Taxes
advertisement

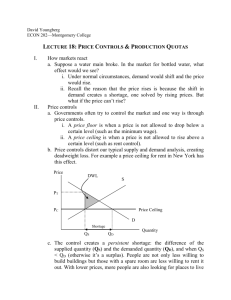
MARKETS IN ACTION 6 CHAPTER Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Explain how housing markets work and how price ceilings create housing shortages and inefficiency Explain how labor markets work and how minimum wage laws create unemployment and inefficiency Explain the effects of the sales tax Explain why farm prices and farm revenues fluctuate and how production subsidies and quotas influence farm production, costs, and prices Explain how markets for illegal goods work Turbulent Times As more people compete for scarce land, house prices and rents rise. As new technologies replace low-skilled labor, the demand for low-skilled workers falls. Can governments control prices and wages? How do taxes affect prices and quantities, and who pays the tax, the buyer or the seller? How are farm prices and incomes affected by fluctuations in harvests? What happens in a market when trading a good is illegal? Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings A Regulated Housing Market A price ceiling is a regulation that makes it illegal to charge a price higher than a specified level. When a price ceiling is applied to a housing market it is called a rent ceiling. If the rent ceiling is set above the equilibrium rent, it has no effect. The market works as if there were no ceiling. But if the rent ceiling is set below the equilibrium rent, it has powerful effects. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings Figure 6.2 shows the effects of a rent ceiling that is set below the equilibrium rent. The equilibrium rent is $20 a month. A rent ceiling is set at $16 a month. So the equilibrium rent is in the illegal region. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings At the rent ceiling, the quantity of housing demanded exceeds the quantity supplied and there is a housing shortage. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings With a housing shortage, people are willing to pay $24 a month. Because the legal price cannot eliminate the shortage, other mechanisms operate: search activity black markets Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings Search Activity The time spent looking for someone with whom to do business is called search activity. When a price is regulated and there is a shortage, search activity increases. Search activity is costly and the opportunity cost of housing equals its rent (regulated) plus the opportunity cost of the search activity (unregulated). Because the quantity of housing is less than the quantity in an unregulated market, the opportunity cost of housing exceeds the unregulated rent. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings Black Markets A black market is an illegal market that operates alongside a legal market in which a price ceiling or other restriction has been imposed. A shortage of housing creates a black market in housing. Illegal arrangements are made between renters and landlords at rents above the rent ceiling—and generally above what the rent would have been in an unregulated market. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings Inefficiency of Rent Ceilings A rent ceiling leads to an inefficient use of resources. The quantity of rental housing is less than the efficient quantity and there is a deadweight loss, illustrated in Figure 6.3 (page 125). Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings Inefficiency of Rent Ceilings A rent ceiling leads to an inefficient use of resources. The quantity of rental housing is less than the efficient quantity and there is a deadweight loss. Figure 6.3 illustrates this loss. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings A rent ceiling decreases the quantity of rental housing, shrinks the producer and consumer surplus by using resources is search activity, and creates a deadweight loss. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings Are Rent Ceilings Fair According to the fair rules view, a rent ceiling is unfair because it blocks voluntary exchange. According to the fair results view, a rent ceiling is unfair because it does not generally benefit the poor. A rent ceiling decreases the quantity of housing and allocates the scarce housing using: Lotteries Queues Discrimination Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings Are Rent Ceilings Fair A lottery gives scarce housing to the lucky. A queue gives scarce housing to those who have the greatest foresight and get their names on the list first. Discrimination gives scarce housing to friends, family members, or those of the selected race or sex. None of these methods leads to a fair outcome. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage New, labor-saving technologies become available every year, which mainly replace low-skilled labor. Does the persistent decrease in the demand for low-skilled labor depress the wage rates of these workers? The immediate effect of these technological advances is a decrease in the demand for low-skill labor, a fall in the wage rate, and a decrease in the quantity of labor supplied. Figure 6.4 on the next slide illustrates this immediate effect. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage A decrease in the demand for low-skill labor is shown by a leftward shift of the demand curve. A new labor market equilibrium arises at a lower wage rate and a smaller quantity of labor employed. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage In the long run, people get trained to do higher-skilled jobs. The supply of low-skill labor decreases, which is shown by a leftward shift of the short-run supply curve. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage If long-run supply is perfectly elastic, the equilibrium wage rate returns to its initial level (other things remaining the same). The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage A Minimum Wage A price floor is a regulation that makes it illegal to trade at a price lower than a specified level. When a price floor is applied to labor markets, it is called a minimum wage. If the minimum wage is set below the equilibrium wage rate, it has no effect. The market works as if there were no minimum wage. If the minimum wage is set above the equilibrium wage rate, it has powerful effects. