Plant Cell
advertisement

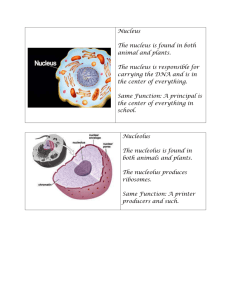
PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Cell Theory: • All organisms are made up of one or more cells. • The cell is the basic unit of organization of all organisms. • All cells come from other cells already in existence. CELL WALL: PLANT • Function: Gives the cell most of its support and structure • A thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell • Bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant Plant Cell Cell Wall CELL MEMBRANE Plant and Animal • • Function: Semi permeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. Thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell Animal Cell Cell Membrane Plant Cell Cell Membrane • Function: Where the organelles are located. • The jellylike material located inside the cell. • In Both Plant and Animal Cell Cytoplasm Animal Cell Cytoplasm Plant Cell Cytoplasm ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • Function: transports materials through the cell • Rough ER is covered with ribosome's that give it a rough appearance • In both Plant and Animal Cell Animal Cell Smooth ER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Plant Cell Smooth ER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Chloroplast • Function: Manufactures food through photosynthesis. Uses energy from sunlight to make sugar. • An elongated or discshaped organelle containing chlorophyll • Only in Plant Cell Plant Cell Chloroplast Golgi Bodies • Function: Golgi bodies are the packaging and secreting organelles of the cell. • Are stacks of membrane-covered sacs that package and move proteins to the outside of the cell. • In Both Plant and Animal Cell Animal Cell Golgi Body Plant Cell Golgi Body Lysosome • Function: Where the digestion of cell nutrients takes place • Also called cell vesicles • Spherical organelles surrounded by a membrane • They contain digestive enzymes • In Both Plant and Animal Cell Animal Cell Lysosome Plant Cell Lysosome Mitochondria • • • • Functions: Where energy is released. Rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane Membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae) In Both Plant and Animal Cell Animal Cell Mitochondria Plant Cell Mitochondria Nucleus: The Manager • Function: Controls many of the functions of the cell • Spherical body containing many organelles, including the nucleolus • Contains DNA (in chromosomes) • Surrounded by the nuclear membrane • In Both Plant and Animal Cell Nucleus Animal Cell Nucleus Plant Cell Ribosomes • Function: Small structures in the cytoplasm that create proteins. • Ribosome's are either free floating in the cytoplasm of a cell or attached to endoplasmic reticulum in a cell. • In both Plant and Animal Cell Animal Cell Ribosomes Plant Cell Ribosomes Vacuole • • • • Function: Like your suitcase, a vacuole is a temporary storage space for the cell. Fluid-filled, membranesurrounded cavities inside a cell Filled with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell Many in Animal, One large in Plant Animal Cell Vacuole Plant Cell Vacuole Nuclear Membrane • Protects and guards the nucleus • Controls movement of materials in and out of the nucleus • Keeps the DNA inside the nucleus • Allows other materials to pass in and out of the nucleus • In Both Plant and Animal Cell Animal Cell Nuclear Membrane Nuclear Plant Membrane Cell Nucleolus • Controls the cells activity… The Brain • Inside the nucleus • The nucleolus is the part of the nucleus which contains most of the genes that code for the synthesis of ribosomal RNA • In both Plant and Animal Cell Nucleolus Animal Cell Nucleolus Plant Cell Chromosomes • Contains the DNA • Located in the nucleus • In Both Plant and Animal Cell Animal Cell Chromosomes Chromosomes Plant Cell Animal Cell Nucleolus Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Chromosomes Mitochondria Cytoplasm Smooth ER Lysosome Golgi Body Vacuole Ribosomes Cell Membrane Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleolus Chromosomes Cytoplasm Smooth ER Nucleus Nuclear Plant Membrane Cell Lysosome Golgi Body Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondria Cell Wall Cell Membrane Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Edible Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell ________ ________ _________ Plant Cell Animal Cell Parts Plant Cell Parts Nuclear membrane Chromosomes Nuclear membrane Chromosomes Mitochondria Nucleus Mitochondria Nucleus Smooth ER Nucleolus Smooth ER Nucleolus Rough ER Rough ER Chloroplast Golgi Body Golgi Body Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Ribosomes Ribosomes Vacuole Vacuole Lysosome Lysosome Cytoplasm Cytoplasm