Chapter 4,Cultural Aspects of Nursing
advertisement

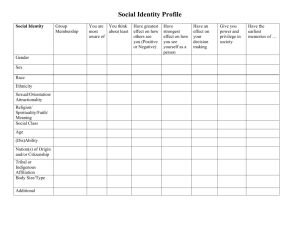
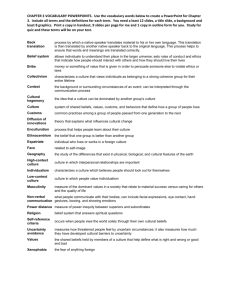
Chapter 4 Cultural Aspects of Health and Illness Transcultural Nursing • Focuses on care, health, illness patterns of people with similarities and differences in cultural belief, values, practices Culture • Not restricted to race, ethnicity • Refers to integrated patterns of behavior acquired over time (e.g., beliefs, values, customs, norms, habits, language, thoughts) • Learned within family unit, generation, and/or other social organizations Cultural Diversity • Differences among people; may or may not be visible • Race – visible physical characteristics (e.g., skin tone, head shape, hair texture) • Ethnicity –common group social customs, values, beliefs Cultural Competence • Respecting all differences; not letting one’s own biases influence others • Understanding/responding effectively to cultural and linguistic needs of patients • Joint Commission and NPSGs require cultural differences be respected Cultural Sensitivity • Aware of, respects; appreciation of cultural differences • Avoid biased/offensive language and actions when interacting with diverse cultures • Avoid stereotyping Health Care Disparities • Differences in incidence of health care problems among minority racial/ethnic groups when compared with white majority • Contributing factors – socioeconomic status, individual discrimination, access to care, language barriers Healthy People 2020 • Health promotion initiatives reflect assessments of major risks to health and wellness • Changing public priorities • Emerging issues related to U.S. health preparedness and prevention Purnell’s Domains of Culture • • • • • • • Culture overview and communication Homelessness Family and workplace issues Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender health Biologic ecology Nutrition Spirituality Homeless • Most avoid health care • Prone to CV disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, high cholesterol, infections • Compensate for limited time • Limit number of visits needed Communication • Language is largest barrier for non-English-speaking patients • Interpreters must be available in health care facilities • Determine which forms of patient communication are acceptable Family & Workplace Issues • Family and gender roles influence plan of care • Assess who makes decisions in the family • Include questions about sexual identity/activity in health assessment LGBT Health • Many fear prejudice; hesitant to seek medical care • Establish patient’s gender identity; do not make assumption based on appearance • Ask questions about sexual identity Biological Ecology • Biologic variations, health disparities, drug metabolism differences • Common biological variation relates to adult body size and type (e.g., dwarfism) Dwarfism • Height below 4’ 10” • Disproportionate or proportionate • Results from genetic mutation, hormone imbalance Ethnopharmacology • Study of effect of ethnicity on how drugs work in the body • • • • Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion Nutrition • Part of comprehensive health assessment • Respect patient’s food preferences/beliefs • Assess rituals and customs Spirituality • Involves behaviors that give purpose to life, provide individual strength • Joint Commission requires all health care facilities to address patients’ spiritual needs • Chaplain is part of health care team • • • • Health Care Practices and Practitioners Assess patient’s health promotion and maintenance practices Determine whether patient is able to afford health care Use of alternative health care systems and healers Folk health beliefs Health Care Obstacles • • • • Transportation difficulties High cost of care Fear and distrust of health care workers Poor communication between patients and professionals Folk Health Chapter 4 Audience Response System Questions 22 Question 1 What nursing priority ensures that culturally competent care is provided to a homeless patient admitted for an infected foot? Contact the case manager to secure a shelter bed upon discharge. B. Provide education regarding foot care to prevent reinfection. C. Help the patient choose a diet high in protein. D. Provide empathetic and clear communication when assessing the patient’s needs. A. Question 2 What is the fastest growing ethnic group in the United States? A. B. C. D. Asian Americans African Americans Hispanic/Latino Americans American Indian Question 3 Which question illustrates the first step of becoming culturally competent? A. “Do I have the skill to conduct a cultural assessment?” B. “How many face-to-face encounters have I had with patients from diverse cultural backgrounds?” C. “Do I have knowledge of my patient’s world view?” D. “Am I aware of my own personal biases and prejudices toward cultures that are different from my own?”