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage If the minimum wage is set above the equilibrium wage rate, the quantity of labor supplied by workers exceeds the quantity demanded by employers. There is a surplus of labor. Because employers cannot be forced to hire a greater quantity than they wish, the quantity of labor hired at the minimum wage is less than the quantity that would be hired in an unregulated labor market. Because the legal wage rate cannot eliminate the surplus, the minimum wage creates unemployment Figure 6.5 on the next slide illustrates these effects. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage The equilibrium wage rate is $4 an hour. The minimum wage rate is set at $5 an hour. So the equilibrium wage rate is in the illegal region. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage The quantity of labor employed is the quantity demanded. The quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. Unemployment is the gap between the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage Inefficiency of a Minimum Wage A minimum wage leads to an inefficient use of resources. The quantity of labor employed is less than the efficient quantity and there is a deadweight loss. Figure 6.6 illustrates this loss. Housing Markets and Rent Ceilings A minimum wage decreases the quantity of labor employed, shrinks the firms’ and workers’ surplus by using resources in job search activity, and creates a deadweight loss. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage The Federal Minimum Wage and its Effects The United States has passed the Fair Standards Labor Act, which currently sets the minimum wage at $5.15 per hour. This minimum wage has historically fluctuated between 35 percent and 50 percent of the average wage of production workers. Most economists believe that minimum wage laws increase the unemployment rate of low-skilled younger workers. The Labor Market and the Minimum Wage A Living Wage A living wage has been defined as an hourly wage rate that enables a person who works a 40 hour week to rent adequate housing for not more than 30 percent of the amount earned. Living wage laws operate in St Louis, St Paul, Minneapolis, Boston, Oakland, Denver, Chicago, New Orleans, and New York City. The effects of a living wage are similar to those of a minimum wage. Taxes Everything you earn and most things you buy are taxed. Who really pays these taxes? Income tax and the Social Security tax are deducted from your pay, and the sales tax is added to the price of the things you buy, so isn’t it obvious that you pay these taxes? Isn’t it equally obvious that your employer pays the employer’s contribution to the Social Security tax? You’re going to discover that it isn’t obvious who pays a tax and that lawmakers don’t decide who will pay! Taxes Tax Incidence Tax incidence is the division of the burden of a tax between the buyer and the seller. When an item is taxed, its price might rise by the full amount of the tax, by a lesser amount, or not at all. If the price rises by the full amount of the tax, the buyer pays the tax. If the price rise by a lesser amount than the tax, the buyer and seller share the burden of the tax. If the price doesn’t rise at all, the seller pays the tax. Taxes Tax Incidence Tax incidence doesn’t depend on tax law! The law might impose a tax on the buyer or the seller, but the outcome will be the same. To see why, we look at the tax on cigarettes in New York City. On July 1, 2002, Mayor Bloomberg upped the cigarette tax in New York City from almost nothing to $1.50 a pack. Taxes A Tax on Sellers Figure 6.7 shows the effects of this tax. Taxes A Tax on Sellers Figure 6.7 shows the effects of this tax. With no tax, the equilibrium price is $3 a pack. A tax on sellers of $1.50 a pack is introduced. The curve S + tax on seller shows the new supply curve. Taxes The vertical distance between the original supply curve and the supply curve with the tax is equal to the amount of the tax--$1.50. Buyers would have to pay $4.50 a pack to induce firms to offer the original quantity for sale. Taxes The tax changes the equilibrium price and quantity. The quantity decreases. The price paid by the buyer rises to $4 and the price received by the seller falls to $2.50. Taxes So buyers pay $1 of the tax. Sellers pay the remaining 50¢. Taxes A Tax on Buyers Now suppose that buyers, not sellers, are taxed $1.50 a pack. Again, with no tax, the equilibrium price is $3 a pack. A tax on buyers of $1.50 a pack is introduced. The curve D - tax on buyer shows the new demand curve. Taxes The vertical distance between the original demand curve and the demand curve minus the tax is equal to the amount of the tax--$1.50. Sellers would have to accept $1.50 a pack to induce people to buy the original quantity. Taxes The tax changes the equilibrium price and quantity. The quantity decreases. The price paid by the buyer rises to $4 and the price received by the seller falls to $2.50. Taxes So, exactly as before when the seller was taxed: The buyer pays $1 of the tax. The seller pays the other 50¢ of the tax. Tax incidence is the same regardless of whether the law says the seller pays or the buyer pays. Taxes The division of the tax between the buyer and the seller depends on the elasticities of demand and supply. Tax Division and Elasticity of Demand To see the effect of the elasticity of demand on the division of the tax payment, we look at two extreme cases. Perfectly inelastic demand: the buyer pays the entire tax. Perfectly elastic demand: the seller pays the entire tax. The more inelastic the demand, the larger is the buyers’ share of the tax. Taxes In this figure, demand is perfectly inelastic—the demand curve is vertical. When a tax is imposed on this good, the buyer pays the entire tax. Taxes In this figure, demand is perfectly elastic—the demand curve is horizontal. When a tax is imposed on this good, the seller pays the entire tax. Taxes Tax Division and Elasticity of Supply To see the effect of the elasticity of supply on the division of the tax payment, we again look at two