Project Integration Slides
advertisement

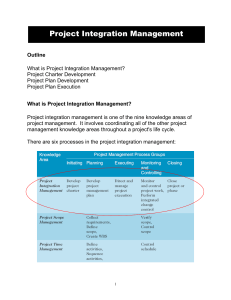
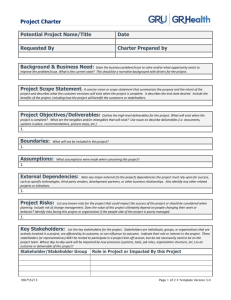
Project Integration Management Sections of this presentation were adapted from A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge 4th Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., © 2009 Integration Management Includes processes to ensure that all the elements of a project are properly coordinated Making tradeoffs among competing alternatives and objectives to meet stakeholder needs Typically the most important knowledge area for the Project Manager Why Do We Manage Integration? Manage change and communication Reduce project time and cost Involve stakeholders early and often Make results visible Identify problems/solutions early Use relevant experience as early as possible Who Manages Integration? Project Manager – Integrator for the project that executes processes Team Members – Concentrate on completing tasks, activities, & work packages Project Sponsor – Protect project from changes and losing resources How Do We Manage Integration? Use the seven integration processes Develop project charter Develop project management plan Direct and manage project execution Monitor and control project work Perform integrated change control Close project or phase Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Integrated Change Control Close Project or Phase How Do We Manage Integration? Each process has: Inputs Tools and Techniques Outputs Remember that inputs and outputs can feed more than one process! Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Integrated Change Control Close Project or Phase Project Charter Project Statement of Work Inputs Tools & Techniques Project Selection Methods Project Management Methodology Enterprise Environmental Factors Outputs Project Charter Project Management Information System Contract Expert Judgment Organizational Process Assets Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Integrated Change Control Close Project or Phase Project Management Plan Inputs Preliminary Project Scope Statement Tools & Techniques Project Management Methodology Project Management Processes Project Management Information System Enterprise Environmental Factors Organizational Process Assets Expert Judgment Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Outputs Integrated Change Control Project Management Plan Close Project or Phase Direct & Manage Execution Inputs Project Management Plan Approved Corrective Actions Approved Preventive Actions Approved Change Requests Approved Defect Repair Tools & Techniques Project Management Methodology Project Management Information System Outputs Deliverables Requested Changes Implemented Change Requests Implemented Corrective Actions Implemented Preventive Actions Validated Defect Repair Implemented Defect Repair Administrative Closure Procedure Work Performance Information Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Integrated Change Control Close Project or Phase Monitor & Control Project Work Tools & Techniques Inputs Project Management Plan Outputs Project Management Methodology Recommended Preventive Actions Project Management Information System Work Performance Information Forecasts Earned Value Management Recommended Defect Repair Expert Judgment Rejected Change Requests Recommended Corrective Actions Requested Changes Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Integrated Change Control Close Project or Phase Integrated Change Control Tools & Techniques Outputs Inputs Project Management Plan Requested Changes Work Performance Information Recommended Preventive Actions Project Management Methodology Approved Change Requests Project Management Information System Project Management Plan Updates Expert Judgment Rejected Change Requests Project Scope Statement Updates Approved Corrective Actions Recommended Corrective Actions Approved Preventive Actions Recommended Defect Repair Approved Defect Repair Deliverables Validated Defect Repair Deliverables Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Integrated Change Control Close Project or Phase Close Project or Phase Inputs Tools & Techniques Project Management Methodology Project Management Plan Contract Documentation Outputs Administrative Closure Procedure Contract Closure Procedure Enterprise Environmental Factors Project Management Information System Final Product, Service, or Result Organizational Process Assets Expert Judgment Organizational Process assets Updates Work Performance Information Deliverables Project Charter Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Execution Monitor & Control Project Work Integrated Change Control Close Project or Phase What Goes in a Project Plan? Project charter Project Management Approach Scope Statement Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Responsibility Chart Network Diagram with Major Milestones Budget Schedule Resources Change Control System Performance Measurement Guidelines Management Plans (Scope, Schedule, cost, quality, staffing, communications, risk response, procurement) PM Responsibility for Change Influence factors that affect change Ensure change is beneficial Determine if a change has occurred Determine if a change is needed Look for alternatives to change Minimize negative impact from change Notify Stakeholders impacted by change Managing those changes that do occur according to project plan Integration Management Summary Know the integration management processes and where they belong Project plan documents the basis for all project decisions Understand the authority and limits of authority of the project manager All changes should be guided by the processes in the project plan Responsibility Responsibility: The duties, assignments, and accountability for results associated with a designated position in the organization. Source: Gain and Maintain Authority to Ensure Project Success, Jason Chavart, 2002 Accountability Being answerable to one's superior in an organization for the exercise of one's authority and the performance of one's duties. Source: Gain and Maintain Authority to Ensure Project Success, Jason Chavart, 2002 Authority The legitimate power given to a person in an organization to use resources to reach an objective and to exercise discipline. Source: Gain and Maintain Authority to Ensure Project Success, Jason Chavart, 2002 Definitions Lessons Learned – Document that identifies what was done right, wrong, and how to improve in the future Baseline – The original project plan with approved changes