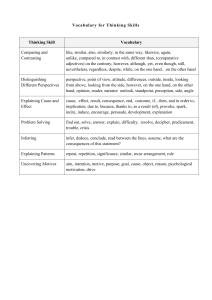
rowan-95

Learning Goals
•
Understand the sequence of oral presentation assignment components
•
Learn how to develop explanations for assigned material
– Listen to lecture on Rowan
–
Start preparing your slides
•
Practice oral skills
– Peer introduction task
Process for Oral Presentation Assignments
Read Rowan article ( handout )
Make slides on assigned material
( check course website for assignments )
Submit slides for professor’s feedback
Practice: Video record, evaluate yourself, chosen peer evaluates
Do Final Presentation
The old way
• Presenting to ‘inform’ or ‘excite’ not for understanding
–
Emphasis on hooking the audience
•
Gain audience attention
• Establish audience’s need for information
•
Not contingent on material; too focused on form
–
Not all material is best explained via examples, visual aids, frameworks, charts,
The NEW way
•
Emphasis on explaining
•
Presentation should answer the question:
–
How? OR
–
Why? OR
–
What does this mean?
Explaining vs. Informing
•
Inform
–
Create awareness of latest information on some topic (E.g., News reports)
•
Explain
•
Improve understanding of something audience is aware of but does not fully grasp
•
Explaining helps deepen understanding or master a skill
What explaining is or is not
•
Learning Check: What is the difference between…
–
Finding
•
Similar to informing
–
Hypothesis
The new way
•
View oral presentation as a process of
anticipating & overcoming potential misunderstandings
–
What is the confusion?
–
What is the strategy for explaining the confusion?
When presenting to explain
• Analyze audience’s source of ‘confusion’
–
What can the audience be confused about?
– Why the audience might not understand info?
•
Identify good, empirically supported techniques (explanations) for overcoming audience confusion
– Rowan article
Concepts are difficult
Processes are difficult to visualize
Ideas are hard to believe
Audience Confusion
3 Sources of Audience Confusion
1. Concept is difficult
• e.g., documenting vs. evaluating
2. Processes are difficult to visualize
• e.g., Extraversion & non verbal skills
3. Ideas are hard to believe
• e.g., pay can lead to decreased motivation
When explaining a concept….
•
Define concept by listing its essential features
–
Distinguish between essential & associated features
•
Define contrasting concept
•
Give examples of concept
•
Show how to differentiate examples from non examples by looking for essential features
•
Give non-examples that are mistaken for examples
Examples of concept & contrasting concept
•
Documenting behavior vs. Evaluating performance
–
E.g. class participation is documented rather than evaluated
–
Doing the practice presentation (i.e., submitting video) is documented, not evaluated
– Final presentation is evaluated
Interpersonal vs. non verbal communication skills
•
Define non-verbal communication skills
–
Ability to perceive & interpret emotions accurately
•
How are non verbal communication skills
(NV) different from interpersonal skills? (IP)
– IP =Establish relationship with other vs. NV = convey emotional information with other
–
IP=Control emotional expression vs. NV=express
& interpret emotions
–
IP= Higher order vs. NV= lower order skills
C24 fall05 Student Paper
To define a concept well, you need to…
1. Define the concept
2. Identify the contrasting concept (via non examples)
3. Give examples that illustrate the concept
4. Give examples of the contrasting concept
(non examples) that can be confused with examples of the concept
3 Sources of Audience Confusion
1. Concept is difficult
2. Processes are difficult to visualize
3. Ideas are hard to believe
Processes difficult to visualize
• Help audience mentally model or ‘picture’ key dimensions of a complex phenomenon
–
Have clear main points and connections b/w them
Processes difficult to visualize
•
Two main obstacles
1. Creating a good general impression
2. Conceptualize parts
1 st step to explaining a process that is difficult to visualize
•
Provide a good general impression of phenomenon via….
•
Graphics/Models
•
Verbal strategies
• Structure suggesting titles
– Five dimensions of personality
• Organizing analogies
– An organization is like a jazz quartet
•
Model suggesting topic sentences
– Need fulfillment works like a pyramid
•
Note: Models/analogies should be commonly shared
2nd step to explaining a process that is difficult to visualize
•
Help audience conceptualize parts, processes, inter-relations via
•
Transitional phrases, previews, summaries & explicit statements of relationships that help in refining mental models
•
Do not use short sentences and sacrifice words like
“because” and “for example”
•
Repeat/recreate initial comparisons
Example Process
Before giving feedback…(linear)
• Decide on…
1. Why evaluate performance
2. How to evaluate performance
A. Who evaluates performance?
–
Train rater
B. Method of performance evaluation
1. Pick dimensions
2. Pick rating scale
3. Document performance
4. Evaluate performance
Before giving feedback…(model)
Why evaluate performance
Dimensions to evaluate
Type of rating scale to use
Who evaluates performance
Train evaluator
Document Performance
Evaluate Performance
Why are extraverts more skilled at non verbal communication?
•
Differences in social experiences
– Extraverts…
• Seek out interactions which help refine & develop NV skills
• Have more social experience which enables more practice
Linear explanation from C24 fall05 Student Paper
Extraversion
+
NV Skills
Extraversion
+
Social experiences
+
NV Skills
Social experiences
+
+
Practice old skills
+
NV Skills
Develop new
Skills
+
Extraversion
+
Social experiences
+
+
Practice old skills
+
NV Skills
Develop new
Skills
+
Using a graph to illustrate range restriction
•
Why GPA–performance correlation decreases after first year on the job?
–
Chalkboard drawing
– http://cnx.rice.edu/content/m11196/latest/
3 Sources of Audience Confusion
1. Concept is difficult
2. Processes are difficult to visualize
3. Ideas are hard to believe
Ideas are hard to believe
1. State implausible idea
–
Participation does not lead to setting more difficult goals
2. Discuss audience’s implicit theory
3. Demonstrate limitations of audience’s theory
4. State the more empirically valid theory and illustrate its effectiveness
Ideas are hard to believe
1. State implausible idea
–
E.g., Participation does not lead to setting more difficult goals
2. Discuss audience’s implicit theory
–
How does it explain the commonly believed idea?
• E.g., Participation results in more difficult goals being set because subordinates want their supervisors to believe that they are highly capable and so choose more difficult goals than those that may be assigned to them by the supervisor
C24 fall05 Student Paper
Ideas are hard to believe
3. Demonstrate limitations of implicit theory
–
Identify inadequacy with familiar examples or data
•
Assumes that all subordinates want to demonstrate superior abilities to their supervisors
•
Assumes that supervisors do not know the abilities of the subordinates and so assign easy goals
4. State the more empirically valid theory and illustrate its effectiveness
•
When supervisors know the abilities of subordinates, participation does not result in more difficult goals
C24 fall05 Student Paper
Another Hard to believe idea
•
Pay does not lead to increased motivation
•
Implicit theory:
–
Pay reinforces behavior
•
Assumptions
–
Pay reinforces all behaviors
•
New findings
– Pay does not reinforce behaviors that are intrinsically motivated
To formulate a good explanation
•
Identify why subject is confusing to audience
•
Introspect, ask peers
•
Classify confusion
•
Is it a concept?
•
Is it a difficult to visualize process/structure
• Is it a ‘hard to believe’ idea?
•
Then generate an explanation that best overcomes the confusion
Is it a concept?
Examples, counter examples etc.
Read assigned material
Focus on one aspect
Classify the aspect
Is it a idea that is hard to believe?
Identify invalid assumptions of implicit theory etc.
Is it a process?
Model to explain processes or parts