HDChap5Student - University of West Florida
advertisement

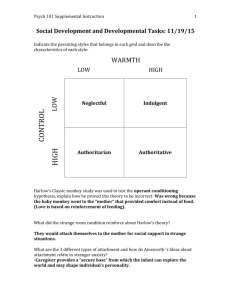
Erikson and Attachment in Toddlerhood DEP 2004 Human Development Across the Lifespan Dr. Erica Jordan University of West Florida Stage 2: Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt 1 – 3 years Goal to obtain will— healthy understanding that we can intentionally cause things to happen in the world Find a Partner and Take a Few Minutes to… 1 Think about one of your parents or another person who cared for you when you were young? 2 How did you feel about this person when you were a child? 3 How do you feel about this person now? What is an Attachment? A strong, enduring, emotional bond Transcends time, space, and death Often begin to develop before birth for expectant parents Vary in quality and fall along a continuum of security Secure Insecure What Attachment is Not Not a new style of parenting Not attachment therapy Not helicopter parenting or “martyr mothering” (or fathering) Not exclusively child-centered Not indulgent or permissive parenting Not only for mothers Before Attachment Theory… People took note of the special relationship that mothers and young children seemed to share. Psychoanalytic theorists and social learning theorists concluded the relationship developed because of feeding. “Father Of Attachment Theory” John Bowlby, a British psychiatrist, realized the feeding explanation did not seem to tell the whole story. The connection was about more than feeding. Noticed boys in a home for troubled youth who had disrupted, problematic relationships with their mothers had difficulties later in life. Harry Harlow (1958) found that infant monkeys sought comfort in “mothers” that did not feed them. Instead, they sought out “mothers” who provided contact comfort. Stages of Attachment Parents often begin the process of attachment when they learn they will have a child. Preattachment (Birth to about 2 months) Attachment in the making (2 – 6 months) True attachment (6 – 18 months) Reciprocal relationships (18 months and up) The Special Role of Fathers Can also be attachment figures Children can form multiple attachments Joy is often important in father-child relationships Fathers also able to provide comfort in times of distress What Determines Quality of Attachment Parenting behaviors & mental health Child’s temperament Attachment contributes to an infant’s… Internal Working Model Infant’s understanding of how responsive and dependable the caregiver is; thought to influence close relationships throughout the child’s life Ainsworth’s Strange Situation Test: Key Points of Interest Exploration of toys Social referencing Separation distress Ability to be soothed Joy upon reunion & proximity seeking behaviors Ability to return to exploration of toys Classifications of Attachment Quality Secure Attachment Avoidant Attachment Resistant Attachment Disorganized (disoriented) Attachment Benefits to Children Have fewer health problems Have better emotion regulation and cortisol balance Are better prepared to explore the world around them Better peer relations in early childhood and adolescence Related to exploration in toddlerhood and IQ in children More positive romantic relationships and more likely to have secure attachment relationships with their own children Internal Working Model Attachment relationships set the stage for a child’s social and emotional development Becomes the framework for other relationships and for regulating down negative emotional states Secure Anxious/Ambivalent Avoidant Benefits to Parents and Caregivers Find it easier to meet their child’s needs Makes discipline easier Promotes a lasting positive relationship with the child The Impact of Work and Childcare on Attachment Quality Best Practices: Low teacher-child ratio Low turnover! Check with the National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) at www.naeyc.org to see if the center is certified. Trained, experienced staff with a knowledge of child development Stimulating environment Effective partnership between parent and childcare providers