Revision notes for End of Year Assessment 2011
advertisement
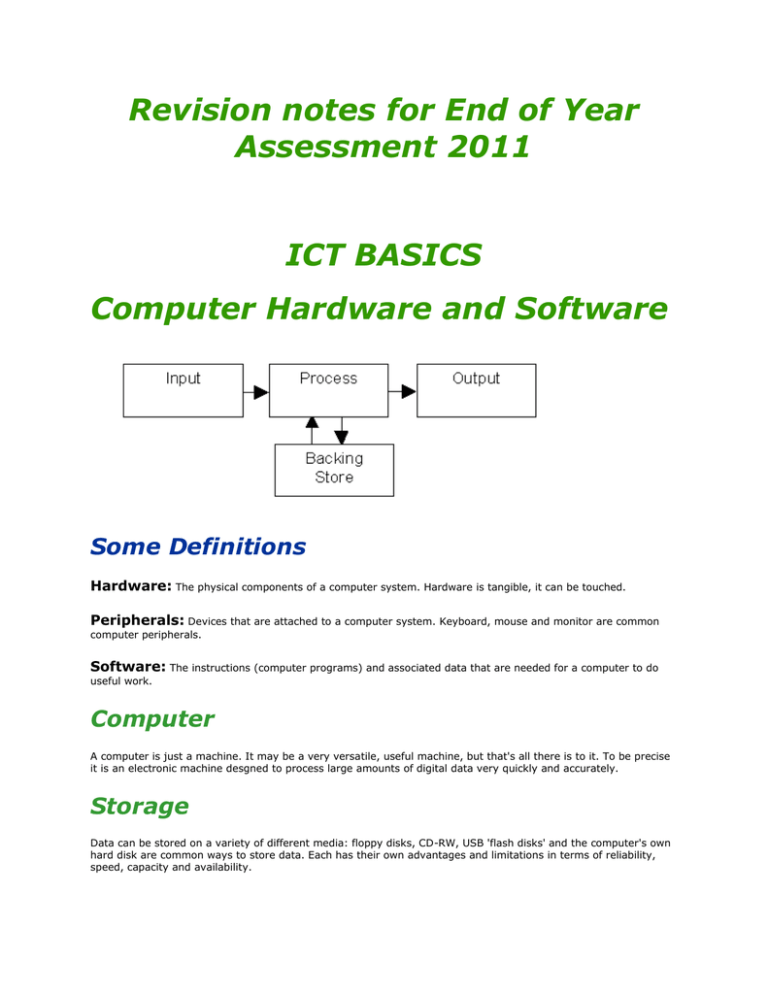
Revision notes for End of Year Assessment 2011 ICT BASICS Computer Hardware and Software Some Definitions Hardware: The physical components of a computer system. Hardware is tangible, it can be touched. Peripherals: Devices that are attached to a computer system. Keyboard, mouse and monitor are common computer peripherals. Software: The instructions (computer programs) and associated data that are needed for a computer to do useful work. Computer A computer is just a machine. It may be a very versatile, useful machine, but that's all there is to it. To be precise it is an electronic machine desgned to process large amounts of digital data very quickly and accurately. Storage Data can be stored on a variety of different media: floppy disks, CD-RW, USB 'flash disks' and the computer's own hard disk are common ways to store data. Each has their own advantages and limitations in terms of reliability, speed, capacity and availability. Output Output from a computer is usually seen via a monitor screen or printed hardcopy. Your choice of monitor and printer will also depend on a number of factors including price and resolution needed. Questions A. Make a list of different storage media and list 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage of each. Networks Network: a network allows several computers to share hardware, software and data stored on any specific machine. Networks are divided into two main groups: Local Area Networks (LANs): where all machines are physically connected to eachother. Typically, all the machines will be fairly close to eachother, but not necessarily in the same room or even building. Wide Area Networks (WANs): where computers communicate with eachother via telephone lines or wireless transmission. Advantages of Using a Network There are many reasons why a business may choose to install a network, including: Cost: a business does not need to buy expensive hardware for each individual machine. Also, site licenses for network versions of applications software may be cheaper than several individual licenses. More significantly, less office space is needed for peripherals when several machines can all share a printer. Efficiency: instead of having to make multiple copies of documents, a single version can be made available to everyone over a network. When this file is updated, everyone has access to the new document at the same time. With all technologies, there are risks. By adding a network, a company may experience: Hacking: people might attempt to gain unauthorized access to sensitive material stored on the network . Vulnerability to Virus Programs: an infected file shared across a network has the potential to infect a large number of machines very quickly. Peer to Peer Networking Many networks rely on one specific machine storing all data that is shared between the terminals connected to it (a file server). However, modern peer-to-peer technology allows data to be shared between individual machines with each of them acting as a server in its own right. Questions A. List three reasons why a school might choose to use a network. B. Your cousin is thinking of adding a wireless network to his home in order to enable him to listen to his extensive music collection from any room in the house. Write a letter to him explaining that a network would allow him to do much more than this (give at least three examples) and also list some of the security issues he should be aware of if he chooses to do this. C. Describe five ways in which a network could help a secretary in a large company do their job more efficiently. D. Describe two problems that installing a network might cause. Discuss different ways to overcome those problems. Appropriate Uses of Application Software Applications software: is general purpose software that allows you to perform a range of related tasks more efficiently than you could by using more conventional technologies. Integrated package: a suite of applications programs with their associated data and documentation. Typically, it is usually much cheaper to buy an integrated package than individual applications programs, it is easier to copy data from one application in a suite to another (eg import a table of data or a chart from a spreadsheet into a word-processing document) and the user interface is similar for the programs in the suite. Common Applications There are many different applications programs: Word-processor: allows you to create, edit, store and print a range of different text documents; from letters and faxes to books and essays. Spreadsheet: enables you to use formulas to perform a large number of calculations on data stored in cells arranged in rows and columns. You can investigate a mathematical problem, create a budget plan to forecast how much you can save in a year or model the results of a science experiment and draw a chart of your results. Database: uses forms to store data in tables made up of records and fields. The data can be searched using queries in order to find out useful information. It can be used to create anything from an address book to a complex application that produces end of year reports. Graphics program: can be used to create posters, perform image processing in order to improve or alter photographs or create original artwork. DTP software: Desk Top Publishing software allows you to manipulate text and graphics in frames on a page in order to create magazines, brochures and other complex documents. Presentation Software: allows