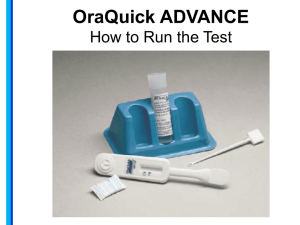
Administering the OraQuick ADVANCE HIV Test
advertisement

OraQuick HIV and HCV Rapid Test Kit Proficiency Training Overview Background Presentation Demo of the basic OraQuick rapid test You will practice running 2 tests, 1 HIV and 1 HCV We will not be testing anyone in the room Proficiency Test - You will run 3 of each test without assistance Run, read, and document 6 tests Read results of 10 test images Pass / fail course, must get 100% to pass What Do You Know About Rapid Tests? Introduction to the OraQuick Rapid Tests One-step test Visual interpretation Uses blood HIV test can also use oral fluid Looks for HIV or HCV antibodies Results in 20 to 40 minutes Who can run tests? California Health and Safety Code Section 120917 allows non-medical personnel that have been trained as HIV test counselors to perform CLIAwaived HCV tests if they: (Next Slide) (continue……..) 1. Have been trained in HIV test counseling by OA or its agents; 2. Work in a HIV testing site that is funded by OA or that uses staff trained by OA or its agents and has a QA plan approved by the local health department and has HIV testing staff that complies with state regulatory QA requirements. 3. Have been trained by OA or its agents in both HIV and HCV test kit proficiency for finger-stick blood tests and in universal infection control precautions, consistent with best infection control practices. Package Insert Contains instructions CLIA requires following the manufacturer’s instructions to the letter!! HIV Subject Information Brochure Contains information about the test that is relevant to the client Package Insert says, “All subjects must receive the Subject Information Brochure” Check in with your site to see how this is handled No brochure for HCV test Test Accuracy We’re going to talk about how well the tests work You do not need to memorize what I’m saying - only need to know test is very accurate There are two components of test accuracy: Sensitivity Specificity Specificity When a test finds something, it should be the right thing Tests ability to detect a true negative HIV Specificity Test True Neg Tested Neg False Pos Specificity EIA 1 467 442 25 94.7% EIA RR 467 463 4 99.1% OraQuick I 464 463 1 99.8% OraQuick RR 464 463 1 99.8% More specific than standard HIV test (EIA) Test is very accurate (but not perfect) Screening test is designed to be very sensitive. Due to this design, we sacrifice a little specificity. Must confirm preliminary positives (SOC, false+) Draw blood and send to lab (conventional oral test is back up) HCV Specificity Total tests OraQuick negative True negative Difference % Specificity 1660 923 937 14 98.5 Not exact, but very accurate Sensitivity The ability of a test to find what it’s looking for and not miss anything. Test’s ability to detect a true positive HIV Sensitivity Test True Pos Tested Pos False Neg Sensitivity EIA 1 340 340 0 100% EIA RR 340 340 0 100% OraQuick 1 340 340 0 100% OraQuick RR 340 340 0 100% Rapid test is at least as sensitive as conventional HIV test (EIA) Same window period RR = repeatedly reactive HCV Sensitivity Total tests OraQuick reactive True positive Difference % Specificity 1660 708 723 15 97.9 HCV test The test’s ability to detect true positives and not miss anything Combining Specificity and Sensitivity An ideal test would find the right thing (specificity) and not miss anything (sensitivity) Think of a Tuna net…. A net that gets all the tuna and none of the dolphins Because the Two Tests are Highly Sensitive… We do not need to confirm negatives For both HIV and HCV, additional testing always needs to be done if a reaction is detected Testing Process for HIV Stat-Pak 1st Test _ Negative, please come back and see us in 6 months + ++ OraQuick Test Reactive, 2nd Test _ Lab Testing Both tests were reactive your next step is to see a doctor and we can help you with that Testing Process for HCV OraQuick Test Negative Reactive Client referred to follow-up HCV nucleic acid testing With Clients… Emphasize that the test is extremely accurate De-emphasize statistics and percentages For example “This test is highly accurate” Quality Assurance Requirements QA are practices and procedures which ensure that every client receives an accurate test result QA reduces human error as much as possible Components of Quality Assurance Personal and logistical characteristics External controls Lab space Universal precautions Must Have… Steady hand Good eye sight Organizational skills Adequate lighting Full/bright light, task light Do not use a flashlight External Controls Fluids made from human plasma Biohazards – wear gloves! 