Minerals Review
advertisement

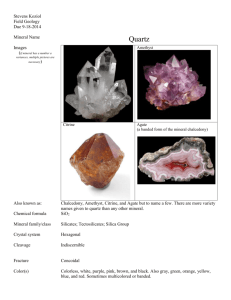
Minerals Review Every mineral… 1. Inorganic 2. Naturally occurring 3. Crystal structure 4. Consistent chemical composition 2 Kinds of Minerals 1. Silicates: contain silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) 2. Nonsilicates: do not contain Si and O together Silicates • Examples: Quartz (SiO2) Serpentine (Mg3Si2O5(OH)4) Muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10)(F,OH)2) • Make up over 90% of Earth’s crust • Arranged as silicon-oxygen tetrahedron Types of Quartz (not the complete list) 1. Quartz (milky) 2. Quartz (rose) 3. Quartz (smokey) 4. Quartz, agate 5. Quartz, amethyst 6. Quartz, jasper Classes of Nonsilicates 1. Iron ores • Contain iron (Fe) • Example: magnetite (Fe3O4) Classes of Nonsilicates… 2. Oxides • Contain oxygen (O) • Example: corundum (Al2O3) Classes of Nonsilicates… 3. Sulfides • Contain sulfur (S) • Example: Pyrite (FeS2) Classes of Nonsilicates… 4. Carbonates • Contain carbonate (CO3) • Example: Calcite (CaCO3) Classes of Nonsilicates… 5. Micas • “sheet silicates” that exhibit basal cleavage • Examples: Muscovite and Biotite Classes of Nonsilicates… 6. Mafic/Ultramafic • Minerals or rocks containing a large amount of iron (Fe) and/or magnesium (Mg) • Examples: Olivine ((Mg, Fe)2SiO4) Serpentine (Mg3Si2O5(OH)4) Classes of Nonsilicates… 7. Phosphates • Contain phosphate (PO4) • Example: apatite (Ca5(PO4)3(F,Cl,OH)) Classes of Nonsilicates… 8. Sulfates • Contain sulfate (SO4) • Example: Gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) Classes of Nonsilicates… 9. Native elements • Minerals that are a single element • Examples: Sulfur (S) Graphite and diamond (C) Gold (Au) Classes of Nonsilicates… 10. Halides • Contain one or more halogens, such as fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), and bromine (Br) • Examples: Halite (NaCl) Fluorite (CaF2) Mineral Properties 1. Color 2. Streak 3. Fracture 4. Cleavage 5. Hardness 6. Luster Color • Not a good identifier • One exception is sulfur Streak • Powdered form of the mineral • Can be used to distinguish gold and pyrite Fracture • When the mineral breaks unevenly • Quartz has fracture Cleavage • When the mineral breaks into smooth, flat planes • Types: Hardness • Scratch test Luster • The way a mineral reflects light • Types: Specific Gravity Specific Gravity… • The higher the specific gravity, the higher the density of the mineral Fluorite • Fluorescence – glows under a UV light Quartz • Hardness of 7 • Used to make glass • Many varieties Amethyst Rose Quartz Muscovite • Basal cleavage • Used to make computer chips Biotite • Basal cleavage • Used in tiles • Found in granite Olivine • Also called peridot, August’s birthstone • A mafic mineral (melts at very high temperatures) Serpentine • A mafic mineral • Releases water under high heat and pressure • Can cause rock to melt at lower temperatures in subduction zones Pyrite • “fool’s gold” • Used for explosives and fertilizer Corundum • Hardness of 9 Magnetite • Naturally magnetic • An iron ore Sulfur • Characteristic bright yellow color • Rotten egg or match smell Halite • Salt rock Gypsum • Used for drywall Galena • High density • Metallic luster Graphite • Used in pencils • Greasy feel • Elemental carbon (C) Hematite • An iron ore • Red streak Chalcopyrite • Softer and darker in color than pyrite • Dark green streak Talc • Hardness of 1 • Used in make-up Calcite • Main mineral in limestone • Effervescent – bubbles in acid • Caves form in calcite Malachite • Found in association with calcite • A carbonate • Green color Dolomite • Found in association with calcite • A carbonate • Less effervescent than calcite