Chapter 7 & 8

Computer Skills
1400 TQN
Level 1
Chapter 7 and 8
Input/Output and Storage
Slide 1
Input Devices Output Devices Storage Devices
Slide 2
What You Will Learn About
The purpose of special keys and the most frequently used pointing devices
Input devices used to get audio and digital data into the computer
The characteristics of a monitor’s quality and the various types of monitors
The two major types of printers
The difference between memory and storage
Slide 3
What You Will Learn About
The categories of storage devices
The performance characteristics of hard drives
How data is stored on both hard and floppy disks
The various optical storage media available for personal computers
Slide 4
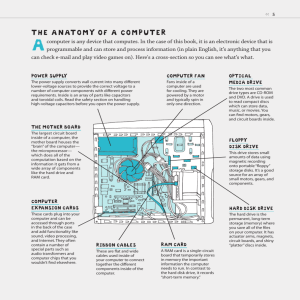
Input
Input is any data entered into the computer’s memory.
Types of input include:
Data – Unorganized information (words, numbers, images, or sounds) that the computer converts to meaningful information
Software – Programs transferred from storage devices to the computer’s memory
Commands
– Instructions that tell the computer what to do
Responses
– Prompts requiring user feedback
Slide 5
Input Devices
• Input device captures information and translates it into a form that can be processed and used by other parts of your computer.
Keyboards
Pointing devices
Game controllers
Scanners
Styluses
Microphones
Digital cameras
Web cams p. 5.130 Fig. 5-1 Slide 6
Input Devices
The keyboard is the most common input device. Types of keyboards include:
Ergonomic
Enhanced / Extended
Keyboard
Keyboard
Enhanced or Extended keyboard
– Typically 101 keys laid out in the QWERTY fashion; connected to the computer by a cable
Cordless keyboard – Uses infrared or radio wave signals
Ergonomic keyboard – Designed to help prevent cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) or damage to nerve tissues in the wrist and hand due to repeated motion
SimNet Concepts Support CD: “Keyboards” p. 5.131 Fig. 5-2 Slide 7
Keyboard
Alphanumeric Keys
Numeric Keys
Function Keys
Arrow Keys
Combination Keys
Keys (Ctrl, Alt, Shift)
Special Keys
Slide 8
Types of Input Devices
p. 5.131 Fig. 5-2 Slide 9
Pointing Devices
Various pointing devices are available
Types of pointing devices:
•
•
•
• Mouse
Mechanical mouse
Optical mouse
Wireless mouse
Trackball
Touchpad
Pointing stick
SimNet Concepts Support CD: “Mice” p. 5.132 & P. 5.133 Fig. 5-3 & Fig 5.4
Slide 10
Game Controller
Game controllers are used mainly to play games
Types of gaming devices
• Gamepads
• Joysticks
• Gaming wheels
• Force feed p. 5.134 Fig. 5-5 Slide 11
Specialized Input Devices
Other types of input devices include:
• Scanners
• Styluses
• Microphones
• Digital cameras
• Web cams p. 5.135 Fig. 5-6 Slide 12
Alternative Scanners
Flatbed
Scanners
Barcode reader
Fax Machines
Slide 13
Scanner
• Scanner is a light sensitive device that helps you copy or capture images, photos, and artwork that exist on paper. Types of scanners include:
Flatbed
SimNet Concepts Support CD: “Scanners”
Slide 14
Styluses
•
•
Stylus is an input device consisting of a thin stick that uses pressure to enter information or to click and point
Styluses are used with:
PDAs
Tablet PCs
Graphics tablets p. 5.135 Fig. 5-6 Slide 15
Microphones
•
•
•
Microphones are used to input audio
Three main types of microphones are:
Desktop microphones
Headsets
Directional microphones
Speech recognition is increasingly being included in application software
Slide 16
Digital Cameras
Digital cameras are used to:
•
• Download images to a computer
Post pictures to the Web
• Produce videos
Resolution is measured in megapixels
Higher the resolution, better the image quality, but the more expensive the camera
SimNet Concepts Support CD: “Digital Cameras”
Slide 17
Web Cams
• Web cam is a video camera that can be used to take images for uploading to the Web
Slide 18
Output Devices
Output devices take information within your computer and present it to you in a form that you can understand
Main output devices:
Monitors
Printers
Speakers
SimNet Concepts Support CD:
“Overview of Output Devices”
Slide 19
Other Types of Pointing Devices
Trackball
Touch
Screen
Pointing
Stick
Joystick
Pen
Touch Pad
Slide 20
Audio Input
Computers can accept input from a microphone.
