semester 1 - WordPress.com
advertisement

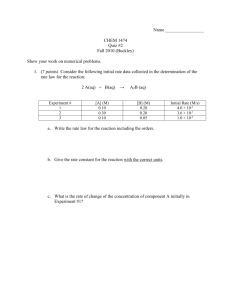
Bonding, Chemical Reactions, and Nomenclature Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Measurements, Units, and the Mole Stiochiometry Energy and Thermochemistry 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 Question 1 - 10 What is the name for HNO3? Answer 1 – 10 Nitric Acid Question 1 - 20 What type of bond represents a sea of electrons? Answer 1 – 20 • Metallic Bonding Question 1 - 30 The electrons in a nonpolar covalent bond are: a)Unequally shared between atoms b)Just exist and do not interact c) Shared equally between atoms Answer 1 – 30 C) Shared equally between atoms Question 1 - 40 Balance this equation: __ HF(aq)+__Ca(OH)2(aq) → __ H2O(aq)+__ CaF2 (aq) Answer 1 – 40 2 HF(aq)+Ca(OH)2(aq) → 2 H2O(aq)+ CaF2 (aq) Question 1 - 50 Name 6 polyatomic ions Answer 1 – 50 NH4+ NO2NO3SO32OHCN- Question 2 - 10 1. What are the products in this double displacement reaction? NaOH (aq) + MgCl2 (aq) → ?? 2. Does a precipitate form? Answer 2 – 10 1. 2NaOH (aq) + MgCl2(aq) → 2NaCl + Mg(OH)2 2. Yes! Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) → Mg(OH)2(s) Question 2 - 20 What is a spectator ion? Answer 2 – 20 • its an ion that is present in solution but does not participate in the reaction Question 2 - 30 • What is the difference between a strong base and a strong acid? Answer 2 – 30 • Strong Acid completely dissociates into H+ and anion in water • Strong Base completely dissociates into OH and cation in water Question 2 - 40 • Explain how to distinguish between the following types of reactions: • • • • Single replacement Double displacement (precipitation) Synthesis Acid-Base Answer 2 – 40 • Single Replacement: element a + compound BC → element B + compound AC • Double Displacement/precipitation: a solid forms after mixing solutions of 2 ionic compounds • Synthesis: 2 reactants → 1 Product • Acid-Base: form H2O from H+ and OH- ions Question 2 - 50 • How do you recognize the correct chemical formula for an ionic compound? Answer 2 – 50 • When the (+) cation(s) combine with the (-) anion(s) in a ratio that results in a net charge of 0 Question 3 - 10 • How many zeros does Avogadro's Number have? Answer 3 – 10 • 24 zeros – 6.02 x 10-23 Question 3 - 20 • What is the molar mass of CO2 expressed with 3 sig figs? Answer 3 – 20 • 44.0 g/mol – Carbon = 12.01 g/mol – Oxygen = 16.00 g/mol (2x) – Add all together = 44.01 g/mol – 3 sig figs! Question 3 - 30 • How many sig figs are in the measurement 0.003540 kg? Answer 3 – 30 • 4 sig figs Question 3 - 40 • If the reactants areNa₂S and Cu(NO₃)₂, what will the products be? Answer 3 – 40 • NaNO₃ and CuS Question 3 - 50 Determine the: 1.Empirical Formula 2.Molecular Formula 3.Percent Composition Of a substance with the molar mass of 78 g/ mol • Percent of C: 92.3 % • Percent of H: 7.7 % Answer 3 – 50 Question 4 - 10 • Stoichiometry heavily relies on _____ ratios. Answer 4 – 10 • Mole Question 4 - 20 • A sample contains 27.1 g of calcium oxide. How many moles of calcium oxide are in the sample? Answer 4 – 20 • 0.483 mol Question 4 - 30 • A 2.00 g sample of ammonia is mixed with 4.00 g of oxygen. Which is the limiting reactant and how much excess reactant remains after the reaction has stopped? 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) Answer 4 – 30 • Limiting Reactant: • Excess Reactant: Question 4 - 40 • Define limiting reactant and excess reactant. Answer 4 – 40 • Limiting Reactant - The reactant in a chemical reaction that limits the amount of product that can be formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed. • Excess Reactant - The reactant in a chemical reaction that remains when a reaction stops when the limiting reactant is completely consumed. The excess reactant remains because there is nothing with which it can react. Question 4 - 50 • 90.0 g of FeCl3 reacts with 52.0 g of H2S. What is the limiting reactant? What is the mass of HCl produced? What mass of excess reactant remains after the reaction? Answer 4 – 50 •Grams of HCL: 60.8 g •Limiting Reactant: FeCl3 •Excess reactant: 23.6 g H2S Question 5 - 10 • Is burning coal an exothermic or an endothermic reaction? Answer 5 – 10 •Exothermic; heat is leaving the system. Question 5 - 20 • A 450 g piece of iron (specific heat: 0.449 J/g°C ) is heated from 22°C to 87°C. How much heat was necessary to cause this change? Answer 5 – 20 • 13,000 J Question 5 - 30 • Which of the following is not a state function? Distance, energy, or temperature? Answer 5 – 30 • Distance Question 5 - 40 • How much energy is required to heat 7.40 mL of water from 25°C to 46°C? Answer 5 – 40 • q = mc delta T • q = (7.40 g) (4.184 J/gC) (21 C) – 7.40 mL X 1g/1mL = 7.40 g water • q = 650. J • 7.40 mL X 1g/1mL = 7.40 g water Question 5 - 50 • 2O3 3O2 • O2 2 O • NO + O3 NO2 + O2 ∆H = - 427 kilojoules ∆H = + 459 kilojoules ∆H = - 199 kilojoules • Calculate the Enthalpy (∆H) for the overall reaction: NO + O NO2 Answer 5 – 50 • • • • Reverse reaction 1 Reverse reaction 2 Multiply reaction 3 by 2 Add the reactions, then divide by 2 • delta H = +427 KJ – 459 KJ – 2 (199 KJ) = -430 KJ / 2 = -215 KJ