3 HIV controls - Negative, Positive for HIV-1, Positive for HIV-2 2 HCV controls – Negative, Positive Store controls at 35 to 46 degrees F Expire 56 days after opening External Controls are Used for: Training, we will use them today Determining if test is working properly Determining if lighting is adequate Determining if the test reader has sufficient eye site When to Run External Controls New operator New setting or conditions changed significantly New test kit lot or shipment Out of range testing area or storage area temperature Two invalid results in a row Every 40 tests or once a month (whichever comes first) Why? Temperature Control Perform test, 59-99 degrees If testing temperature is out of required temperature range stop testing If out of temp range, run controls before proceeding Store test: HIV – 35 to 80 degrees HCV – 36 to 86 degrees Lab Space A space for undisturbed test processing Your site is a lab Separate from counseling area No smoking, eating or drinking Universal Precautions The universal practice of avoiding contact with patients' bodily fluids, (blood) by means of the wearing of nonporous articles such as medical gloves Gloves Wear them when handling blood or blood products, and…. TODAY – whenever you touch the control fluid vials!!!! How often do you change them? How do you remove them? Sharps: Handling & Disposal Medical instruments that are used to puncture the skin (syringes, lancets, needles) Dispose of sharps immediately, in a hard red plastic bio bin! Do NOT dispose of sharps in a red bio hazard bag Biohazard Bags Handling & Disposal Bandages, used cotton and gauze, and gloves with body fluids on them are bio hazardous waste By law, if fluid cannot be squeezed out of the cotton, gauze, etc., the waste item can be disposed of in regular trash. For Today’s Training Place loops and used Place gloves and all test kits in the sharps other trash in the container brown paper bag Paperwork Needed Expanded Checklist Short Checklist (Competency Assessment Test list) Rapid testing log or lab slip Lab stickers HIV/HCV Testing Form Always use blue or black ink only! Test Device Control line Test line Flat pad Paddle must be inserted into the vial no later than 60 minutes after sample has been introduced Vent holes – Do NOT obstruct Trainers Demo Trainer Reads Other Trainer preforms test Participants follow along (Expanded Checklist) Participants’ First Practice No food or drink Listen to detailed steps: Only do what we tell you to do Do all steps in order If you finish a step quickly, wait for the next step Reading Time Results in 20-40 minutes If a reactive result appears before 20 minutes have passed, the result may still not be read until at least 20 minutes have passed OraQuick Test Results Two lines: “C” - Control line “T” - Test line Negative result Reactive result Invalid result What causes invalids? Human error (e.g., no specimen) Unknown Manufacturer error If you ever have an unusual result, do not deliver it What does it mean if a client has an invalid test result? What does the darkness of the lines mean? NOTHING A B D C C C C C T T T T G F E H C C C C T T T T Participants’ Second Practice Pair up One person run a test at their own pace, using the short checklist Partner observe them and help only as needed (e.g., if you see any steps that were missed, say something) Switch Use the checklist!!!! Internal Control The “C” Line The control line is the “C” line Internal control tells us: Specimen was adequately applied Proper hydration Migration of reagents past the “T” zone. Internal & external controls are standard lab practice – not a sign of test kit unreliability Test Line The “T” Line The “T” line is the “test line”. It works with the external control fluids to: tell us if the result is reactive or non-reactive. tell us if the reader can see lines. tell us if there is proper lighting. tell us if the reader’s eyesight is adequate to run the test. Controls Work Together If the internal control & the external controls both tell us the test kit is working, why do we need both? Because they tell us something different! “C” line tells us test kit is working properly “T” line tells us the test kit can detect HIV or HCV antibodies when they’re present Results of Practice Test Did you get the correct result? Any questions? The control fluid that we use provides a “challenge sample” Light control line verifies lighting is OK Verifies test kit detecting small amount of antibody Darkness of line NOT related to viral load, disease progression, or anything else about the client If a Client Asks to See the Test Kit, What Would You Do? Say “No” – Why? Could compromise confidentiality Only trained personnel may read the test Test is disposed of in biohazard bag as soon as it’s read Think about the picture with the pink background – if you have a light line would you be able to see it on this test? How Do You Correct a Written Mistake? Use blue or black ink only on all forms A single crossed-out line, corrected entry written clearly above, include date and initials of the individual making the change. At no time should an original entry be obliterated or otherwise made illegible by a change on the record. 7:22pm T.K. 12/15/2011 End time: 7:12pm Any questions? Proficiency tests coming next…. OraQuick Test Proficiency: Words of Caution Follow the checklist!!!! This is not a test of memorization Run 3 HIV and 3 HCV tests using different vials Put your name on the top of your paper(s) Take your time, double & triple checking your work If you make a mistake on your paperwork and you catch it, you can fix it. and I catch it, you will have to come back another day