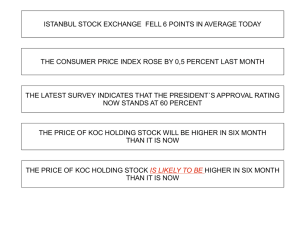
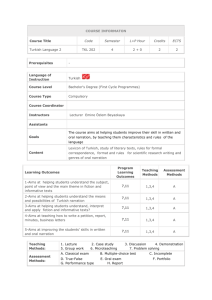
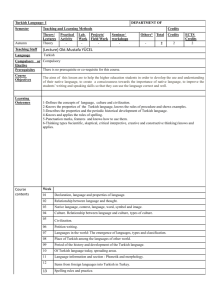
I.TERM THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION
advertisement

I.TERM COURSE CODE TAR 101 Course tittle THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCES HISTORY EDUCATION DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION THE OPTICAL Office Hours T+U CODE OF COURSE Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 The Ottoman Script CREDITS AKTS 2 3 Half term Obligatory/ Ottional The Name of Programme Education Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Responsibility of the Students Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAS, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com, Tel:8832 Course Lecturer History education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Course Assistance Purpose of the Course The main purpose of this course is to give theoritical and practical information about the Ottoman Scripts. . Learning outcome Reading and Writing in the Ottoman Scripts Content of the Course, Teaching Activities Weeks Content of the Course Teaching Activities 1. Introduction and writing of the Arabic words 2. Technics about the words 3. Vowels and using of them 4. Spelling 5. Reading 6. Reading of the simple words 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Reading of the simple texts Exam text reading technics Simple writings in Arabic Simple writings in Arabic Kinds of writing in the Ottoman script and their features 13. Kinds of writing in the Ottoman script and their features 14. Text reading 15. Text reading 16. General estimation Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Explanation Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz X 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects X 15 Course attending X 10 Others (Files, PProbation reports, Thesis and so forth). Fınal Exam X 40 Kurt Y., Osmanlıca Dersleri I-II, İstanbul 1989 Course Book Auxiliary Sources 1. Beken, S., Osmanlıca Okumaya Giriş, A.Ü. Yay., Ankara, 1972. 2. Ergin, M., Osmanlıca Dersleri, Boğaziçi Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 3. Gökbilgin, T., Osmanlı Paleografya Ve Diplomatik İlmi, Enderun Kitabevi, İstanbul, 1992. 4. Kütükoğlu, M., Osmanlı Belgelerinin Dili, Kubbealtı Neşr., İstanbul, 1994. 5. Osmanlı Paleografyasına Giriş, Elhan Kitabevi, 6. Timurtaş, F., Osmanlı Türkçesine Giriş, Alfa Yay., İstanbul, 2000 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE Course Code TAR103 Name of the Course ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCES HISTORY EDUCATION COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Office Hours T+U Credits 2+0 2 History of the Civilisation of the Ancient Times (I.) AKTS 3 Half Term Obligatory/ Optional Name of the Program Education Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Responsibility of Students Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Lecturer Mehmet Ali YASAR mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Dersi Veren Öğretim Elemanı Dersin Asistanı Purpose of the Course Learning Outcome History Education Turkish Learning of the life of the society in the Ancient Times. IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Giving information about Ancient Times contributing to the today’s civilisation Students have information about Ancient Times civilisation at the end of this course The Content of Course, Teaching Technics Weeks The Content of Course Teaching Technics 1. The ambition of this course is to introduce to the The Examination of teaching technics teaching technics and assessment 2. Description of History, direction and sources 3. Mesopotamia civilisation ( Sumarians the Akkadians, Babylon) 4. Babylon and Assyrian 5. The Sumarian’s, Babylon’s and Assyrian’s culture and civilisation 6. Eggypt Political History in the Ancient Times 7. Mid Term Exam 8. Eggypt’s Culture and civilisation in the Ancient Times 9. Syria’s and Palestine’ s Civilisation 10. the Phoenicians and Hebrews 11. İran’s Civilisation 12. The Meds and Persians 13. India’s Civilisation 14. China’s Civilisation 15. The Greek’s Civilisation in the Ancient Times 16. The Greek’s Civilisation in the Ancient Times Rating Criteria Percentages(%) Explanation Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz X 05 Homework/Term Paper X 10 Projects X 15 Participation to the Course X 10 Others (File, Internship report, Thesis, ect.). Final Exam X 40 Course Book M. Şemsettin Günaltay, Yakın Şark I-III W. Durant, ., Medeniyetlerin Temelleri, A. İnan, Eski Mısır Tarihi Ve Medeniyeti. Yusuf Ziya Özer, Mısır Tarihi Ivar, Lıssner, Uygarlık Tarih S. N. Kramer, Tarih Sümerde Başlar, Gılgamış Destanı, Teoman Durali F. Kınal, Eski Mezopotamya Tarihi. Recep Yıldırım, Uygarlık Tarihine Giriş W. Eberhart, Çin Tarihi İplikçioğlu,B., Eskiçağ Tarihinin Ana Hatları, Aydın Sayılı, Mısırlılarda ve Mezopotamyalılarda Matematik, Astronomi ve Tıp A.Müfit Mansel, Ege ve Yunan Tarihi Auxiliary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY SOCIAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT HISTORY EDUCATION DEPARTMENT Course Code TAR105 Course name COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 Central Asia Turkish History T+U 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Mid-term Obligatory/ Obtional The Name of Program Education Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Responsibilities of the Students Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAŞ, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com Tel:8832 Lecturer Assistant of the Course The Purpose of Course Teaching Autcome All program training teachers Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Türk tarihinin İslamiyet’in kabulünden önceki devirleri hakkında genel bilgi verilmesi Bu dersin ana amacı ders bitiminde öğrencilere Orta Asya Türk kültür ve medeniyetini öğretmektir. The main aim of this course is to teach to the student the Turkish culture and civilisation in the Central Asia at the end of this course. The Content of This Course, Teaching Technics Weeks The Content of This Course Teaching Technics 1. Sources Examination of the Content of Course 2. The name of theTurk, The Origin of the Turk, Discussing in the Group, Questions and the emigration ways of Turks and the Answers Motherland of Turks. 3. The First appearence of the Turks in Hıstory,The Foundation of The Khun Emp, The Mete Khan period (B.C. 209-174) Presentations of the Students 4. The political period of the Khun Empire after Mete Khan and the period of Ki-ok (B.C) Koşullama deneyleri örnekleri üzerinde tartışma, Öğrenci sunumu, soru sorma, 5. Ak Hun-Eftalit Devleti ve siyasi faaliyetleri, Tabgaç Devleti ve siyasi faaliyetler 6. Avrupa Hunları diye anılan Türk devletinin Türk, Avrupa ve dünya tarihinde oynadığı rol sorulara cevap verme Sınıf ortamında koşullamanın etkisini tartışma, öğrenci sunumu, soru sorma, sorulara cevap verme Sosyal öğrenme ile ilgili deneyleri tartışma, öğrenci sunumu, soru sorma, sorulara cevap verme 7. 8. 