Unit 5Sensation and Perception Study Guide
advertisement
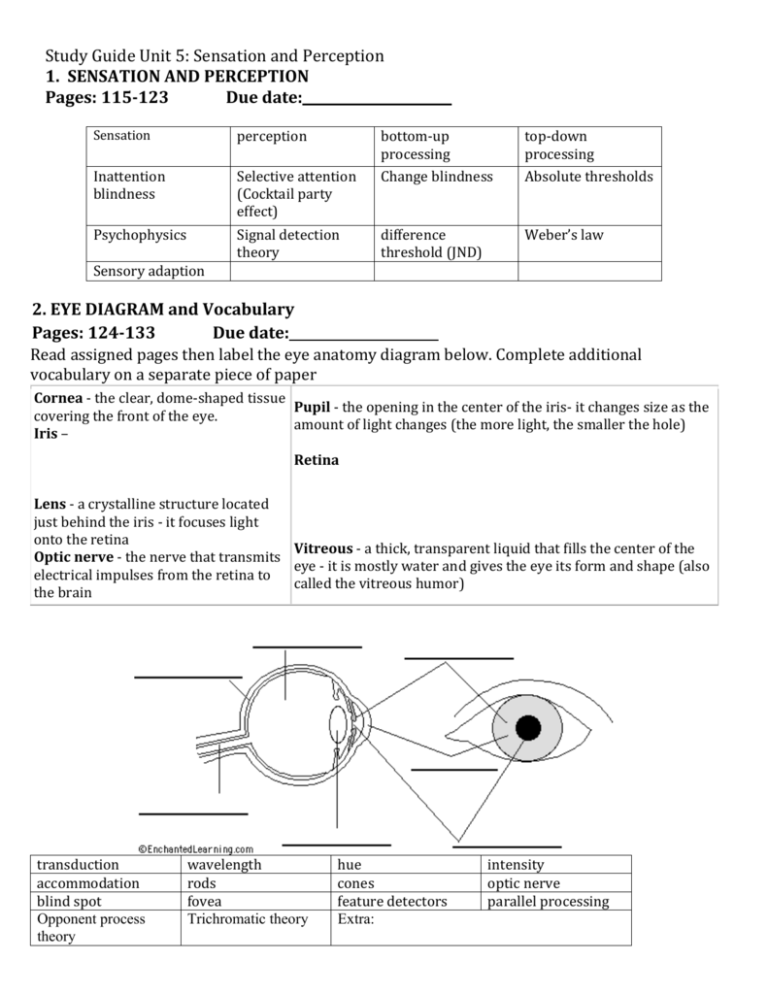
Study Guide Unit 5: Sensation and Perception 1. SENSATION AND PERCEPTION Pages: 115-123 Due date: Sensation perception Inattention blindness Selective attention (Cocktail party effect) Psychophysics Signal detection theory bottom-up processing Change blindness top-down processing Absolute thresholds difference threshold (JND) Weber’s law Sensory adaption 2. EYE DIAGRAM and Vocabulary Pages: 124-133 Due date: Read assigned pages then label the eye anatomy diagram below. Complete additional vocabulary on a separate piece of paper Cornea - the clear, dome-shaped tissue Pupil - the opening in the center of the iris- it changes size as the covering the front of the eye. amount of light changes (the more light, the smaller the hole) Iris – Retina Lens - a crystalline structure located just behind the iris - it focuses light onto the retina Vitreous - a thick, transparent liquid that fills the center of the Optic nerve - the nerve that transmits eye - it is mostly water and gives the eye its form and shape (also electrical impulses from the retina to called the vitreous humor) the brain transduction accommodation blind spot Opponent process theory wavelength rods fovea Trichromatic theory hue cones feature detectors Extra: intensity optic nerve parallel processing Study Guide Unit 5: Sensation and Perception 3. EAR DIAGRAM and Vocabulary: Pages 134-141 Due date: Read assigned pages then label the eye anatomy diagram below. Complete additional vocabulary on a separate piece of paper Sound is collected by the pinna (the visible part of the ear) and directed through the outer ear canal. The sound makes the eardrum vibrate, which in turn causes a series of three tiny bones (the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup) in the middle ear to vibrate. The vibration is transferred to the snail-shaped cochlea in the inner ear; the cochlea is lined with sensitive hairs which trigger the generation of nerve signals that are sent to the brain. Read assigned pages, then label the ear anatomy diagram. anvil - (also called the incus) a tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. cochlea – nerves - these carry electro-chemical signals from the inner ear (the cochlea) to the brain. outer ear canal eardrum - (also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. Eustachian tube - a tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. When you "pop" your ears as you change altitude (going up a mountain or in an airplane), you are equalizing the air pressure in your middle ear. hammer – Hair cells middle ear frequency cochlea pinna - (also called the auricle) the visible part of the outer ear. It collects sound and directs it into the outer ear canal semicircular canals stirrup - (also called the stapes) a tiny, Ushaped bone that passes vibrations from the stirrup to the cochlea. This is the smallest bone in the human body (it is 0.25 to 0.33 cm long). pitch inner ear Place theory sensorineural hearing loss Study Guide Unit 5: Sensation and Perception conduction hearing loss 4. OTHER SENSES Pages 141-150 frequency theory Audition cochlear implant Due date: The tongue is a strong muscle in the mouth that is covered with papillae (small bumps on the tongue) and taste buds (that sense bitter, salty, sweet, and sour tastes). The taste buds are clustered along the sides of the tongue. Read the descriptions, then label the tongue below. bitter - Bitter tastes (like the taste of tonic water) are mostly sensed towards the back and rear sides of the tongue. salty and sweet - Salty tastes and sweet tastes (like sugar) are mostly tasted at the tip of the tongue. sour - Sour tastes (like lemon juice) are mostly tasted at the sides of the tongue, at the middle and towards the front. *Extra: Gustatory sensations- 5. PERCEPTUAL ORGANIZATION Pages 151-159 Due date: Gestalt Figure-ground grouping depth perception visual cliff (experiment) binocular (depth) cues retinal disparity monocular cues phi phenomenon perceptual constancy Vestibular sense Kinesthesis Gate-control theory 6. PERCEPTUAL INTERPRTATION Page 159-169 Due date: Perceptual adaptation perceptual set Extrasensory perception (ESP)