An expansion card called a sound card records and plays back sound files.
Sound files contain digitized sound data.
Popular sound file formats include:
Windows WAV
Moving Pictures Expert Group (MPEG)
MP2 and MP3
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI)
Slide 21
Digital Cameras
The image’s light falls on a charge-coupled device
(CCD) which transforms the light’s patterns into pixels (individual dots).
Images are stored in the camera using flash memory.
The most popular types are CompactFlash and
SmartMedia.
Photo-editing programs enable the user to edit the images.
Slide 22
Digital Video
A video capture board transforms analog video into digital video.
Digital video cameras use digital technologies to record video images.
A Web cam is a low resolution video camera.
Web cam
Digital video camera
Slide 23
Output Devices
Output devices take information within your computer and present it to you in a form that you can understand
Main output devices:
Monitors
Printers
Speakers
SimNet Concepts Support CD:
“Overview of Output Devices”
Slide 24
Monitors
CRT LCD
A monitor is a peripheral device which displays computer output on a screen.
Screen output is referred to as soft copy .
Types of monitors:
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD or flat-panel)
LED: Light Emitting Diode
Plasma
Slide 25
Cathode-ray tube (CRT)
Resemble televisions
Use picture tube technology
Less expensive than a LCD monitor
Take up more desk space and use more energy than LCD monitors
Slide 26
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
Cells sandwiched between two transparent layers form images
Used for notebook computers, PDAs, cellular phones, and personal computers
More expensive than a CRT monitor
Take up less desk space and use less energy than CRT monitors
Types of LCD monitors:
Passive-matrix LCD
Active-matrix LCD
Gas plasma display
Field emission display
Slide 27
Monitor Specifications
Screen size measured as a diagonal line across the screen – from corner to opposite corner (15,17,20)
Resolution the number of pixels displayed on the screen (the higher the resolution, the closer together the dots) 600*800
Pixels ( or picture element) dots that make up the image on your screen
Dot pitch is the distance between the centers of a pair of likecolored pixels
Refresh rate the speed with which a monitor redraws the image of the screen, and is measured in hertz
Slide 28
Printers
A printer is a peripheral device that produces a physical copy or hard copy of the computer’s output.
Slide 29
Types of Printers
Inkjet
Laser
Inkjet printer , also called a bubble-jet , makes characters by inserting dots of ink onto paper
Letter-quality printouts
Cost of printer is inexpensive but ink is costly
Laser printer works like a copier
Quality determined by dots per inch (dpi) produced
Color printers available
Expensive initial costs but cheaper to operate per page
Slide 30
Difference Between Dot.Matrx, Inkjet and Laser
Printer
Dot Matrix
InkJet
Laser
1. Very Cheep
2. Less quality
3. 20-30 sec-A4
4. Less
Maintenance cost
1. More cost than
Dot
2. Good quality
3. 5-10 Sec-A4
4. High
Maintenance cost
1. High Cost
2. Excellent quality
3. 1-2 Sec-A4
4. Low
Maintenance cost
Slide 31
Plotter
A plotter is a printer that uses a pen that moves over a large revolving sheet of paper.
It is used in engineering, drafting, map making, and seismology.
Slide 32
Memory vs. Storage
RAM – memory
Hard Drive – storage
Storage , also known as mass media or auxiliary storage , refers to the various media on which a computer system can store data.
Storage devices hold programs and data in units called files .
Memory is a temporary workplace where the computer transfers the contents of a file while it is being used.