9. Göktürk Devletinin kuruluşu, yükselişi, doğu-batı olmak üzere ikiye ayrılışı ve çöküşü, Çin'in Türkleri hâkimiyet altına almaları Vize Nörofizyolojik kuramla ilgili araştırma Çin esaretinden kurtuluş için gerçekleşen teşebbüsler, İlteriş Kağan'ın bağımsızlığı kazanması, İkinci Göktürk Kağanlığı'nın kuruluşu 10. Tonyukuk, Bilge Kağan ve Kültigin üçlüsünün idaresinde Göktürk Kağanlığı'nın kazandığı siyasi başarılar Bilgisayar destekli öğretim uygulamalarının alan bağlamında kullanılabilirliğinin araştırılması Grupla öğretim modellerini karşılaştırma 11. Uygur hakanlığının kuruluşu, yükselişi, Maniheizmin etkisi ve yerleşik hayata geçiş Kan-çou Uygur Devleti, Doğu Türkistan Uygur Devleti gibi siyasi teşekküllerin tarihdeki rolleri, ayrıca Uygurların Türk tarihinde ve kültüründe bıraktığı izler 12. Kırgızlar ve Siyasi Faaliyetleri 13. Öğretim stratejilerinin alanda kullanılmasını tartışma Stil odaklı tasarımları inceleme Türgişler ve siyasi faaliyetleri, Karluklar ve siyasi faaliyetleri, Oğuzlar ve siyasi faaliyetleri Strateji örnekleri üzerinde çalışma 14. Türgişler ve siyasi faaliyetleri, Karluklar ve siyasi faaliyetleri, Oğuzlar ve siyasi faaliyetleri 15. Hâkimiyet anlayışı, devletin teşekkülündeki aşamalar, devleti oluşturan unsurlar ve genel değerlendirme 16. Hâkimiyet anlayışı, devletin teşekkülündeki aşamalar, devleti oluşturan unsurlar ve genel değerlendirme Değerlendirme ölçütleri Ara sınavlar Quiz Ödevler/Dönem Ödevi Projeler Öğretim yaklaşımları ile ilgili ders planları hazırlama Ders programların yapılandırmacı yaklaşıma uygunluğunun incelenmesi. Yüzdelikler (%) X 20 X 05 X 10 X 15 Açıklama Ders geçme başarısını belirlemek için öğrencinin süreçte Ders kitabı Yardımcı kaynaklar Derse Devam ve Katılım X Diğer (Dosya hazırlanması, staj raporu, arazi çalışması raporu, tez hazırlanması vb). Dönem sonu sınavı X Kafesoğlu, İ., Türk Millî Kültürü, Boğaziçi Yay., İstanbul, 1988. 10 yaptığı etkinliklere belli oranda puanlar verilecektir. 40 1. Grosset, R., Bozkır İmparatorluğu, (çev.) R. Üzmen, Ötüken Yay., İstanbul, 1999. 2. Taşağıl, A., Gök-Türkler, TTK Yay., Ankara, 1995. 3. Czeledy, K., Bozkır Kavimlerinin Doğudan Batıya Göçleri, çev: E. Çoban, İstanbul, 1998. 4. Ögel, B., Büyük Hun İmparatorluğu Tarihi, Ankara, 1981. 5. Ögel, B., Türk Kültürü’nün Gelişme Çağları, Ankara, 1988. 6. Ligeti, L., Bilinmeyen İç Asya, (çev.) S. Karatay, Ankara 1986. 7. Orkun, H. N., Eski Türk Yazıtları, Ankara, 1994. 8. Ergin, M., Orhun Abideleri, İstanbul, 1980. 9. Eberhard, W., Çin Tarihi, Ankara, 1947. 10. Barthold, W., Moğol İstilasına Kadar Türkistan, Ankara, 1987. 11. İzgi, Ö., Wang Yen-te Seyahatnâmesi, Ankara, 1988. 12. İzgi, Ö., Uygurların Siyasî ve Kültürel Tarihi (Hukuk Vesikalarına Göre), Ankara, 1987 Course Code TAR107 The Name of Course THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Salı, 15.00-16.00 2+0 The History of Islam I. Credit 2 AKTS 3 Midterm Compulsory/ Optional The Name of Program Education Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 1 Compulsory Responsibility of the Students Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAS, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com Tel:8832 Lecturer Course Lecturer The Purpose of Course Learning Outcome All programmes training teachers Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER The life before Islam, Big transformation occuring after Islam, giving information about political events and established countries. Understanding of the social, economic and political life before Islam. - The life of Prophed Muhammed, Rising of Islam, Difficulties of living in Islam, Emigration to Medina, -Wars during the Prophed Muhammed period - Hülefa-yı Raşidin period, understanding of theoretical information about political, military development and Institutes. - establishing of The Umayyad Dynasty, Andalucia Endülüs Umayyad State and Abbasi State. The Content of Course, Teaching Activities Weeks The Content of Course Teaching Activities 1. Arabic life before Islam Ders içeriğini inceleme 2. Discussing in the group, Questions and The social life in Arabia before Islam Answers 3. Prophed Muhammed and islamic period Student presentations 4. Koşullama deneyleri örnekleri Mekka üzerinde tartışma, Öğrenci sunumu, Period soru sorma, sorulara cevap verme 5. 6. Mekka period Emigration from Mekka to Ethiopia. 7. Emigration to Medina. 8. 9. Midterm Exam Medina Period 10. Medina Period 11. Medina Period 12. Medina Period Student presentations, questions and answers Student presentations, questions and answers. 13. Medina Period 14. Medina Period 15. Demise of prophed Muhamed and life after his death. 16. Demise of prophed Muhamed and life after his that. Rating Criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attending Others (Files, PProbation reports, Thesis and so forth). Fınal Exam Course Book Percentages (%) X 20 X 05 X 10 X 15 X 10 X Explanation 40 Auxiliary Sources 1. Ahmet Cevdet Paşa, Kısas-ı Enbiya (Peygamberler Tarihi), 2 cilt, Türk Neşriyat Yurdu, İstanbul 1952. 2. Doğuştan Günümüze Büyük İslam Tarihi, ilk 3 cilt, Çağ Yay., İstanbul, 1986. 3. Muhammed Hamidullah, İslam Peygamber, 2 cilt, İrfan Yay., İstanbul, 1962. 4. Hitti, P. K., Siyasî ve Kültürel İslam Tarihi, Boğaziçi Yay., (çev. S. Tuğ), İstanbul, 1980. 5. İslam Ansiklopedisi, MEB Yay., ilgili maddeler. 6. İslam Ansiklopedisi, TDV Yay., ilgili maddeler. 7. İslam Tarihi ve Kültür ve Medeniyeti, Hikmet Yay., 4 cilt., İstanbul, 1998. 8. Köksal, A., Peygamberler Tarihi, TDV Yay., Ankara, 2004. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAR 109 Course name Course Optical Code Office Hours Salı, 15.00-16.00 History of the Great Suljukis Semester Compulsory / optional Name of the Programme Language of instruction precondition Disabled Students Student Responsibilities 3 Compulsory T+U 2+0 Credits 2 ACTS 4 History Education Turkish İn case os necessity , they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course . Attending to the activies in the course . Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course The political history of the Great Seljuk Empire to provide information onGreat Seljuk State's overall role and importance in the history of Turkish history and teaching of Turkey . Learning Outcomes Weeks 1. - Great Seljuk Empire Turkish history and the general administration of the place and importance in the history of Turkey. - During this period, the subject of the events in their entirety understanding. The content of course , Teaching technics The content of course Teaching technics The formation period of the great Suljukis State and Oghuzs 2. Dandanakan War and the Establishment of the Great Seljukis State (1040) 3. Seljukis and Ghazne Relations 4. Seljukis and Karahanlı Relations 5. Ali Tekin and Seljukis 6. the East and the West diplomacy of the Seljukis State 7. The Seljukis invasion of Anatolia and theTurkicization of Anatolia 8. Midterm Exam 9. Malazgirt War and its results with regard to Turkish and islamic history 10. The Period of Melik Şah İn the Great Seljukis State 11. The Great Seljukis Crusader Relations 12. The Great Seljukis Crusader Relations 13. Period of Sencer 14. Oghuz Revolt and the ending of the Great Seljukis State 15. The Importance of the Great Seljukis State in the Turkish History 16. General consideration Rating criteria percentages (%) expalanation Midterm exams X To pass the course the Quiz student to Assignments / Term Papers X determine the projects success of his activities in the Attendance and Participation X process will be Other (File preparation, internship given a certain reports, field work reports, thesis amount of points. preparation). End-of-term exam X Turan, Selçuklular Zamanında Türkiye, İstanbul 1998 Textbook Auxiliary 1- Köymen, M., A., Selçuklu Devri Türk Tarihi, TTK Yay., Ankara, 2000. 