Inhaled corticosteroids in asthma
advertisement

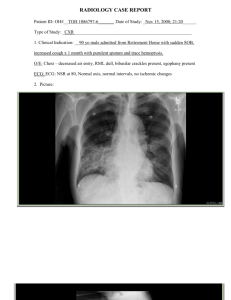
Respiratory Medicine II FRACP teaching – Wed 24 Oct 2007 Respiratory Medicine Middlemore Hospital Programme – 1300-1700hrs • Asthma and COPD – Jeff Garrett • Sleep disorders – Andy Veale • Pulmonary physiology and lung function tests – Conor O’Dochartaigh • Break (1510-1530) • Respiratory multi-choice questions – Anna Tai • Pulmonary infections – Conroy Wong Evaluation Form • Please complete and hand-in at end of day! Pulmonary infections • Pneumonia • TB • Empyema • Airway infections – Bronchiectasis – Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) – Aspergillus infection Pneumonia Which statement from the IDSA/ATS* (2007) guidelines about community-acquired pneumonia does not have Level I evidence? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Locally adapted guidelines should be implemented Inpatients should be treated with a ß-lactam plus macrolide Patients should be treated with antibiotics for a minimum of 5 days The first antibiotic dose should be administered while still in ED Healthcare workers should receive annual influenza vaccination *Infectious Diseases Society of America / American Thoracic Society This patient has a community-acquired pneumonia. Which statement is true? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The CXR shows consolidation associated with a mass in the R middle lobe The lobar distribution indicates that Streptococcus pneumoniae is likely to be the pathogen This patient should routinely have paired serological tests A CURB-65 score of < 2 has a 30-day mortality of < 2% PCR for legionella is indicated for severe pneumonia Legionella pneumonia – lobar Serology: acute = negative convalescent = 1024 Severity assessment - CURB-65 • British Thoracic Society – Severity assessment of all patients with pneumonia • • • • • • • Confusion (Mental status score 8 or less) Urea > 7 mmol/L Respiratory rate ≥ 30 Blood pressure – systolic <90 and/or diastolic ≤ 60 Age over 65 Score ≥ 3 (‘Severe’) – high risk of death (>20%) Also: Hypoxaemia (SaO2<92%), multilobar involvement PSI – Pneumonia Severity Index N Engl J Med 1997;336:243 Procalcitonin in pneumonia Which statement about procalcitonin in communityacquired pneumonia is false? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Procalcitonin levels are increased in bacterial infections Persistently elevated levels of procalcitonin are associated with adverse outcome Procalcitonin guidance of antibiotic therapy reduces the duration of antibiotic use CRP is a better marker of sepsis Procalcitonin levels rise within 6 to 12 hours A 75 year-old man presents with a 4 month history of cough and mild dyspnoea He did not respond to augmentin but has a good response to prednisone. His chest xray and CT scan are shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Chlamydia pneumonia 2. Legionella pneumonia 3. Organising pneumonia 4. SLE pneumonitis 5. Pneumocystis pneumonia Organising pneumonia • Consider if non-resolving pneumonia • Causes – Cryptogenic (COP), Infection, Drugs (amiodarone) • Cough, fever, malaise – Dyspnoea usually mild • Radiology – patchy peripheral and bilateral distribution • Differential dx: chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, alveolar cell carcinoma, pulmonary lymphoma Mycobacterium tuberculosis Positive acid-fast stain Positive culture TB pleural effusions Which statement about tuberculous pleural effusions is false? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The diagnostic value of pleural investigations is dependent on the pretest probability Pleural aspirates show lymphocytic predominance Microscopy and culture for TB are often negative Adenosine deaminase has high sensitivity and specificity in TB effusions with lymphocyte predominance PCR is the gold standard for diagnosis Isoniazid prophylaxis A medical registrar has a repeat Mantoux test after 2 years and there is a ≥ 10mm increase. Isoniazid is considered. Which statement is false? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The risk of hepatitis increases with age The risk of hepatitis is about 2% at age 60 Isoniazid is recommended only if aged <35y The lifetime risk of tuberculosis is 5-10% Interferon release assays are more specific than Mantoux tests Blood tests for TB – TIGRA For T cell interferon release assays, which of the following statements is false? 1. Interferon is produced by T cells in response to antigens specific to M tuberculosis 2. They are more rapid than tuberculin tests 3. They are more specific than tuberculin tests 4. There is no boosting effect 5. They cross react with BCG more often than tuberculin tests Interferon release assays (Sensitised) TB QuantiFERON-TB Gold Assay TB AG TB AG Mitogen T-Spot.TB assay A B C Peripheral blood mononuclear cells D A:Null B:Antigen A C:Antigen B D:Positive A 32 year-old man presents with a 2 week history of cough, fevers and pleuritic chest pain. The ALT was 192 and ALP 391. His CT scan is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Lung abscess 2. Haemopneumothorax 3. Empyema with pneumothorax 4. Mesothelioma 5. Cavitating carcinoma with liver metastases A chest drain was inserted. This obtained pus and Streptococcus milleri was cultured. The best evidence for the role of intrapleural streptokinase for empyema indicates that: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Streptokinase is no better than saline flushes Urokinase is superior to