Genetics ppt. - Miss. Browning's Science Class
advertisement

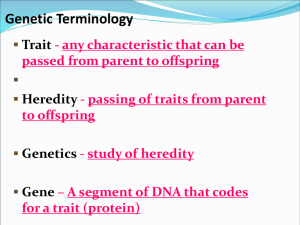
Genetics, Heredity, DNA Objectives: • Define Genetics, heredity, and genes. • Explain the relationship between traits and heredity. • Explain Gregor Mendel's contribution to the development and understanding of genetics. 1. What do we call different forms a gene may have for a trait? 2. What height of pea plant (tall or short) did Mendel find to be dominant? 3. How are dominant and recessive traits represented? (upper or lower case) Give an example! • Heredity : the passing of traits from parent to offspring Traits are controlled by genes, SO what is GENETICS? Genetics: The study of how traits are inherited. GREGOR MENDEL o First known geneticist and “father of genetics” o Was an Austrian monk and was born in 1822 o Did most of his genetic studies on pea plants o He performed cross-pollination o He became the pollinator himself o He controlled which plants mixed. o Some traits Mendel worked with were shape of pea and it’s pod, color and shape of seeds, plant height, flower position and flower color. Genetics Part II Traits and Inheritance Objectives: • Explain the relationship between dominant and recessive traits • Compare and contrast homozygous and heterozygous alleles. • Explain the relationship between genotype and phenotype. • Compare and contrast homozygous and heterozygous alleles. WHAT ARE ALLELES? o Alleles are ONE FORM of a gene (there can be more than one form) o Sex cells have one form of a gene on their chromosomes o Body cells have two forms or ALLELES for a single gene (you got one from Mom and one from Dad) o One may be dominant over another. If this happens, the dominant gene is the one expressed. If not, the recessive trait is expressed. DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE o A Dominant trait: (CAPITAL LETTERS) will always be expressed and will “mask” a recessive trait o A recessive trait (lowercase letters) can only be expressed if there are no dominant alleles present. Example: Eye color—Brown color is dominant and blue is recessive. A person can have a brown allele and a blue allele but still have brown eyes because the brown allele is dominant and “hides” the blue allele. • Generally, dominant alleles are represented with a capital letter, and recessive alleles are represented with a lower case letter. Example: R= dominant r = recessive Each organism is represented by TWO letters, one for each allele. o “Purebred” species have two alleles of the same trait o Represented by two of the same letters. This is called homozygous. For instance: BB or bb. o Species with two different alleles or two different forms of the gene would be “hybrid” o Represented by two different “letters” and is called “heterozygous”. For instance: Bb o The alleles present in the organism are referred to as its genotype. For instance, BB, Bb, or bb. o The PHYSICAL trait that shows, regardless of genotype is called a PHENOTYPE. o For instance, Blue or Brown Eyes. Genetics by Brainpop Mom has blue eyes (bb) Dad has brown eyes (BB or Bb) Therefore, Dad must have the Bb genotype, because he must have given her the “b” allele. His “b” allele is masked by his “B”/dominant allele. Daughter has blue eyes (bb) Genetics Part III Punnett Square Objectives: • Predict and analyze the genetic (genotype) and physical (phenotype) characteristics of offspring using Punnett Squares and pedigrees. • Differentiate between genotype and phenotype. • Predict possible parental genotype based on observable phenotype of offspring. PROBABILITY o Helps predict the chance that something will happen o Example: the probability of throwing heads or tails on a coin is 50% (1/2 chances) o Your predictions become more accurate with the more trials you run! Using a Punnett Square… o Used to help predict Mendelian genetics Steps for using the Punnett square: 1) One parent’s alleles (genotype) go along the top 2) The other parent’s alleles go down the side. 3) You fill in the squares like doing the communicative property of B b multiplication. B b BB Bb Bb bb Steps for using the Punnett square: Let’s say the parents are Bb and Bb (the same genotype). What would be their phenotype? Brown Eyes So you would predict: ¼ offspring to be BB, or Brown Eyes 2/4 or 1/2 to be Bb, or Brown Eyes and ¼ to be bb or Blue eyes B b B BB Bb b Bb bb So, if Miss Carnigan had children with her husband to be …what color eyes would they have? b b b b bb bb bb bb Mr. Ellinger Miss Carnigan Blue eyes (bb) Blue eyes (bb) All of their kids would have blue eyes! Using a Punnett Square Clip Let’s try some practice problems… PUNNETT SQUARE Practice Problem #1 • Predict the fur color of the offspring of a brown heterozygous hamsters and a white homozygous hamster. Brown is dominant. White is recessive. • Use any letter you like. Practice Problem #1 b b B b Bb Bb bb bb Practice Problem #2 • Predict the offspring of 2 white homozygous cows. Black is dominant over white. • Use any letter you like. Practice Problem #2 b b b b bb bb bb bb Practice Problem #3 • Predict the offspring of 2 Grey Heterozygous rats. Gray is dominant over white, which is recessive. • Use any letter you like. Practice Problem #3 G g G g GG Gg Gg gg Practice Problem #4 • Predict the pea shape of the offspring of one Heterozygous Round Pea plant and one homozygous wrinkled pea plant. Round is dominant over wrinkled. • Use any letter you like. Practice Problem #4 r r R r Rr Rr rr rr Practice Problem #5 you don’t have to write this one down… • What are the chances of having a boy or a girl? • How would you solve this one? Practice Problem #5 X X X Y XX XX XY XY Heredity by Brainpop Heredity by Brainpop 1What do we call different forms a gene may have for a trait? 2What height of pea plant (tall or short) did Mendel find to be dominant? 3Which kind of trait can’t be passed from parent to child? a)Eye color b) height c) broken arm