gravity changes, the weight of an object changes but the mass stays the same. Mass vs. weight continued… • For example if you were to compare your weight on Earth to your weight on the moon, you would weigh less on the moon, but your mass would not change. • Also, if you were to go to deep space, far from any planet or moon, you would be “weightless” but you can never be “mass-less”. Mass vs. weight continued… Since weight is dependent on the force of gravity, the unit used when measuring weight is the Newton (N). Weight continued… The tool used to measure weight is called the scale. Scales work by compressing or stretching a spring. Tools Mass Weight Units Tools Mass Weight Balance Units Tools Mass Units Grams (g) Balance Milligrams (mg) Kilograms (kg) Weight Tools Mass Units Grams (g) Balance Milligrams (mg) Kilograms (kg) Weight Scale Tools Mass Units Grams (g) Balance Milligrams (mg) Kilograms (kg) Weight Scale Newtons Density Density is described in our text book as “the amount of matter in a given space” and “the ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume of the substance”. I like to explain it as… … “how heavy something is for its size”. Density continued… The easiest way to picture it is if you had several objects all the same size, the heaviest one is the most dense. Even a small piece of lead is pretty heavy so we would say lead is a dense material. A piece of Styrofoam is not heavy compared to its size so we say Styrofoam is a low density material. Density continued… To measure the density of a material, you must measure both the mass and the volume of it. Measure the mass Measure to volume Then you find the ratio of these two measurements. This is pretty easy, you just divide the mass by the volume (D = M / V). Density continued… Since mass is measured in grams (g), the volume of solids is measured in cubic centimeters (cm3) and the volume of liquids is measured in milliliters (mL)… …the units will be… …grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) for solids and… …grams per milliliter (g/mL) for liquids. Density continued… • When scientists were creating the metric system of measurements they planned ahead to make sure the volume and mass systems worked together. • They decided that one (mL) of water would have a mass of one (g). This insured that the density of water would be 1 g/mL. Density continued… Any object that floats in water has a density of less than water (less than 1 g/cm3). Any substance that sinks in water will have a density more than water (more than 1 g/cm3).