What is the big problem with metals?
advertisement

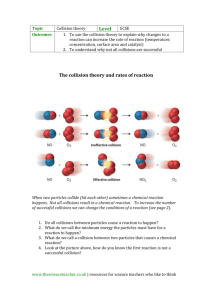
Warm Up: How does Pharmaceutical Chemist determined on the label, how often and when to take a pill? Potassium Permangnate and Glycerin/Glycerol Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide View Quick LAB Rates of Reaction •Describe how the rate of a reaction can be measured Identify factors Analyse data on that affect the the rate of a rate of reaction reaction KEYWORD: rate STARTER : Put these in order from fastest to slowest Rotting Fruit Firework Baking a cake Cooking an egg rusting of nail What do we mean by ‘rate’? Q. What do you understand by the term ‘rate of reaction’? The rate of a reaction is ‘the time taken for a product to form, or reactants to be used up’ Rate = amount of product produced (reactants used up) / time taken Do we always get a reaction? 2 VOLUNTEERS PLEASE! REVIEW Measuring the rate at which ____1___ are used up or ____2__ are made are two ways of measuring the ___3___ of a chemical reaction. An example of a reaction that happens quickly is a ____4_______ . A reaction that happens slowly is _____5_____ . Measuring Rate How could you measure the rate of these reactions? Use your definition to help you. magnesium + hydrochloric REVIEW magnesium acid chloride + hydrogen Q. How could you measure the rate of the reaction? Include the units you would use? The amount of hydrochloric acid used up (cm3/min). The amount of magnesium chloride produced (g/min). The amount of hydrogen product (cm3/min). Calculating rate of reaction from graphs 70 hydrogen produced (cm3) 60 x 50 rate of reaction = 40 y x 30 y 20 10 0 0 10 20 time (seconds) 30 40 50 The gradient of the graph is equal to the initial rate of reaction at that time 3 = 45 cm 2.25 cm3/s rate of reaction = 20 s Graphs tell a story. Sketch these two graphs and write a sentence to explain what the graph shows you. PP Question: Rate = amount of product produce / times takes = 5 / 25 Please take out a new note sheets for this. Title it…… Collision Theory All substances are made of atoms or molecules. Collision theory All substances are made of atoms or molecules. For a reaction to take place the particles of different substances must collide. Collision theory All substances are made of atoms or molecules. For a reaction to take place the particles of different substances must collide. Collision theory All substances are made of atoms or molecules. For a reaction to take place the particles of different substances must collide. Collision theory All substances are made of atoms or molecules. For a reaction to take place the partciles of different substances must collide. The more collisons between particles in a given time, the faster the reaction. Collision theory Not all collisions result in a reaction. For a collision to be successful, the molecules must have a minimum amount of energy called the ACTIVATION ENERGY AND the particles must have the correct orientation Collision theory POTENTIAL ENERGY DIAGRAM Exothermic or Endothermic? Endothermic or Exothermic? Copy and Complete. What does A,B,C,D stands for? Who Wants to be a Millionaire Check For Understanding Please take out the learning target log. Write date and scale yourself Learning Target Log 7D & 7E FACTORS AFFECTING RATE REACTIONS As we increase the surface area, we increase the rate of reaction Why? Rate and Surface area http://ca.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/l sps07.sci.phys.matter.expldust/dustexplosion/ Watch video Why is sugar powder so much more combustible when it is dispersed? Can you think of another substance that is not combustible until it is airborne in tiny droplets or particles? TPS Many fine solids, like sugar powder, are dangerous in their dust form. As a dust, the surface area of a material is high. In addition, when dust is airborne, the particles are surrounded by oxygen. As a result, combustion can happen at a very rapid rate. The rapid combustion can lead to an explosion if the resulting heat and gas cannot dissipate quickly enough. Dust explosions are a serious hazard in many industries, and extreme care must be taken in factories to control dust and to prevent ignition. Dust from wheat, corn, wood, plastic, and even metals can produce dangerous combustion reactions. VIDEO FEEDBACK The bigger the surface area, the more particles are exposed and so can react. Rate and surface area CuSO4 • 5H2O = copper sulfate pentahydrate water vapor CuSO4 • 5H2O + energy CuSO4 + 5H2O If you heat copper sulfate pentahydrate crystals, they will give off water molecules into the air and become anhydrous copper sulfate. However, if the crystals are large, lots of water molecules are trapped deep inside the crystals, so they can’t escape into the air as easily. If you grind the pretty blue crystals up with a mortar & pestle, they will turn into a powder. Now, the copper sulfate is made of smaller particles, so it has more surface area. Now, it will be easier for H2O molecules to escape from the crystals and fly into the air as water vapor. Rate and Concentration As we increase the concentration, the rate of reaction increases. Rate and concentration As we increase the concentration, the rate of reaction increases. Why? Rate and concentration As we increase the concentration, there are more particles in the same volume so the greater chance of a collision. Rate and Concentration Please take out the learning target log and rate yourself Learning Target Log “Would You Supersize My Cancer Please? A Case Study Exploring Chemicals in the News” CASE STUDY RECIPROCAL Prediction TEACHING: ◦ Please predict what you think the reading may be about. Think about what is going to happen by asking questions like a detective might do. Question as you go ◦ Please generate questions as they listen and read. Please note that there are three levels of questions: Right-There questions (answer in the text) Between-the-lines questions (inference needed) Critical Thought questions (require your opinion) Case Study Clarify ◦ As you listen and read, remind to ask yourself what words and phrases that are unclear to you. These clarifications may take the form of the following questions. How do you pronounce that? What does the word mean? I think the author is saying… I'm guessing 'pie-in-the-sky' means… Summarize ◦ Please write down and summarize verbally by read it aloud to your small group. Please respond to the questions at the end of the case study Due in 3days HOMEWORK: Research Writing assignment Animation of a case of an explosion Why should we care about rate reaction? Watch Video Rate and Temperature As we increase the temperature, we increase the rate of reaction. The increased speed of the particles mean that collisions occur more often in a certain time, and it is more likely that a collision will result in the particles reacting. Rate and temperature Rate and Temperature Rate and Catalysts Rate and Catalysts A catalyst provides an alternative route with a lower activation energy barrier. At the end of the reaction the catalyst is unchanged. Inhibitor is a substance that interferes with the action of a catalyst. Examples? Please take out the learning target log and rate yourself then submit Learning Target Log/Submit Lets Play Who wants to be a Millionaire Game Check for Understanding Complete the concept map Concept Map Complete the mind map/matching game Mind Map/Matching Game Complete the exit slip Exit Slip Please take out your learning target log and rate yourself Learning Target Log Exploring the Importance of a Catalyst Inhibitors Poisoning a Catalyst Industrial Uses of a Catalyst Coming Up Next