extreme cases. Perfectly inelastic supply: the seller pays the entire tax. Perfectly elastic supply: the buyer pays the entire tax. The more elastic the supply, the larger is the buyers’ share of the tax. Taxes In this figure, supply is perfectly inelastic—the supply curve is vertical. When a tax is imposed on this good, the seller pays the entire tax. Taxes In this figure, supply is perfectly elastic—the supply curve is horizontal. When a tax is imposed on this good, the buyer pays the entire tax. Taxes Taxes in Practice Taxes usually are levied on goods and services with an inelastic demand or an inelastic supply. Alcohol, tobacco, and gasoline have inelastic demand, so the buyers of these items pay most the tax on them. Labor has a low elasticity of supply, so the seller—the worker—pays most of the income tax and most of the Social Security tax. Taxes Taxes and Efficiency Except in the extreme cases of perfectly inelastic demand or supply when the quantity remains the same, imposing a tax creates inefficiency. Figure 6.11 shows the inefficiency created by a $10 tax on CD players. Taxes With no tax, the market is efficient and the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized. A tax shifts the supply curve, decreases the equilibrium quantity, raises the price to the buyer, and lowers the price to the seller. Taxes The tax revenue takes part of the consumer surplus and producer surplus. The decreased quantity creates a deadweight loss. Subsidies and Quotas Fluctuations in the weather bring big fluctuations in farm output. How do changes in farm output affect the prices of farm products and farm revenues? How might farmers be helped by intervention in markets for farm products? Stabilizing Farm Revenues Harvest Fluctuations Figure 6.12(a) shows the market for wheat. Once the crop is planted, supply is perfectly inelastic along the momentary supply curve MS0. The price is $4 a bushel and farm total revenue is $80 billion. Stabilizing Farm Revenues A poor harvest decreases supply. Farmers lose $20 billion of total revenue on the decreased quantity sold. But they gain $30 billion from the higher price. Because demand is inelastic, total revenue increases—to $90 billion. Stabilizing Farm Revenues Now a bumper harvest increases supply. Farmers lose $40 billion of total revenue on the original quantity because the price falls. They gain only $10 billion from the increased quantity. Because demand is inelastic, total revenue decreases—to $50 billion. Stabilizing Farm Revenues Intervention in markets for farm products takes two main forms: Subsidies Production quotas A subsidy is a payment made by the government to a producer. A production quota is an upper limit to the quantity of a good that may be produced during a specified period. Stabilizing Farm Revenues Subsidies The producers of peanuts, sugarbeets, milk, wheat, and many other farm products receive subsidies. Figure 6.13 shows how a subsidy works. With no subsidy, the price is $40 and the quantity is 40 million tons a year Stabilizing Farm Revenues Subsidies A subsidy of $20 a ton is introduced. Marginal cost minus subsidy falls by $20 and the new supply curve is S – subsidy. The new equilibrium is at 60 million tons and $30 a ton. Stabilizing Farm Revenues Subsidies The equilibrium quantity increases. The equilibrium price falls. The farmer receives more on each ton sold--$50 a ton in this example. Stabilizing Farm Revenues Production Quotas The markets for sugarbeets, tobacco leaf, and cotton, among others, are regulated with production quotas. Figure 6.14 shows how a production quota works. With no quota, the price is $30 and the quantity is 60 million tons a year. Stabilizing Farm Revenues Production Quotas A production quota limits total production to 40 million tons a year. The equilibrium quantity decreases to this amount. The price rises to $50 a ton and marginal cost falls to $20 a ton. Markets for Illegal Goods The U.S. government prohibits trade of some goods, such as illegal drugs. Yet, markets exist for illegal goods and services. How does the market for an illegal good work? A Free Market for Drugs To see how the market for an illegal good works, we begin by looking at a free market and see the changes that occur when the good is made illegal. Markets for Illegal Goods Figure 6.15 shows the market for a drug such as marijuana. The equilibrium is at point E. The price is PC and the quantity is QC. Markets for Illegal Goods A Market for Illegal Drugs Prohibiting transactions in a good or service raises the cost of such trading. If sellers (drug dealers) are penalized, we must add the cost of breaking the law to the minimum supply price. Markets for Illegal Goods If the penalty on the seller is the amount HK, the quantity supplied at a market price of PC is QP. A new supply curve passes through point H. The new equilibrium is at point F. The price rises and the quantity decreases. Markets for Illegal Goods Starting again at the equilibrium point E, suppose that buyers are penalized (and not sellers). Now, we must subtract the cost of breaking the law from the maximum price that the buyer is willing to pay. Markets for Illegal Goods If the penalty on the buyer is the amount JH, the quantity demanded at a market price of PC is QP. A new demand curve passes through point H. The new equilibrium is at point G. The market price falls and the quantity decreases. Markets for Illegal Goods But the opportunity cost of buying this illegal good rises because the buyer pays the market price plus the cost of breaking the law. Markets for Illegal Goods Now suppose that both buyers and sellers are penalized for trading in the illegal drug. We add the cost of breaking the law to the minimum supply price and get a new supply curve. Markets for Illegal Goods The new equilibrium is at point H. The quantity decreases to QP . The market price is PC. The buyer pays PB and the seller receives PS. Markets for Illegal Goods Legalizing and Taxing Drugs An illegal good can be legalized and taxed. A high enough tax rate would decrease consumption to the level that occurs when trade is illegal. Arguments that extend beyond economics surround this choice. THE END