2- Turan, O., Selçuklular ve Türk-İslam Medeniyeti, İstanbul, 1998 3- Kafesoğlu, İ., Selçuklu Tarihi, MEB Yay., İstanbul, 1992. 4- Merçil, E., Selçuklular, Doğuştan Günümüze İslam Tarihi, C.6, Çağ Yay., Ankara, 1989. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAR 111 Course Title Course Optical Code Office Hours Salı, 15.00-16.00 History of Ottoman I (1300-1453) Term Compulsory / optional Programme name Language of instruction precondition Disabled Students Student Responsibilities 3 Compulsory T+U 2+0 Credits 2 ACTS 3 History Education Turkish İn case os necessity , they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course . Attending to the activies in the course . Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book Lecturer Asst.Prof. Serkan SARI Course Assistant Course purpose Learning Outcomes This course belongs to the Ottoman classical period of Ottoman documents are aimed at students read and evaluated by Reding and understaning of presented Ottoman Turkish writting The content of course , Teaching technics Weeks The content of course Teaching technics 1. Kayı tribe and family of Ottoman Course review content 2. The establishment of Ottoman state Students read the text of the assessment 3. Ottoman – Byzantine relationship until the middle Students read the text of the of XIV. of the XVI century assessment 4. Conquests in the Balkan peninsulaof Ottoman State Students read the text of the assessment 5. Ottoman-Bulgarian Relaitonship Students read the text of the assessment 6. Ottoman-Serbian Relaitonship Students read the text of the assessment 7. Mid term exam Students read the text of the assessment Students read the text of the assessment 8. Ottoman-Albania relationship 9. Ottoman-Eflak-Boğdan and Bosnian kingdom Students read the text of the relationship assessment 10. Ottoman- states of Mediterranean 11. 12. Reign of Yıldırım Bayezid and Anatolia action Rumeli action 13. Siege of İstanbul 14. Students read the text of the assessment Students read the text of the assessment Students read the text of the assessment Karaman Expedition and Expendition over the Students read the text of the Kadı Burhaneddin assessment 15. Timur and Bayezid Tartışma ve değerlendirme 16. General Consideration Rating Criteria percentages (%) explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the course the Quiz Homework / Term Papers X 10 student to determine the projects success of his Participation to the course X 10 activities in the process will be Other (File preparation, internship given a certain reports, field work reports, thesis amount of points. preparation). End-of-term exam X 60 Uzunçarşılı İ. Hakkı, Osmanlı Tarihi c.1, Ankara 1972. Textbook 1. İslam Ansiklopedisi, MEB Yay., ilgili maddeler Auxiliary 2. İslam Ansiklopedisi, TDV Yay., İlgili maddeler 3. İnalcık, Osmanlı İmparatorluğu: Klasik Çağ (1300-1600), (çev.) R. Sezer, YKY, İstanbul, 2005. 4. İnalcık, H., “Osmanlı Tarihine Toplu Bir Bakış”, Osmanlı (Siyaset), Yeni Türkiye Yay., c.1 ve 2, Ankara, 1999. 5. Emecen, F., “Kuruluştan Küçük Kaynarca’ya”, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, (ed.) E. İhsanoğlu, İstanbul, 1994. 6. İnalcık, H., “Türkler (Osmanlılar)”, İA.,XII/2 Course Code THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U TAR 113 Tuesday, 15.0016.00 2+0 Credit AKTS 2 4 The Name of Course Methodology of History I. Midterm 1 Compulsory/ Optional The Name of Program Language of Instruction Prerequisite Compulsory Disabled Students IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Responsibility of the Students Lecturer Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAS, e-mail:sari@dicle.edu.tr, Tel:8931 Course Assistant - The Aim of course Learning outcomes Understanding of methodology and work writing technics History Turkish None Students learn terminology about methodology understand scientific research technics and criticise the works at the and of the course The content of course, Teaching technics Weeks The content of course Teaching technics 1. The ambition of this course is to introduce to the teaching technics and assessment The Examination of teaching technics 2. Description of the history Expression, questions and Answers 3. Sources of the History Expression, questions and Answers 4. Auxiliary disciplines Questions and Answers 5. Discussion 6. Scientific research technics Q Midterm Exam 8. The method of criticise Presentation 9. Critice and examples Presentation, questions and answers 10. Criticise and examples questions and answers 11. the stage of arrangement the work. Practice 12. Bibliography Practise 13. Tagging of an article and a work Presentation, questions and answers 14. Note-taking technic Presentation, questions and answers 15. Searching for the Archive records Presentation, questions and answers 16. Searching for the Archive records Presentation, questions and answers Rating Criteria Discussion, Questions and Answers Percentages (%) Midterm Exams X Quiz Homework/term paper Auxiliary Sources 20 05 X Projects Course Book Explanation 10 15 Attending to the course X 10 Other (File, Internship report, Thesis and so forth). Final Exam X 60 Kütükoğlu, Mübahat S. (1991) Tarih Araştırmalarında Usul, Kubbealtı Neşriyat, İstanbul Togan, A. Zeki Velidi (1985). Tarhte Usul, Enderun Kitabevi, İstanbul. Öztürk, Mustafa (1999). Tarih Felsefesi, Elazığ. Doğan; Özlem (1984). Tarh Felsefesi, Ege Üniversitesi Edebiyat Fakültesi Yayınları, İzmir. Toynbee, Arnold (1978). Tarih Bilinci, Bateş Yayınları, İstanbul. DICLE UNIVERSITY ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SCIENCE Course Code: EBB 151 Course Title: Year/Semester Status Name of the Programme Prerequisites Disable Students Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant Language of instruction Course Objectives Learning Outcomes Optic Code: Consultation Hours: Tuesday,15:00-16:00 Introduction to education science Fall Compulsory All programs instructing teachers T-A-C 3+0 ECTS: 3 None Disabled students can ask necessary help, if they need, from instructor by giving information about his status Prepare to lesson, take part in the activities of the lesson, co his duties(homework,project,discussion,reading the related parts,etc.)by considering lesson context. Assitant Prof Abidin DAĞLI e_mail:dagli@divle.edu.tr tel:8855 --Turkish Acquiring fundamental information,concept,skills At the end of this lesson student can: - Explain the main concept about education - Conceive the historical base of education in Turkey - Concive the philosohopical base of education - Concive the psychologic base of education - Explain the social base of education - Explain the economical base of education - Concive the legal base of education - Explain the methods in education - Analyse the roles of education - Classif the Tüekish education system - Concve the importance of teaching as a profession - Asses the teaching job and developments in instruction teachers Contents, learning activities Week Topic 1. 2. 3. 4. Introducing the objective, the content ,instruction type and evaluation of lesson The main concepts about education The historical base of education in Turkey The philosophical base of education Learning Activities Analyze the content of lesson Group discussion,question_ansver Student presentation,asking question,ansvering them Discussing the relationship of science and philosophy,student presentation,ask and ansver questions 7. The psychological base of information 1 The psychological base of information 2 Mid-term exam 8. The social base of education 5. 