you to create a slideshow to illustrate a talk, or a presentation for other people to investigate as a kiosk application. Communications software: could include a web browser or email client software as well as other programs that allow you to communicate with Flexibility With modern applications software, there is a great deal of overlap. Many spreadsheet programs have a range of database functions built in, and the graphics tools within a word-processor might rival a graphics program - let alone a DTP package. Questions A. List three reasons why a school would teach its students how to use applications software. B. A scientist has an integrated package installed on his computer. List two different tasks that he could use a word-processor, spreadsheet, database and communications software to help him work more effectively. Appropriate Uses of Application Software Applications software: is general purpose software that allows you to perform a range of related tasks more efficiently than you could by using more conventional technologies. Integrated package: a suite of applications programs with their associated data and documentation. Typically, it is usually much cheaper to buy an integrated package than individual applications programs, it is easier to copy data from one application in a suite to another (eg import a table of data or a chart from a spreadsheet into a word-processing document) and the user interface is similar for the programs in the suite. Common Applications There are many different applications programs: Word-processor: allows you to create, edit, store and print a range of different text documents; from letters and faxes to books and essays. Spreadsheet: enables you to use formulas to perform a large number of calculations on data stored in cells arranged in rows and columns. You can investigate a mathematical problem, create a budget plan to forecast how much you can save in a year or model the results of a science experiment and draw a chart of your results. Database: uses forms to store data in tables made up of records and fields. The data can be searched using queries in order to find out useful information. It can be used to create anything from an address book to a complex application that produces end of year reports. Graphics program: can be used to create posters, perform image processing in order to improve or alter photographs or create original artwork. DTP software: Desk Top Publishing software allows you to manipulate text and graphics in frames on a page in order to create magazines, brochures and other complex documents. Presentation Software: allows you to create a slideshow to illustrate a talk, or a presentation for other people to investigate as a kiosk application. Communications software: could include a web browser or email client software as well as other programs that allow you to communicate with Flexibility With modern applications software, there is a great deal of overlap. Many spreadsheet programs have a range of database functions built in, and the graphics tools within a word-processor might rival a graphics program - let alone a DTP package. Questions A. List three reasons why a school would teach its students how to use applications software. B. A scientist has an integrated package installed on his computer. List two different tasks that he could use a word-processor, spreadsheet, database and communications software to help him work more effectively. APPLICATION OF ICT Databases Data: can be words, numbers, pictures etc. It is important to remember that we get useful information from our raw data by processing it in different ways. Database: a database is an ordered collection of related data that a user can process in different ways in order to extract useful information. Computerised Databases Using a computer to store a database has a number of advantages:/p> Speed: a computer can search through a large amount of data much more quickly than a human can. Accuracy: computers don’t get tired, bored or accidentally skip a number of records. You can be sure that the results found in a computer’s database are as accurate as they were when the data was entered in. Main Features of a Computer Database Databases are made up of four main parts: Tables: data is stored in individual tables made up of records and fields. A relational database will link tables of related data together so that it can be stored more efficiently. o Records: represent all the data held on an individual item. o Fields: are the different categories into which the data has been organized. o A key field has a unique value for each record in a database table, it can be used to index the records in the database. Forms: are used to allow people to enter data easily into a database. A database form might look very similar to one that someone has already filled in on paper. Queries: allow a user to filter out the data that they don’t want, and display only those records which contain data that they are interested in. A simple query might only search the database for data that matches one criterion. A complex query is more likely to search for records that match two or more criteria. Reports: allow you to print just the data that you want. You can choose to display only those records matching a query, and only those fields that are relevant to your search. You may choose to order or group your data in different ways and add summary details to your printout. This means that the same database of personal information can be used to print out address labels, attendance registers and contact lists of