Second Grade Pacing Guide Draft
advertisement

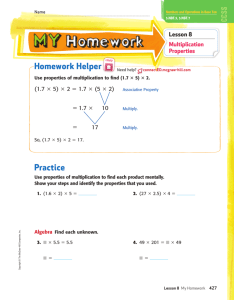
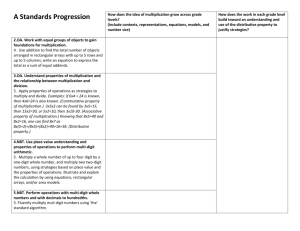
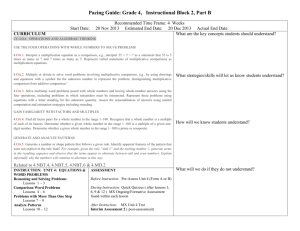
Third Grade Pacing Guide Quarter 1 Cedar Fork Elementary Reading RL3.1 – Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RI 3.1 – Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. FS3.3c – Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis in decoding words. Decode multi-syllable words. FS3.4c – Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary. RL3.2 – Recount stories, including fables and folktales, and myths from diverse cultures: determine the central message, lesson, or moral and explain how it is conveyed through key details in the text. RL3.3 – Describe characters in a story (e.g., their traits, motivations, or feelings) and explain how their actions contribute to the sequence of events. RL3.6 – Distinguish their own point of view from that of the narrator or those of the characters. FS3.3a - Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis in decoding words. Identify and know the meaning of the most common prefixes and derivational suffixes. FS3.4b - Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive reading. Writing W3.3a - Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, descriptive details, and clear event sequences. Establish a situation and introduce a narrator and/ or characters; organize an event sequence that unfolds naturally. W3.3c - Use temporal words and phrases to signal event order. W3.3b - Use dialogue and descriptions of actions, thoughts, and feelings to develop experiences and events or show the response of characters to situations. W3.3d - Provide a sense of closure. W3.5 - With guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, and editing. Speaking and Listening SL3.1b – Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., gaining the floor in respectful ways, listening to others with care, speaking one at a time about the topics and texts under discussion). SL3.1a - Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 3 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL3.2 - Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. Language L3.1e - Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. Form and use the simple (e.g., I walked; I walk; I will walk) verb tense. L3.1i - Produce simple, compound, & complex sent. L3.2f - Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. L3.4a – Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 3 reading and content, choosing flexibly from a range of strategies. Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. L3.4c - Use a known root word as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word with the same root (e.g., company / companion). L3.1a - Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences. L3.1c - Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood). L3.2a - Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. Capitalize appropriate words in titles. L3.2c - Use commas & quotation marks in dialogue. L3.3a – Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. Choose words and phrases for effect. L3.5c – Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings. Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered). RL – Reading Literature, RI – Reading Informational, FS – Foundational Skills, W – Writing, SL – Speaking and Listening, L – Language, OA – Operations & Algebraic Thinking, NBT – Number & Operations in Base Ten, E – Earth Science, L – Life Science, P – Physical Science, G – Geometry, H - History August 2012 Third Grade Pacing Guide Quarter 1 Cedar Fork Elementary Math 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 3.OA.1 Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7. 3.OA.2 Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 56 ÷ 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as 56 ÷ 8. 3.OA.3 Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. 3.OA.4 Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 × ? = 48, 5 = _ ÷ 3, 6 × 6 = ? 3.OA.5 Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply & divide. Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known.(Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) =(8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) 3.OA.6 Understand division as an unknown-factor problem. For example, find 32 ÷ 8 by finding the number that makes 32 when multiplied by 8. 3.OA.7 Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Gr. 3, know from memory all products of 2 one-digit nos. 3.OA.9 Identify arithmetic patterns (including patterns in the addition table or multiplication table), and explain them using properties of operations. For example, observe that 4 times a number is always even, and explain why 4 times a number can be decomposed into two equal addends. 3.G.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share attributes (e.g., having four sides), and that the shared attributes can define a larger category (e.g., quadrilaterals). Recognize rhombuses, rectangles, and squares as examples of quadrilaterals, & draw ex. of quadrilaterals that do not belong to any of these subcategories. 3.G.2 Partition shapes into parts with equal areas. Express the area of each part as a unit fraction of the whole. For example, partition a shape into 4 parts with equal area, and describe the area of each part as 1/4 of the area of the shape. Science 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments. 3.L.2.1 Remember the function of the following plant structures as it relates to the survival of plants in their environment: Social Studies 3.H.1.1 Explain key historical events that occurred in the local community and regions over time. 3.H.1.2 Roots -absorb nutrients Analyze the impact of contributions made Stems -provide support by diverse historical figures in local Leaves - synthesize food Flowers - attract pollinators and produce seed for communities and regions over time. reproduction 3.L.2.2 Explain how environmental conditions determine how well plants survive and grow. 3.L.2.3 Summarize the distinct stages of the life cycle of seed plants. 3.H.1.3 Exemplify the ideas that were significant in the development of local communities and regions. 3.H.2.1 Explain change over time through 3.L.2.4 Explain how the basic properties (texture historical narratives. (events, people and and capacity to hold water) and components places) (sand, clay and humus) of soil determine the ability of soil to support growth and survival of many plants 4.L.1 Understand the effects of environmental changes, adaptations and behaviors that enable animals (including humans) to survive in changing habitats. 3.H.2.2 Explain how multiple perspectives are portrayed through historical narratives. 4.L.1.3 Explain how humans can adapt their behavior to live in changing habitats (e.g., recycling wastes, establishing rain gardens, planting trees and shrubs to prevent flooding and erosion). RL – Reading Literature, RI – Reading Informational, FS – Foundational Skills, W – Writing, SL – Speaking and Listening, L – Language, OA – Operations & Algebraic Thinking, NBT – Number & Operations in Base Ten, E – Earth Science, L – Life Science, P – Physical Science, G – Geometry, H - History August 2012