6. Discussing the development of man,physical,mental and morale development,ask and ansver the questions Discussion the foctors affecting development,student presentation,ask and answer the questions 12. Student presentation,ask and answer the questions,discussing the importance of elements taking part in social process The economical base of education Student presentation,ask and answer the questions, discussing the importance of individual and social profits of education The legal base of education Student presentation,ask and answer the questions, discussing importance of Türkish constitutional provision about education Method in education science 1 Student presentation,ask and answer the questions, discussing about getting information systematically Method in education science 2 Searching and discussind concept about science 13. The roles of educating 14. Turkish education system 15. the teaching job as a profession 16 Innovations and developments in the teaching job and teachinf 9. 10. 11. Assessment criteria Textbook / Material Recommended Reading Student presentation,ask and answer the questions, discussing the effects of globalisation on education Discussing the importance of formal and informal education Student presentation,ask and answer the questions, discussing the place of it in society Student presentation,ask and answer the questions, discussing the place of teachers . If any, mark as (X) x x x x x x Percent (%) Midterm Exams 20 Quizzes 5 Homeworks 10 Projects 15 Term Paper 10 Lab Work Other Final Exam x 40 Demirel, Özcan ve Zeki Kaya (Ed.). (2009). Eğitim bilimine giriş. 4.Baskı, Pegem Yay., Ankara Celep, Cevat. (Ed.) (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Anı Yay., Ankara Karip, Emin. (Ed.) (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Pegem Yay., Ankara. Karslı, Mehmet Durdu. (Ed.) (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Pegem Yay., Ankara. Kesinkılıç, Kadir. (Ed.) (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Pegem Yay., Ankara. Oktay, Ayala. (Ed.) (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Pegem Yay., Ankara. Sayalan, Nevin.. (Ed.) (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Anı Yay., Ankara Şişman, Mehmet. (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Pegem Yay., Ankara. - Sönmez, Veysel (Ed.) (2008). Eğitim Bilimine Giriş. Anı Yay., Ankara II. TERM Course Code TAR 102 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Salı, 15.00-16.00 2+0 Course tittle The Ottoman Script II. Term Obligatory/ Optional The Name of Program Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 2 Obligatory Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAŞ, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com, Tel:8832 Lecturer Credit 2 History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Course Assistant The Aim of Course The main purpose of this course is to give theoritical and practical information about the Ottoman Scripts. . Learning Outcomes AKTS 3 Reading and Writing in the Ottoman Scripts Course Content, Teaching Technics Weeks Course Content Teaching Activities 1. Arabic and Persian words being in the Ottoman texts 2. Arabic and Persian conjugations being in the Ottoman texts. 3. Practice about conjugations 4. Okunan metinlerde sıfat ve zamirlerin tesbiti Finding pronouns and adjectives in the texts 5. Plural making technics 6. Teaching Rika writing 7. Reading Rika writing texts 8. Vize 9. Rika yazıyla yazılmış belgelerin okunması 10. Text reading 11. Text reading 12. Text reading 13. Text reading 14. Text reading 15. Text reading 16. General Consideration Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Explanation Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects 15 Course attendance X 10 Diğer (Dosya hazırlanması, staj raporu, arazi çalışması raporu, tez hazırlanması vb). Dönem sonu sınavı X 60 Kurt Y., Osmanlıca Dersleri I-II, İstanbul 1989 Course Book Auxiliary Sources 1. Beken, S., Osmanlıca Okumaya Giriş, A.Ü. Yay., Ankara, 1972. 2. Ergin, M., Osmanlıca Dersleri, Boğaziçi Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 3. Gökbilgin, T., Osmanlı Paleografya Ve Diplomatik İlmi, Enderun Kitabevi, İstanbul, 1992. 4. Kütükoğlu, M., Osmanlı Belgelerinin Dili, Kubbealtı Neşr., İstanbul, 1994. 5. Osmanlı Paleografyasına Giriş, Elhan Kitabevi, 6. Timurtaş, F., Osmanlı Türkçesine Giriş, Alfa Yay., İstanbul, 2000 Course Code TAR104 Course tittle THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Credits 2+0 2 History of the Civilisation of the Ancient Times II. Term Compulsory/ Optional Program Name 2 Compulsory Prerequisite Disabled Students Student Responsibilities Eskiçağ toplumlarının siyasi ve medeniyeti hakkında bilgi sahibi olmak Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes ACTS 3 History Eduction Turkish Learning of the life of the society in the Ancient Times. IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Mehmet Ali YASAR mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Giving information about Ancient Times contributing to the today’s civilisation. Students have information about Ancient Times civilisation at the end of this course. Course Content, Teaching Technics Weeks Course Content Teaching Technics 1. The aim of this course is to introduce to the Examining of teaching technics teaching technics and assessment 2. Source information 3. Anatolia Geography Prehistoric cultures 4. The period of Asur commercial colonies and Anatolian civilisations in the III. Century (B.C) 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. The Political history of The Hittites Cultural history of The Hittites Midterm Exam Hurris The Phrygia’s Civilisation Lidyas’ Civilisation İonia’s Civilisation Urartu’s Civilisation Anatolia’s Culture and Civilisation 14. Anatolia’s Culture and Civilisation 15. Anatolia’s Culture and Civilisation 16. General Consideration Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Explanation Ara sınavlar X 20 Quiz X 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects X 15 Course Attendance X 10 Other (File, Internship report, Thesis and so forth) Final Exam X 40 1. Akurgal, E., Anadolu Kültür Tarihi, Ankara 1998. Course Book 2. Altan Çilingiroğlu, Urartu Tarihi 3. Ezra Erhat , Mitoloji Sözlüğü 4. B. İplikçioğlu, Eskiçağ Tarihinin Ana Hatları, İstanbul 1990. 5. B. İplikçioğlu, Eskibatı Tarihi, Ankara 1997. 6. Recep Yıldırım,Eskiçağda Anadolu 8. F. Kınal, Eski Anadolu Tarihi. 9. E. Memiş, Eski Anadolu Tarihi, Konya 1995. 10. Auxiliary Sources Course Code TAR 106 Course tittle V. Sevin, Eski Anadolu Ve Trakya, İstanbul 2003. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Credits Friday, 15.002+0 2 16.00 Central Asia Turkish History AKTS 3 Halfterm Compulsory/ Optional Program Name Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Spring Compulsory Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAS e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com Tel:8832 Lecturer History Education Turkish In case of necessıty, they can demand some facılıtıes by gıvıng ınformatıon about themselves to the lecturer Course Assistance Dersin amacı Course Outcomes students may explanation about Turkish culture of Central Asia at the end of this course. Course Content, Teaching Technics Weeks Course Content Technics 1. Introducing of course content, teaching technics, Course content examining consideration 2. The life style of Central Asian Turks. 