PowerPoint Cells, Tissues, Organs, Systems PART 1
advertisement

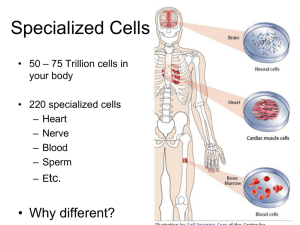
1.3 How do cells work together in the human body? SNC2P1 Unit #1: Biology Levels of Biological Organization CELLS Single-Celled ORganismS • Like all single-celled organisms, the AMOEBA relies on the organelles in just ONE CELL to perform all of its life’s functions Amoebas are plentiful in nature. They can strive in salt or freshwater, but are often found in mud beneath the water than floating in the water itself. The common amoeba species, are often found attached to the underside of leaves of water plants such as mosses. There are also about a dozen parasitic amoeba species that live inside the digestive tract of human beings and most animals. Multi-cellular Organisms Need Specialized cells • However, larger organisms with many cells need specialized cells to perform specific functions. They also need to work together (as a tissue) to carry out specific tasks . Specialized construction workers are need to carry out the different jobs at a construction site. Specialized cells in the human body are needed to do different jobs Therefore, the definition of Cell Specialization is…. • CELL SPECIALIZATION: refers to the fact that different types of cells have different structures and abilities that enable them to perform their functions efficiently. • In total there are 200 different types of cells in the human body…below is a list of just a handful. Specialized Cells How Structure Influences Function Muscle Cells • • • Long and thin structure allowing the cells to change shape when they contract Some have a branching pattern, which increases muscle strength Cells have several mitochondria to supply energy Nerve Cells (called neurons) • Cells have long, threadlike branches that help them to receive and transmit signals from one cell to another Red Blood Cells • Doughnut-like shape with a sunken middle to provide a large surface area to carry oxygen Bone Cells • Have a framework of hard material containing minerals that provide strength and support to hold the cells together Skin Cells • Thin, flat, and layered cells that form a gap-free barrier to keep out invaders (viruses and bacteria) and to keep in moisture. So the next question is then… HOW do cells becomes specialized???? • ANSWER: CELL DIFFERENTIATION: which is the series of events through which stem cells develop into specialized cells. • All cells start out as identical cells called STEM CELLS • Each stem cell then has the potential to become SPECIALIZED • Cells become specialized through the process of DIFFERENTIATION Cell Differentiation Stem Cells Internal/External Signals Gene Regulation Cell Specialization Why are Scientists interested in STEM CELLS? • Stem Cells are Interesting to Scientists because…. Stem cells have the potential to differentiate into any specialized cell Stem cells offer the potential to treat diseases TWO types of stem cells Embryonic Stem Cells Can make all cell types Wider range of medical treatments are possible Ethical Issues (they come from embryos/babies) Adult Stem Cells Can make only a few cell type Fewer medical treatments possible Ethically not a concern (come from our own tissues) VIDEO: Stem Cells Explained (3min8sec) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uC0fLXdu56g TISSUES Tissues: A tissue is specialized cells working together to perform a function Cells Tissues Organs Introductory Video: Specialized Cells and Tissues (4m26s) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I8uXewS9dJU&feature=youtu.be Four Major Tissue Types 1. Epithelium • Function: Covers the external and internal body surfaces • Ex. skin, gut, glands, hair, lining of the gut 2. Connective Tissue • Function: Strengthens, supports or connects cells and tissues • Ex. bone, blood, fat, ligaments and tendons 1. Muscle • Function: Enables the body to move, exert force or change shape • Ex. muscle cells in the stomach, heart, and arm (voluntary and involuntary muscle) 1. Nervous Tissue • Function: Senses, conducts and transmits information • Ex. brain, nervous tissue and sense cells Tissues, and Their Cell Types