names and telephone numbers grouped by residential area. Questions A. Describe how a teacher could print out the names of the students in a year 9 form, if they had a database of all students in their school. B. What would be an appropriate key field for a school library to use in a database of its books? Desktop Publishing (DTP) DTP: a DTP program allows you to combine text and graphics using frames to build up multi-column pages, like newspapers, magazines and brochures. The text and graphics need not be entered directly into the program, but can be prepared in advance using word-processing or image-processing software. Frames: are objects on a page which can be given different colours or borders and into which text and graphics can be imported. Text frames in a publication can be linked together so that a story can easily flow from one frame into another. Advantages of Using DTP Software There are a number reasons why a business may choose to use DTP, including: Cost: a business does not need to hire a commercial printing bureau to professionally typeset every publication. Efficiency: instead of having to spend time approving proofs from an outside printer, the final document can be previewed and changes made immediately using the company's own hardware and software. Small printing jobs or re-prints of a publication can be done quickly by a company's own staff. Disadvantages of Using DTP Software As with all technologies, there are disadvantages: Expense: additional software and hardware may need to be bought. Training: staff will need to be trained to develop new skills if they are to use the new hardware and software effectively. Hardware Special hardware is often needed in order to work effectively with DTP software – this could include buying a new printer to cope with the demand and quality of publications required. Other input devices might be needed in order to capture images for a publication. Also, if the final output is to be sent to a printing bureau for a larger print run, you will need to be able to store and distribute extremely large files. Questions A. List three different types of document that could be produced using DTP software. B. Your friend is thinking of starting a small printing business using DTP software. Write a letter that he could use to explain to his customer the advantages of allowing him to produce their brochures and other promotional material. C. Describe five items of hardware (in addition to your computer, monitor, mouse and keyboard) that could be needed to produce DTP documents. D. Describe two reasons why a company would prepare documents and images in advance, before importing them into a DTP program. The Social Impact of IT in the Workplace Social Impact: using information technology in business has caused a number of changes in the way that people communicate and work with eachother. Communications Improvements in communications technologies have made some issues particularly interesting: The electronic office: allows people to produce reports and other documents far more quickly, with greater access to relevant information. Variety of contacts: people can communicate by email, fax, mobile phone, pager or any one of several other methods including teleconferencing - which has the advantage of being far cheaper than flying several people to the same conference room.. Responsibility: new laws have been made in order to make sure that people do not misuse the large amounts of personal information they now have access to with new technologies, or to deter them from trying to get unauthorized access to information they are not entitled to. Working With new technologies, new practices have been adopted in the workplace this affects issues like: Training: people might need to be trained to use the new hardware and software. If they can’t learn these new skills, they might end up without a job. Productivity: using a computer, more work can be achieved in less time by fewer people. Working from home: people no longer need to commute into a large city to work in an office with other employees. New jobs: although some jobs have disappeared through introducing new technologies, whole new industries have been created in order to build, maintain, write software and provide support and training related to IT. Questions A. A company is upgrading its computer system. Your friend is worried that they may lose their job as a result. Write a note to them, outlining some of the possible advantages to them arising from the upgrade. B. Describe two problems that could result from personal data being accessed by unauthorized people in a company. The Impact of IT in the Home Recent advances in information technology have caused a number of changes in the way that people communicate and spend their leisure time. Communication Improvements in communications technologies have meant that it is now far cheaper for families and friends to keep in regular contact including. E-mail: allows you to not only send text, but you can also attach files, or links to web addresses where other information can be displayed or downloaded. Internet telephony/VoIP: using a computer and internet connection to send and receive sound allows you to take advantage of phone rates that are far cheaper than international lines. Instant messaging: allows you to ‘chat’ by typing in real time with other people online at the same time as you. Digital photographs: are shared by family and friends much more easily via CDs, telephones, email and websites - and if people want an extra printed copy, they can do it themselves. Leisure