3. The social and cultural situation of Central Asian Turks 4. Family, pople,tribe of the Central Asian Turks. 5. Religious belief and customs of Central Asian Turks. 6. Games and entertainment of the Central Asian Turks 7. Midterm Exam 8. Music and Musical enstruments of Central Asian Turks. 9. Dresses of the Central Asian Turks. 10. Cousine and food of Central Asian Turks 11. Army of Central Asian Turks 12. Economic situation of Central Asian Turks 13. Agriculture and livestock of Central Asian Turks 14. Calendar of Central Asian Turks 15. The importance of Central Asian Turks in terms of the history of world civilisation 16. Final sınavı Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Explanation Midterm Exam X 20 Ders geçme Quiz X 05 başarısını Homework/Term Paper X 10 belirlemek için Projects X 15 öğrencinin süreçte yaptığı Course attendance X 10 etkinliklere belli Other (File,internship report, thesis oranda puanlar and so forth) verilecektir. Final Exam X 40 Ögel, Bahattin, Türk Kültür Tarihine Giriş, Kültür Bakanlığı Yayınları, Course Book Ankara, 1991 Auxiliary Sources Barthold, W., Orta Asya Türk Tarihi Hakkında Dersler, Ankara, 1975. Genç, R., Karahanlı Devlet Teşkilatı, İstanbul, 1981. Kafesoğlu, İ., Türk Milli Kültürü, İstanbul, 1988. Kafesoğlu, İ., Harezmşahlar Devleti Tarihi, Ankara, 1992. Köymen, M. A., Büyük Selçuklu İmparatorluğu Tarihi, Ankara, 1987. Merçil, E., Müslüman Türk Devletleri Tarihi, İstanbul, 1988. Ögel, B., Türk Kültürünün Gelişme Çağları, İstanbul, 1988. Ögel, B., Büyük Hun İmparatorluğu Tarihi I,II, Ankara, 1981. Sümer, F., Oğuzlar, İstanbul, 1980. Şahin, M., Türk Tarihi Ve Kültürü, Ankara, 1999. Taşağıl, A., Göktürkler, Ankara, 1995. Togan, Z. V., Umumi Türk Tarihi’ne Giriş, Ankara 1981 Turan, O., Selçuklular Zamanında Türkiye Tarihi, İstanbul, 1971. Yakubovsky, A. Yu., Altın Ordu Ve Çöküşü, (çev.) H. Eren, Ankara, 1992. Course Code TAE108 Course Title THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTOR Y DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Office Hours T+U Credit 2+0 2 The Hıstory of Islam II. AKTS 3 Halfterm Compulsory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Spring Compulsory Students’ Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAS, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com, Tel:89 33 Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outposts Hıstory Educatıon Turkish Having general knowledge about the history of religions from Prophed Adam to Prophed Mohammed In case of necessity, they may request facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer Giving information to the students about the History of Islam and let them learn a lesson from some experiences in the past. Giving information to the students about the History of Islam and let them learn a lesson from some experiences in the past. Course Content, Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content Teaching Activities 1. Settlement wors and some religious corporations Course content examining 2. Socio-politic situation in Medina. 3. Prophed Mohammed’s relatitions with nonmüslims from Mekka. 4. Prophed Mohammed’s relatitions with Jewish 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. people Prophed Mohammed’s relatitions with the other Arab tribes Universal Calling for Islam and Relations between Muslims and Christians Midterm Exams Important events occuring during the last two years of Prophed Mohammed. Collapsing of the Dirar Mesjid The Envoys’ year Ebubakr’s Hadj emirate and the ending of Paganism Farewell Hadj Appearing of pretended propheds 14. Last Seriyye 15. Prophed Mohammed’s illness, demise and funeral 16. People after the Prophed Mohammed Rating Criteria Persentages (%) Explanation Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz X 05 Homeworks/Term paper X 10 Projects X 15 Course Attendance X 10 Other (Filing, Internship report, Thesis and so forth). Dönem sonu sınavı X 40 Course Book Berki Ali Himmet-Keskioğlu Osman, Hz. Muhammed ve Hayatı, Diyanet Yay., Ankara, 2006 Auxiliary Sources Aktan, Ali, İslam Tarihi,II. Baskı, Nobel Yay., Ankara, 2011 Suruç Salih, Kainatın Efendisi Peygamberimizin Hayatı 2, Baskı 168, Nesil Yay., İstanbul Suruç Salih, Kainatın Efendisi Peygamberimizin Hayatı 2, Baskı 168, Nesil Yay., İstanbul Hadimȋ M. İslam Ahlakı, Hakikat Kitabevi, İstanbul, 2006 Course Code TAR 110 Course tittle Term Compulsory/ Optional Pogram Name Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Görüşme Saatleri T+U Credit Office Hours 2+0 2 The First Müslim Turkish States AKTS 2 Spring Compulsory History Department Turkish ın case of necessıty, they can demand some facılıtıes by gıvıng ınformatıon about themselves to the lecturer Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Mehmet Ali YASAR mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Teaching the becoming of Muslim of Turkish people, which is important period in the Turkish history, by way of sources. Introducing the new cultural environmet appearing with uniting of Turkish and Islamic cultures Understanding and describing of historical events Course Content, Teaching Technics Weeks Course Content Teaching Technics 1. The ambition of this course is to introduce to the The Examining of teaching technics teaching technics and assessment 2. Introducing the classical sources of the Turkish Islamic history 3. The Turks during the first period of Islam. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Conquests during the Umayyad Dynasty and Abbasits and Turk-Islam relations. Eggyp Tolunoğlu State. Culture and civilisation in Tolunoğlu State. Ihşidi State. Culture and civilisation in Ihşidi State. Midterm Exam The political history of Karahans Culture and civilisation in Karahans 10. The political history of Gazne State 11. Culture and civilisation in Gazne State. 12. The political history of Eyyubis 13. Culture and civilisation in Eyyubis 14. The political history of Memluks 15. The political history of Memluks 16. Considerations Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Explanation Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects 15 Course Attendance X 10 Other(Filing, Internship Report, Thesis and so forth). Final Exam X 60 Course Book Erdoğan Merçil, Müslüman Türk Devletleri Tarihi, Hakkı Dursun Yıldız, İslamiyet ve Türkler, Nesimi Yazıcı, İlk Müslüman Türk Devletleri Tarihi, Reşat Genç, Karahanlı Devlet Teşkilatı Yaşar Kopraman, Memlükler Oktay Aslanapa, Türk Sanatı I-II Auxiliary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAR 112 Course Title Term Compulsory / optional Programme name Language of instruction precondition Disabled Students Student Responsibilities Course Optical Code Office Hours Salı, 15.00-16.00 History of Ottoman II (1300-1453) T+U 2+0 Credits 2 ACTS 3 Compulsory History Education Turkish İn case os necessity , they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course . Attending to the activies in the course . Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book Lecturer Course Assistant Course purpose Learning Outcomes This course belongs to the Ottoman classical period of Ottoman documents are aimed at students read and evaluated by Reding and understaning of presented Ottoman Turkish writting The content of course , Teaching technics Weeks The content of course Teaching technics 1. Timur_bayezid relationship Course review content 2. Ankara War Students read the text of the assessment 3. disintegration of the Ottoman Empire Students read the text of the assessment 4. Sultanate Challenge of princes Students read the text of the assessment 5. Period of I. Mehmed Students read the text of the assessment 6. Event of Şeyh Bedrettin Students read the text of the assessment 7. Mid term exam Students read the text of the assessment 8. Reign of II. Murad and activities in Anatolia Students read the text of the assessment 9. activities in Rumeli Students read the text of the assessment 10. the crusades Students read the text of the assessment 11. 12. administrative activities of II. Murad Period of II. Mehmed 13. Statü of Byzantine and Europe Students read the text of the assessment 14. Preparations for conquest of İstanbul Students read the text of the assessment Tartışma ve değerlendirme Students read the text of the assessment 15. conquest of İstanbul 16. General Consideration Rating Criteria percentages (%) explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the course the Quiz Homework / Term Papers X 10 student to determine the projects success of his Participation to the course X 10 activities in the process will be Other (File preparation, internship given a certain reports, field work reports, thesis amount of points. preparation). End-of-term exam X 60 Uzunçarşılı İ. Hakkı, Osmanlı Tarihi c.1, Ankara 1972. Textbook 1. İslam Ansiklopedisi, MEB Yay., ilgili maddeler Auxiliary 2. İslam Ansiklopedisi, TDV Yay., İlgili maddeler 3. İnalcık, Osmanlı İmparatorluğu: Klasik Çağ (1300-1600), (çev.) R. Sezer, YKY, İstanbul, 2005. 4. İnalcık, H., “Osmanlı Tarihine Toplu Bir Bakış”, Osmanlı (Siyaset), Yeni Türkiye Yay., c.1 ve 2, Ankara, 1999. 5. Emecen, F., “Kuruluştan Küçük Kaynarca’ya”, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, (ed.) E. İhsanoğlu, İstanbul, 1994. 6. İnalcık, H., “Türkler (Osmanlılar)”, İA.,XII/2 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY EDUCATION COURSE INFORMATION Course Code Course Optical Code TAR 114 Offices Hours T+U Credit AKTS Thursday, 15.0016.00 2+0 2 4 Course tittle Methodology of History II. Midterm 2 Compulsory/ Optional Program Name Compulsory Instruction Language Prerequisite Türkçe Disabled Students ın case of necessıty, they can demand some facılıtıes by gıvıng ınformatıon about themselves to the lecturer. Students Responsibilities Lecturer Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Asst. Prof. Serkan SARI, e-mail:ssari@dicle.edu.tr Tel:8931 Course Assistant - The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes The aim of this course is to give information about methodology of history. History Education None Students may describe the basic conception of teaching theories at the and of this course. The content of course, Teaching technics Weeks The content of course Teaching technics 1. The ambition of this course is to introduce to the teaching technics and assessment Work writing(note taking about course, enveloping-filing) The Examination of teaching technics 3. Planning Practice 4. According to topic, the features of plan Practice 2. Practice 5. Writing (note reading , expression, complation of ideas, dictation) Practice 6. Elements completing the writing Practice, Questions and answers 7. Midterm Exam 8. Finalising Practice 9. Sonuç, Bibliyografyanın Hazırlanması Questions and answers 10. Ekler, Önsöz Exercise 11. Publishing (Tiping) Exercise 12. Revising Presentation 13. Endeks Presentation 14. Revising, Contents, covering Questions and answers 15. Appendix (Examples for different kinds of work plans) Exercise 16. Plan for the history of institution Exercise Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Midterms X Quiz Homeworks/Term paper Auxiliary Sources 20 05 X Projects Course Book Explanation 10 15 Course attendance X 10 Other (filing, internship report, thesis and so forth). Final exam X 60 Kütükoğlu, Mübahat S. (1991) Tarih Araştırmalarında Usul, Kubbealtı Neşriyat, İstanbul Togan, A. Zeki Velidi (1985). Tarhte Usul, Enderun Kitabevi, İstanbul. Öztürk, Mustafa (1999). Tarih Felsefesi, Elazığ. Doğan; Özlem (1984). Tarih Felsefesi, Ege Üniversitesi Edebiyat Fakültesi Yayınları, İzmir. Toynbee, Arnold (1978). Tarih Bilinci, Bateş Yayınları, İstanbul. Açıkgöz, Halil (1988). İlmî Araştırma Yazılarında uyulacak Esaslar, Türk Dünyası Araştırmaları Vakfı Yayınları, İstanbul. Tütengil, Cavit Orhan (1981). Sosyal bilimlerde Araştırma ve Metod, Ayko Yayınları, İstanbul. DICLE UNIVERSITY ZİYA GÖKALP EDUCATION FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code: EBB 152 Course Title: Year/Semester Status Name of the Programme Prerequisites Disable Students Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant Language of instruction Course Objectives Learning Outcomes Optic Code: Consultation Hours: Thu 1400-1500 Developmental Psychology Fall Obligatory All the programmes which educate a teacher T-A-C: 3+ 0-3 ECTS: 3 None If the disable students need an information about their situations, they can ask lecturers. Prepare for the lesson, be active in the lesson activities, make the responsibilities (homework, project, reading, discussion ) Ass.Prof.Dr. Behçet ORAL, e-mail:oralbehcet@dicle.edu.tr, Tel:8856 Turkish Acquire the students that acquisitions Development, development areas, main information about development theories, principle and ability At the end of the lesson, the student: - describes main concepts about development. - explain the factors that influce development - Explain the development areas. - Explain the terms of development.. - Explain the relationship with education and development Contents, learning activities Week Topic Learning Activities 1. Introduce the target, index, type of education, revaluations methods of the lesson. The subjects which are discussed Developmental Psychology the main concepts, principles about development and the factors that influce development. The development theories Examine the lesson Terms of development ,development of baby and child I Physical development) development of baby and child II ( sexual and cognitive development) Midterm exam Students seminar, example events development of baby and child III (cognitive development) Students seminar, example events, discussions 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. group discussions and question and answer Students seminar group discussions Students seminar, example events 9. 10. development of baby and child IV (language development) development of baby and child V (social development) 11. development of baby and child VI (moral development) 12. Adolescence I( the meaning of adolescence) Students seminar, example events, discussions Students seminar, example events, discussions discussions about moral developments, ask questions adolescence term, example events 13. Adolescence II ( Physical and sexual development) example events and discussions 14. Adolescence III (social development) 15. The child’s and adolescence’s Spirituals defects I adolescence and social environment, example events and discussions discussions and example events. 