Wage and Hour Law
advertisement

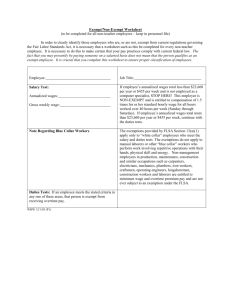
Wage and Hour Law: Your Company’s Not Exempt from Litigation Presented by Robert E. Lewis, Ph.D. and Toni S. Locklear, Ph.D. 2015 APTMetrics About APTMetrics Global Talent Management Solutions Provider Comprised of: • Ph.D. industrial/organizational psychologists • Human resource consultants • Information technology specialists What Sets APTMetrics Apart: • • • • Professional integrity Evidence-based approach Technical expertise Customer service Diversity Supplier • Certified as a women-owned business by WBENC • Certified as a women-owned small business by the US SBA Global Strategies for Talent Management. 1 Our Areas of Expertise • • • • • • • • • Leader Assessment Employee Selection Litigation Support Diversity Strategy & Measurement Job Analysis Competency Modeling Performance Management Staffing for Mergers & Acquisitions Organizational Surveys Global Strategies for Talent Management. 2 Our Web-Based Solutions Platform APTMetrics® SelectionMetrics® Employee Selection System LeadINsm Leadership Assessment Suite JobMetrics® Job Analysis System 360Metrics® 360-Degree Feedback System SurveyMetrics® Organizational Survey System 3 APTMetrics’ U.S. Offices 4 Agenda • Introduction to wage-hour law • Why care about wage-hour laws? • Difficulties implementing wage-hour laws • How to limit risks associated with wage-hour laws 5 Introduction to Wage-Hour Law • What is regulated by wage-hour law? • Federal law: • • • • overtime pay minimum wage child labor record-keeping requirements • State law: • meal and rest breaks • discharge notices • pay upon discharge 6 Introduction to Wage-Hour Law • Key issue in wage-hour litigation: Exemption • Exempt—not subject to overtime pay regulations • Non-exempt—subject to overtime pay regulations 7 Exemption Standards • Based on the work as it is done • Individual determination • Exemption types: • • • • • Executive Administrative Professional Computer Professional Outside Sales 8 Exemption Standards • Key work tests: • Salary level test • Duties test • Discretion • Independent judgment • Authority • Hire/fire authority • Prolonged course of specialized instruction 9 Polling Question 1. What percent of jobs in your company are classified as exempt from federal and state wagehour laws? a. b. c. d. e. f. Less than 20% 20 – 40% 41 – 60% 61 – 80% 81 - 100% I don’t know 10 Little Known Facts • Classifying jobs as exempt is voluntary • No requirement to claim exemption for any job • Employers bear the burden of proof when claiming exemption • The Department of Labor estimates 70 percent of employers are not in compliance with the FLSA in some way 11 Wage-Hour Issues are Important • Lawsuits are on the rise • Wage hour suits outpace others (e.g., discrimination) • 77 percent rise in lawsuits filed between 2004 and 2009 • Multi-million dollar settlements— • $1.77 billion in settlements in 2007-2010 • Average settlement of $12.8 million per case • Damages • Back pay for lost wages, interest, liquidated damages, and attorneys’ fees • Treble damages in some states • Changing exemption status can create litigation risk 12 Difficulties Implementing Wage-Hour Laws • Wage-hour administration crosses organizational lines • The HR, finance, legal functions generally have some responsibility • Little coordination among them • Key players: legal and HR • Work is changing • Leaner staffing levels require managers to do more “non-managerial” work • Laws require interpretation • What is “work time”? • When is doing non-management work “essential” to doing management work? 13 Polling Question 2. Which jobs do you wrestle with most regarding wage-hour issues? a. b. c. d. e. Assistant managers/team leaders Computer technicians Accountants Project managers Other 14 Key Wage-Hour Concerns • Employees working off the clock • Ensuring that employees take meal breaks • Determining a job’s exemption status 15 Level of Effectiveness Reactions to Wage-Hour Challenges • Delegate wage-hour compliance to field/district management • Conduct compensation/market analyses • Empower Staffing to make exemption decisions at hire • Create policy manual section on wagehour compliance • Regular audits of wage-hour policies/implications • Train managers on managing meal breaks and overtime • Conduct job analysis 16 Case Study – Guinup v. Petr-All Petroleum Are retail store managers entitled to overtime pay? • The Plaintiff’s Claim -- the company misclassified all of its store managers as exempt from both the FLSA and state wage-hour law • Plaintiff managed a convenience store/gas station in NY state • Plaintiff spent: • 80% of her time on nonexempt duties such as counting cigarettes and verifying gas readings • 20% of her time on exempt duties such as scheduling, supervising, and evaluating employees • Most of her day free from supervision; the regional manager was generally not in the store 17 Limiting the Risk of Wage-Hour Issues • Knowing the work that is done is the number one way to limit wage-hour risk • Job Analysis is the preferred method for documenting work requirements • • • • Structured Defensible Drives coordination Documents critical job components • Frequency and importance of work activities • Entry requirements for knowledge, skills and abilities • Level of discretion and autonomy • Policy creation versus enforcement versus execution 18 Limiting the Risk of Wage-Hour Issues • Job analysis process • Determine jobs that present risk • Collect structured, verifiable data • Develop a comprehensive work activity and knowledge/skill/ability list with job experts • With your employment attorney, decide which activities are exempt • Identify the ratings you need based on your state (importance, time spent, level of autonomy, etc.) • Administer the survey to the entire population • Analyze the data, including for exemption implications • Means and standard deviations • Illustrate the findings using visuals to facilitate comparing jobs on relevant dimensions 19 Limiting the Risk of Wage-Hour Issues Job Analysis Results • How important are these job activities for the Manager job? • • • • 3 – Critically important– this activity has significant impact on profit, performance, or safety 2– Important-- poor performance on this activity hinders performance 1-- Minor Importance– this activity must be done but has little impact on profit, performance or safety 0– Not Applicable– this activity is not performed in this job 20 Limiting the Risk of Wage-Hour Issues Job Analysis Results • Including both exempt and non-exempt activities allows you to assess the degree to which job respondents meet exemption criteria 21 Limiting the Risk of Wage-Hour Issues • Develop job descriptions based on the job analysis • Key activities and responsibilities • Key and required KSAs • Minimum and preferred qualifications 22 Job Profiles 23 Job Profiles 24 Job Profiles 25 Limiting the Risk of Wage-Hour Issues • HR Audit • Policies—are wage-hour considerations reflected in policies? • Use of pagers and smartphones for email access • On-call duty for computer operators/technicians • Use of company-owned vehicles • Practices—are processes in effect for managing issues on an ongoing basis? • Grievance process for work time complaints • Active training program for managers to understand their responsibilities • Cross-functional committee responsible for wage-hour issues that meets regularly • Regular employee survey to determine how employees spend their time in important work activities 26 Summary • Wage-hour issues require cross-functional management • Typically from Legal, HR and Finance • Knowing the job is your best proactive and defensive measure • A job analysis is a court-tested method of determining status • Changing an employee’s exemption status without knowing and changing activities/skills is a recipe for litigation • Audit your policies and practices to ensure coordination and proactive measurement • Policies to ensure guidance • Practices to ensure execution 27 Contact Information APTMetrics, Inc. One Thorndal Circle Second Floor Darien, CT 06820 203.655.7779 TalentSolutions@APTMetrics.com www.APTMetrics.com Global Strategies for Talent Management. 28