streptokinase Streptokinase reduces mortality Streptokinase reduces the need for surgical drainage Streptokinase reduces the length of stay in hospital 1 Sept 2005 28 Oct 2005 Largest clinical trial in pleural infection UK: Multicenter Intra-Pleural Sepsis Trial (MIST) 52 centers Pleural fluid >1 of criteria: • purulent • Gram stain +ve • Culture +ve • pH<7.2 & clinical evidence of pneumonia 430 patients (age >18): Most have severe disease 80% frankly purulent fluid Pleural fluid pH 6.8 (mean) MIST trial - results • Streptokinase has no benefit over placebo for the following endpoints – Primary • Mortality or surgery at 3 months – Secondary • • • • Mortality Surgery Radiograph outcome Length of hospital stay • SK group had increased serious adverse events (p=0.08) Conclusion • No benefit of streptokinase over saline flushes – For any outcome measure • Not to be used routinely • Also metaanalysis (Tokuda. Chest 2006;129) – 5 trials with 575 patients • MIST II – DNAse v TPA v DNAs + TPA v Placebo Bronchiectasis Treatment of bronchiectasis Which one of these statements is (most) correct? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Oral steroids are beneficial for acute exacerbations? Inhaled steroids are beneficial for stable bronchiectasis? Prolonged antibiotics are superior to standard courses of antibiotics for patients with bronchiectasis? Physiotherapy is recommended but has not been shown to be effective Short-acting beta-agonists are effective in bronchiectasis Steroids for bronchiectasis • Oral steroids for bronchiectasis – Cochrane review • No randomised trials – Benefit unknown • Inhaled steroids for bronchiectasis – Cochrane review • Three trials • Limited, if any, effect on any outcomes • May improve lung function (trend) and sputum volume – Benefit unclear Antibiotics and bronchiectasis • Cochrane review • 6 trials, 302 patients – One study contributed 40% • Antibiotics for between 4 weeks and 1 year • Prolonged antibiotics – Improved response rates (OR 3.4) – No effect on exacerbations • Conclusions – Limited data. Small benefit from prolonged antibiotics Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) Which one of these statements is correct? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. MAC is found in various sources including water, house dust, soil and animals? ‘Hot tub lung’ is MAC infection that responds to antibiotic therapy MAC lung disease rarely occurs in patients with pre-existing lung disease or immunosuppression? In patients without pre-existing lung disease, MAC usually affects young men? The presence of bronchiectasis and multiple small nodules are not predictive of MAC lung disease? 2007 ATS/IDSA criteria for diagnosis • Clinical features • Radiographic – Fibrocavitary disease • CXR - cavitary opacities – Noncavitary disease • CXR – nodular opacities • HRCT Multifocal bronchiectasis with multiple small nodules • Bacteriologic – Sputa – two positive in one year – Bronch wash – one positive culture – Tissue – positive culture or granuloma & +ve sputum/wash Multifocal bronchiectasis MAC infection Peripheral nodules Which statement is correct about macrolide antibiotics? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. They act by disrupting cell membranes of microorganisms They have no activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa They have minimal anti-inflammatory effects on neutrophils and macrophages They substantially reduce mortality in panbronchiolitis? Low dose azithromycin taken for 6 months improves lung function in patients with cystic fibrosis but causes irreversible hearing loss Macrolide antibiotics • Anti-infective, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory properties • Low dose azithromycin is effective in cystic fibrosis • Highly effective in panbronchiolitis 20 yr Indian man with panbronchiolitis Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis Which statement is false? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ABPA occurs more commonly in patients with cystic fibrosis than in chronic asthmatics? ABPA is unlikely if the total IgE level is less than 400 IU/mL Skin prick testing is a useful screening test to identify patients with ABPA Almost 100% of patients with an established aspergilloma have aspergillus precipitins Proximal bronchiectasis is a prerequisite for diagnosis ABPA • Key diagnostic features – – – – – – – – Asthma* Positive skin prick test to Aspergillus fumigatus* Total IgE > 400 IU/mL (1000 ng/mL)* Elevated specific IgE (and IgG) to Aspergillus* Aspergillus precipitins (IgG) Pulmonary infiltrates Proximal bronchiectasis Also eosinophilia, sputum culture ABPA • • • • • • • June 04 Poorly controlled asthma Eosinophilia – 1.1 Total IgE - 3959 IU/ml Precipitins – negative Specific IgE – 3+ Asp. skin prick – 7mm HRCT – ‘central bronchi have irregular walls’ (2004) Itraconazole Which one of the following adverse effects does not occur with itraconazole treatment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Rise in ALT Nausea Peripheral neuropathy Cholestatic jaundice SIADH Itraconazole and ABPA • Cochrane review • 2 studies only • Reduction in sputum eosinophils by 35% compared to 19% with placebo (p < 0.01) • More likely to have decline in serum IgE over 25% or more (OR 3.3) • number of exacerbations requiring oral corticosteroids was 0.4 per patient with itraconazole compared with 1.3 per patient with placebo (p < 0.03). Aspergilloma Almost all pts have +ve aspergillus precipitins