16 The child’s and adolescence’s example events, Spirituals defects II Assessment criteria discussions and example events If any, mark as (X) X X X Percent (%) Textbook / Material Midterm Exams 20 Quizzes 10 Homeworks 10 Projects Term Paper X 10 Lab Work Other Final Exam X 50 Yazgan İnanç, B., M. Bilgin ve M. Kılıç Atıcı (2007). Gelişim psikolojisi, Pegem A, Ankara. Recommended Reading Kaya, Alim ve diğerleri (2009). Eğitim Psikolojisi, 3.Baskı, Pegem A Yay., Ankara. Senemoğlu, Nuray (2006). Gelişim Öğrenme ve Öğretim -Kuramdan Uygulamaya, Gazi Kitabevi yayınlar, Ankara. Ulusoy, Ayten vd. Gelişim ve Öğrenme. Anı yayıncılık, Ankara. Yeşilyaprak, Binnur (Ed.). Gelişim ve Öğrenme Psikolojisi. Pegem Akademi yayınları, Ankara. Morgan, Cliford T. Psikolojiye Giriş. Hacettepe Üniversitesi yayınları. Atkinson, Rita L. Psikolojiye Giriş. Arkadaş yayınlar, Ankara. İlgili diğer Türkçe ve yabancı kaynaklar. III. TERM Course Code TAE 201 Course tittle THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 OTTOMAN HISTORICAL TEXTS-I Credit 2 AKTS 3 Term Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 1 Compulsory Course Content Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes to read and disccuss the Ottoman Text. Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mehmet KARATAŞ to read and disccuss the Ottoman Text. Students can read and understand the Ottoman Historical text. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Knowledge of general concepts related to the Ottoman course, making transcription procedures Hijri (Hicri) and Rumi dates, translated into Gregoryen calender. the sources of Ottoman History Aşıkpaşaoğlu Tarihi (Asikpasaoglu's history),reading text Dursun Bey, Dursun Bey Tarihi ve Tarih-i Ebu'l-Feth,reading text Kemalpaşazade Şemseddin Ahmed, Tevarih-i Al-i Osman,reading text Peçevi İbrahim Efendi, Tarih-i Peçevi, reading text Midterm Exam Lutfi Paşa, Tevarih-i Al-i Osman, reading text Feridun Bey, Münşeatüs-Selatin, reading text Hoca Sadeddin, Tacüt-Tevarih, reading text Gelibolulu Mustafa Ali, KünhülAhbar, reading text Hasanbeyzade Ahmed Paşa, Tevarih-i Al-i Osman, reading text Katip Çelebi, Tuhfetül-Kibar fi Esfaril-bihar, reading text Koçi Bey Risalesi,reading text Final Exam Percentages (%) Explanation Criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) X X 20 05 10 15 10 Final Exam X 60 X Course Book Auxiliary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAE203 Course Title Course Optical Code Office Hours Roman and History of Byzantıum I T+U 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Öğretim Dili Ön koşul Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Course Contents Foundation of the Rome city and its periods from the Kingdom to the Empire, Division of the Empire in two parts, Völkerwanderung and the period of the German Invasions, Instructor Kürşat KORKUT Course Coordinator Course Assistant Course Objective Learning Outcomes History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER The purpose of this course is to enable the students to understand the steps taken on the way to be Roman Empire by examining the political and social events occurring in the period between the foundation of Rome and the fall of Western Roman Empire, and to perform comparisons by establishing links with the other areas of history. Acquiring the impacts and roles of Roman and Byzantine history in Turkish and world history State the policies pursued by the Roman Dynasties. The social order and the state administration in the Republican Period. Course Content , Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content 1. The bibliographic info and the scope of the history of Rome 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. The Early Roman Kingdom: the social order and the state administration The Roman Republican Period: The formation of the republic The social order and the state administration in the Republican Period The struggle for dominance in the Mediterranean: The First Punic War (264-241 BC) The Second Punic War (218-201 BC) Midterm Exam The Roman hegemony over the Hellenistic world and the innovations brought by the battles The last years of the Roman Republic and struggles for the power The decline of the Roman Republic and the first period of the Empire The changes in the 2nd century AD 13. The last period of the Empire: Severan Dynasty (193-235 AD) The military anarchy and the period of dissolution The period of recovery and the reorganization of the Empire 14. The fall of the Western Roman Empire Teaching Activities reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion 15. Final excam Rating Criteria Midterm Examination Course Book Auxiliary Sources Percentages (%) X 40 Explanation Quiz Ödevler/Dönem Ödevi Projeler Derse Devam ve Katılım Other (Filing, Thesis and so forth). Final Exam X 60 Hasan Bahar, Roma ve Bizans Tarihi, Kömen Yay., Konya 2012. Akşit O. (1976). Roma İmparatorluk Tarihi. İstanbul: İ.Ü. Edebiyat Fak. Yay. Demircioğlu, H., Roma Tarihi, TTK Yay., Ankara, 1998. Halil Demircioğlu, Roma Tarihi: Cumhuriyet (Ankara 1987) Oğuz Tekin, Eski Yunan ve Roma Tarihine Giriş (İstanbul 2012) Ostrogorsky, G., Bizans Devleti Tarihi, TTK Yay., Ankara, 1999. Prokopius, Bizans’ın Gizli Tarihi, T.İş Bank. Yay., Ankara, 2001 Üçyiğit, E., Türk Ansiklopedisi, Roma İmparatorluğu ve Bizans Maddeleri Course tittle THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 HISTORY OF ISLAM-III Term 1 Course Code TAE 205 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students Obligatory Course Content The initial relations between Muslim Turks and Arabs, to turn into the reign of the Caliphate, the Umayyad period to the Turkish conquest abroad and Kuteib b. The role and importance of Muslim conquests of the People during the reign of the Umayyads and the struggle with beytl the end of the Umayyad rule. Associate Prof. Dr. Mehmet KARATAŞ Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Geography of the Islamic Umayyad period and the Turkish-Arab Relations. . Learning Outcomes The individuals who are major in their field and experienced are being grown as dependent on main principles of Republic of Turkey and convenient for the main aims of Turkish national education system. They will achieve some behaviour such as being open-minded while doing scientific investigations, being suspicious and delaying decisions in the situation of having no complete proof, and they can maintain their studies with patience and care. They will apply the modern methods writing and investigating history by being loyal to scientific ethical rules. By learning other disciplines which can be an assist to science of history, they will benefit from the branches which will help them in their investigations and studies. They will have the information of archive, library and documents. In addition, by evaluating these sources in decent way through its originality, they will present service and being of academic society. Umayyad dynasty until the end of the political history of the Islamic state to summarize. Islamic conquests and to specify the dynamics of the spread of the Islamic State. Mawali the spread of Islam to the effects of the policy to analyze. Course Content, Teaching Technics Weeks 1. Course Content Teaching Activities Of the Umayyad dynasty (661-750) establishment and Muawiyah period. Muawiyah and Yazid periods of 2. Ahl-i Beyt'l Relations Umayyads new era: Marwan b. 3. Referee Malik b. Marwan I. Walid and 4. Solomon b. Abd al-Malik (715-717) periods. The first Turkish-Arab Relations. 