With new technologies, people have new ways to do a variety of things: Shopping: with a credit card and an internet connection, you can order food, clothing, books, book holidays or participate in auctions for antiques, all without leaving the comfort of your own home, or at 2.00am when local shops may be closed. Hobbies: users can interact with other fans via message boards, read news about the latest craze or even create their own website or fanzine using applications software. Learning: you can now buy packages to help you learn a new language, revise for exams, become a better typist or just look up interesting facts in multimedia encyclopedias. Media: you can record and distribute your own music (and design the CD cover), create and edit your own movies and animations, write a play (and perform it online as a podcast for others to download) or create your own computer games. Questions A. List three reasons why people use new technologies to keep in contact with eachother. B. Your cousin is thinking of producing a magazine about model making. Discuss how using a computer could help him put together and distribute the magazine to its readers. C. Describe two problems that.people sometimes have with online shopping. The Social Impact of the Internet The Internet: A wide area network of computer networks, allowing the free exchange of large amounts of data across the world. The Internet is more than the World Wide Web. You can use the Internet to send and receive electronic mail, participate in discussions through newsgroups and even control other computers and devices remotely. Who uses the Internet? Different people use the Internet to help them do their jobs in a variety of ways: A lawyer might interrogate a huge database of the results of cases held in different courts nationwide. A doctor could get in touch with specialists and patients when trying to treat extremely rare diseases. A teacher can control a university’s radio telescope with a science class without leaving their own classroom. Positive and Negative As with all tools, the Internet is not always used for good purposes. Different crimes, like identity theft can be done much more easily over the Internet because people may not realize that they are sending sensitive personal information to someone who is not who they claim to be. Questions A. List three jobs that have been created through the introduction of the Internet. B. List one job which is threatened by increased use of the Internet. C. Describe five ways in which different professions have found that using the internet helps them to achieve much more than before. D. Describe two ways that the Internet can be used to enhance leisure time. E. Describe two ways in which the Internet can be misused and discuss the ways these problems can be dealt with. Computer Security Computer Crime: crimes that are committed with the aid of a computer. For example, using a computer to commit fraud by identity theft. Hacking: attempting to gain unauthorized access to someone else’s computer. Phishing: impersonating an official organization in the hope that the victim will pass on personal information like bank account details to the fraudster. Pharming: hijacking the way that a browser finds specific websites over the internet, and pointing a user to a fraudulent website instead. Virus: a self-replicating program, written to disrupt the normal use of a computer system. Trojan: a program which the user runs thinking it will do one thing, but in reality, it does harm to the computer system. Who is responsible? You are responsible for the security of your own computer. However, as with breaking and entering someone else’s property; leaving a door unlocked is unwise, but it does not give a burglar the right to rob your house. If you do suspect something is wrong, get expert help and advice quickly. But prevention is far better than cure. What to do? Much of what you will do is common sense here are a selection of things to remember. Always keep your antivirus software up to date. Never open email attachments from unrecognized senders, and always ask yourself whether a person known to you is likely to be sending you an attachment. Always use passwords that are impossible for someone else to easily guess. Never install software from an unrecognized source - not only pirated software, but be careful where you download patches and upgrades to existing programs from. Never give anyone your password for any service. If they are authorized to investigate something, they don’t need it. If they aren’t, they shouldn’t have it. Always check warnings you receive via email with an authoritative source of information. If you receive an offer from someone that seems too good to be true, it almost certainly is. Questions A. Your best friend has just lost his entire Social Studies project due to a virus infection on his computer. What advice would you give him to ensure that this doesn’t happen again? B. List one new job which has become more important due to the rise in computer security problems. C. Describe two ways that the Internet can be used to help you improve your computers security, and one way in which it makes your system more vulnerable to attack. D. Design a poster to illustrate some of the computer security advice listed above. Computer Analyst 1. List 3 methods of collecting data/information. Give examples. 2. Design suitable screen input. 3. Verification and Validation. Describe and give examples. 4. Describe methods of implementation with examples. 5. Evaluation. 6. Documentation. 7. Design cycle.





