1.00 x 10 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

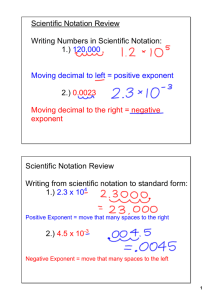
Re-teach week continued Boon Chemistry January 10 and 11, 2013 Catalyst Write at least five sentences answering any or all of the following questions: What is your favorite type of environment for studying or doing homework? Describe the place, time, noise level, other surrounding circumstances. Objectives I can calculate the concentration of a solution. I can describe the dissolving process on the molecular level. I can perform scientific notation calculations. Agenda Catalyst Benchmark Redo Quiz Scientific Notation Review Acids and Bases Vocabulary Benchmark Redo Quiz Expectations: Tools: You will work silently and independently. When you are done, cover your quiz with your handouts. You may use your concentration foldable and intermolecular forces handout to help you. You may use your own calculator. What do I turn in? You will turn in your quiz, concentrations foldable, and intermolecular forces handout. Scientific Notation Our next unit is acids and bases and we will be working with numbers in scientific notation. Scientific notation is a shorthand way of expressing really large numbers or very small numbers. There are two rules to keep in mind when writing a number in scientific notation. 2.5 x 105 The first number has to be greater than or equal to 1 and less than 10. The second number is 10 to a power. The power will show how many places to move the decimal point. Scientific Notation Quick Check Thumbs up for proper scientific notation and thumbs down for incorrect scientific notation. 4.0 x -2 10 Scientific Notation Quick Check Thumbs up for proper scientific notation and thumbs down for incorrect scientific notation. 15 x 8 10 Scientific Notation: Conversions To translate a number from scientific notation to standard form, look at the exponent on the 10. 2.5 x 105 If the exponent is positive move the decimal to the right. 2.5 x 105 = 250,000 2.5 x 10-4 If the exponent is negative move the decimal to the left. 2.5 x 10-4 = 0.00025 Scientific Notation: Conversions To translate a number from standard notation to scientific notation put the decimal after the first digit, keep all other different digits, but drop the repeated zeros. 23,000 Determine the exponent by counting how many places you have to move the decimal point to get back to your original number. 2.3 x 10? 2.3 x 104 Scientific Notation: Addition Addition: Example – A chemist mixes a solution by combining 3.0 x 102 mL KOH to 5.0 x 103 mL water. What is the total volume of the solution in mL? Step 1: In order to add, the exponents must be the same. Convert the first quantity to a multiple of 103 to match the second quantity. 3.0 x 102 mL KOH = 0.30 x 103 mL KOH because the exponent is increased by one, the decimal point moves one place to the left. Step 2: Add. Remember to line up the decimal points. 0.30 x 103 mL KOH + 5.0 x 103 mL water Answer: 5.30 x 103 mL solution Step 3: Convert to proper scientific notation! The answer is already in the proper notation because 5.3 is between 1 and 10. Scientific Notation: Subtraction Subtraction: Example – A chemist opens a 1.0 x 104 mL bottle of 1 M Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and removes 7.5 x 102 mL HCl. What volume is left in the bottle? Step 1: In order to subtract, the exponents must be the same. Convert the second quantity to a multiple of 104 to match the first quantity. 7.5 x 102 mL HCl = 0.075 x 104 mL HCl because the exponent is increased by two, the decimal point moves two places to the left. Step 2: Subtract. First line up the decimal points. 1.000 x 104 mL HCl + 0.075 x 104 mL HCl 0.925 x 104 mL HCl Step 3: Convert to proper scientific notation! 0.925 x 104 mL HCl = 9.25 x 103 mL HCl because the decimal point moves one place to the right, the exponent decreases by one. Scientific Notation: Multiplication Multiplication: Example – At 25°C any sample of pure water contains the following ion concentrations: 1.00 x 10-7 M H3O+ and 1.00 x 10-7 M OH-. Calculate the product of these concentrations. This value is called the selfionization constant of water. (1.00 x 10-7)x(1.00 x 10-7) = ? Step 1: Multiply the coefficients. 1.00 x 1.00 = 1.00 Step 2: Add the exponents. 10-7 + -7 = 10-14 Step 3: Convert to proper scientific notation. 1.00 x 10-14 The answer is already in the proper notation because 1.00 is between 1 and 10. Scientific Notation: Division Division: Example – The hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration of an acid or base solution can be found by dividing the self ionization constant of water (1.00 x 10-14) by the solution’s H3O+ concentration. If the H3O+ concentration is 3.00 x 10-5, what is the OH-concentration? 1.00 x 10-14 = [OH-] 3.00 x 10-5 Step 1: Divide the coefficients. 1/3 = 0.33 Step 2: Subtract the exponents. 10-14 - -5 = 10-9 Step 3: Convert to proper scientific notation. 0.33 x 10-9 = 3.3 x 10-10 = [OH-] because the decimal point moves one place to the right, the exponent decreases by one. Acids and Bases Flashcards Front of card: Back of card: Vocabulary word Picture/diagram definition Sentence using the word Resources: Textbook Chapter 15 Words are also posted on the wall. Words Strong acid Weak acid Strong base Weak base Neutral pH Amphoteric Bronsted-Lowry acid Bronsted-Lowry base Conjugate acid Conjugate base Hydronium ion Hydroxide ion Self-ionization constant of water Electrolyte indicator Independent Work Time Expectations: You may work on the following: You must work at your seat. You may speak quietly to the students next to you. Raise your hand if you need help. You may get up to check your answers. Scientific notation worksheet. Acids and Bases Flashcards. Answers are posted at the front of the class. Correct your work. Homework Finish the scientific notation worksheet and your flashcards. I will collect your daily work organizer. Highly recommended by optional: Buy a scientific calculator and a white board marker.