Slide 33
Difference Between Memory & Storage
Memory
Volatile
Cheep
Less Space(2-8GB)
Faster
Storage
Non Volatile
More cost
More Space(1 TB)
Slower than Memory
Slide 34
Sequential vs. Random Access Storage
Tape Drive – sequential storage
Floppy Disk Drive – random-access storage
Hard Disk – random-access storage
Sequential – Storage devices that read and write data in a serial (one after the other) fashion
Random-Access – Storage devices that read and write data without going through a sequence of locations
Slide 35
Storage Technologies: Magnetic and Optical
Magnetic Storage
Optical Storage –
CD/DVD drive
– Storage devices use disks or tapes that are coated with magnetically sensitive material
– Storage devices that use laser beams to read patterns etched into plastic disks
Slide 36
Magnetic Disk Storage
Sector
A disk is formatted ; it is divided into tracks and sectors , and a file allocation table (FAT) is created.
Track
– circular band
Sector
– pie shaped section
Cluster
– two or more adjacent sectors
FAT
– keeps track of specific locations of files
Track
Cluster
Slide 37
Optical Disk Storage
Disk surface magnified
Cross-section of a disk
Microscopic indentations called pits scatter the laser beam’s light. A light-sensing device receives no light from the pits. A signal is sent to the computer corresponding to a 0 in the binary system.
Flat, reflective areas, called lands , bounce the light back to the light sensing device, which sends a signal corresponding to a 1.
Slide 38
The Storage Hierarchy
The three levels of storage hierarchy are:
Online storage
– Also called primary storage , it is made up of the storage devices that are actively available to the computer system. User action is not required.
Near-online storage
– Also called secondary storage , it is not readily available to the computer system. The user performs an action, such as inserting a disk, to make it available.
Offline storage – Also called tertiary storage or archival storage , it is not readily available to the computer system.
Devices such as tape backup units store data for archival purposes.
Slide 39
Floppy Disk
Storage Capacity and Speed
Hard Drive CD ROM / DVD
Capacity – 720 KB to
1.44 MB
Access Time – 100ms
Capacity – Up to 80 GB
Access Time – 6 to 12ms
Capacity – CD-ROM 650
MB; DVD 17 GB
Access Time – 80 to 800ms
A storage device’s performance is measured by:
Capacity
– The number of bytes of data that a device can hold
Access Time
– The amount of time, in milliseconds (ms), it takes the device to begin reading data
Slide 40
Hard Disks
Platter
Read/Write head
Hard disks are high-speed, high-capacity storage devices.
They contain metal disks called platters .
They contain two or more stacked platters with read/write heads for each side.
Hard disks can be divided into partitions to enable computers to work with more than one operating system.
Slide 41
Factors Affecting a Hard Disk’s Performance
Seek time or positioning performance – How quickly the read/write head positions itself and begins transferring information. It is measured in milliseconds (ms).
Spindle speed or transfer performance
– How quickly the drive transfers data. It is measured in rotations per minute (RPM).
Slide 42
Floppy and Zip Disks and Drives
Zip Drive
Floppy Drive
Click on the picture to see it work.
A disk or diskette is a portable storage medium.
High-density floppy disks that are commonly used today store 1.44 MB of data.
Disks work with a disk drive.
Zip disks store up to 750 MB of data and are not downwardly compatible with floppy disks.
Floppy Disk
Slide 43
Performance Enhancement for HD
Slide 44
CD-ROM Discs and Drives
CD-ROM stands for Compact Disc-
Read Only Memory.
CD-ROM drives can not write data to discs.
They are capable of storing 650 MB of data.
They are used for storing operating systems, large application programs, and multimedia programs.
Slide 45
CD-R and CD-RW Discs and Recorders
CD-R
Discs can be read and written to
Discs can only be written to “once”
CD-R drives are capable of reading and writing data
CD-RW
Discs can be read and written to
Discs are erasable
Discs can be written to many times
CD-RW drives are capable of reading, writing, and erasing data
Slide 46
DVD-ROM Discs and Drives
DVD stands for Digital Video Disc.
DVD technology is similar to CD-
ROM technology.
DVDs are capable of storing up to
17GB of data.
The data transfer rate of DVD drives is comparable to that of hard disk drives.
DVD-R and DVD-RW drives have the ability to read/write data.
Slide 47