5. Kuteib b. Muslim and the conquest 6. of Turkestan. Umar b. Abdul Aziz (717-720) 7. Period Events Midterm Exam 8. Yazid b. Abd al-Malik (720-724), 9. Hisham b. Abd al-Malik (724-743) periods. II. Walid b. Yazid (743-744), III. 10. Yazid b. Walid (744) periods Arab Nationalism and the 11. Umayyads mawali Policy The Relation between the 12. Umayyads to the Ahl-i Beyt'l Relations with the Umayyads and 13. the Caspian Turgish II. Marwan b. Muhammad (74414. 750) and the End of the Umayyad Dynasty II. Marwan b. Muhammad (74415. 750) and the End of the Umayyad Dynasty 16. Final Exam Rating Percentages (%) Criteria Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects 15 Course attendance X 10 Others (Filing, Thesis) Course Book Auxiliary Sources Explanation Final Exam X 60 Bartold, W. (çev. Fuat Koprülü), (1939) İslam Medeniyeti Tarihi, Ankara. Üçok, Bahriye (1968), İslam Tarihi: Emeviler ve Abbasiler Ankara. 4. Lewis, Bernard (çev. H.D.Yıldız) (1969), Tarihte Araplar, İstanbul. 5. Zeydan, Corci (çev. Z. Meganiz) (1328/19..), İslam Medeniyeti Tarihi (IV Cilt), İstanbul (Osmanlıca) 6. Wellhausen, J. (çev. Fikret Işıltan) (1963) Arap Devleti ve Sukutu, Ankara. Course Code TAE 207 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Course tittle TURKISH CULTURAL HISTORY Term Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Course Content Lecturer Kürşat KORKUT Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of To teach development and historical period of Turkish culture. Course Learning Outcomes to be able to conclude learning about Turkish culture from the first period. to be able to interpret learnings about Turkish culture from the first period. to be able to learn Turkish culture from the first period. Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Introduction to the course, sources Culture and civilization Name of the "Turk", motherland of the Turks, Turkish language Turkish social life and elements, "Oguş" (Family) "Urug" (Union of families), tribe/Bod, Bodun/Budun (Union of tribes) 6. İl(Government), elements of government 7. 8. 9. 10. Elements of government 11. 12. Government officials Midterm exam Political domination Administrative structure, governance, Kagan and Katun's positions and missions. Turkish social and economic life 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Turkish military system Religious of "Kök Tnegri" - I Religious of "Kök Tnegri" – II Final exam Course Book Auxiliary Sources Course Code TAE 209 Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Dönem sonu sınavı X 60 Saadettin Gömeç, Türk Kültürünün Ana Hatları, Ankara 2006 Bahaeddin Ögel, Türk Mitolojisi, C.I-II, Ankara 1971 Bahaeddin Ögel, Türk Kültür Tarihine Giriş, C.I-IX, Ankara 1984 Bahaeddin Ögel, Türk Kültürünün Gelişme Çağları, İstanbul 1988 Bahaeddin Ögel, Türklerde Devlet Anlayışı/13. Yüzyıl Sonlarına Kadar, Ankara 1982 Faruk Sümer, Oğuzlar/Türkmenler, Ankara 1972 İbrahim Kafesoğlu, Türk Milli Kültürü, İstanbul 2003 Abdülkadir İnan, Makaleler ve İncelemeler, C.I-II, Ankara 1998. Saadettin Gömeç, Türk Destanlarına Giriş, Ankara 2009 Zeki Velidi Togan, Oğuz Destanı, İstanbul 1971 Mustafa Aça, Oğuznamecilik Geleneği ve Andalıp Oğuznamesi, Konya 2011 V.V.Barthold, Moğol İstilasına Kadar Türkistan, haz.Hakkı Dursun Yıldız, İstanbul 1981 V.V.Barthold, Orta Asya Türk Tarihi Hakkında Dersler, haz.İ.Aka-K.Y.Kopraman, Ankara 1975 W.Eberhard, Çin'in Şimal Komşuları, çev.N.Uluğtuğ, Ankara 1942 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Course tittle The History of Anatolian Suljukis Term Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Course Content At the end of this course, the student will learn about Principalities thar established after the Malazgirt war, Anatolian principalities that became strong after declining Otoman and their contributions to the civilization Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Turkey Seljuks, Turkish principalities of the first period and fourteenthcentury principalities to teach political dates. Turkey Seljuks, Turkish principalities of the first period and fourteenthcentury principalities to teach political dates. To be able to learn the importance of Turkey Seljuks in the Turkish States in the other Turkish States which had founded in Anatolia. To be able to learn political history of Turkey Seljuks ,Principalities of the fişrst period,Pirincipalities of 14.th.century. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Introduction to the course (course content, significance and feature presentation of literature). Turkization process of Anatolia. Turkey Seljuks established. Rükneddin Süleyman, Abu'l Kasım, Abu'l Mansur periods. Kılıçarslan I, Şahinşah, İzzeddin Mesud I periods. Kılıçarslan II period (Karamıkbeli war and That the finalization of the Turkish homeland of Anatolia). Gıyaseddin Keyhüsrev I,Rükneddin Süleymanşah II,Kılıçarslan III periods. Midterm Exam Gıyaseddin Keyhüsrev I (second reign),İzzeddin Keykavus I periods. Alaaddin Keykubad I period (Yassıçimen war, the emergence of the Mongol threat). Gıyaseddin Keyhüsrev II period (Babais rebellion, the defeat of 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Kösedağ). Administration of the Mongol of Suljukis. Last Seljuk Sultan Gıyaseddin Mesud II and destruction of the state Turkish principalities of The fourteen Century and Turkization of Anatolia Bbrief political history of Principalities of Fourteenthcentury Final Exam Course Book Auxiliary Sources Course Code TAE 211 Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Final Exam X 60 Osman Turan,Selçuklular Tarihi ve Türk-İslam medeniyeti,Ötüken yayınları Osman Turan,Selçuklular Zamanında Türkiye,Ötüken yayınları Ali SevimErdoğan Merçil,Selçuklu Devletleri Tarihi,T.T.K.yayınları. İsmail Hakkı Uzunçarşılı,Anadolu Beylikleri ve Akkoyunlu,Karakoyunlu devletleri,T.T.K.yayınları. Yaşar Yücel,Anadolu Beylikleri Hakkında Araştırmalar,Cilt I-II,T.T.K.yayınları. Erdoğan Merçil,Müslüman Türk Devletleri tarihi,T.T.K.yayınları. Türkler,Cilt VI,Yeni Türkiye yayınları THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Wednesday, 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Course tittle 15.00-16.00 Suljukis’s Institutions and Civilisation History Term Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Course Content Chronological and geopraphical size of the Seljuk civilization,Seljuks government,military,economic life,social life,freedoms,science,religion,fine arts. Asst. Prof. Dr. Serdar ERKAN History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of To be able to learn civilization created by the Sejuks and Seljık civilization,about its place in the Tukisch-Islamic and world civilization. Course Learning Outcomes To be able to learn the civilization created by the Seljuk State. To be able to learn controbition and place of Seljuk civilization in Turk-İslam and world civiklization. To be able to learn how Seljuk civilization origin the other following turkish States after. Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Introduction to the course (course content, significance and feature promotion of literature, civilization, as the explanation of a word and concept) State definition, components, and Seçuklularda state structure. State definition, components, and Seçuklularda state structure. Seljuks state agency. Symbols of dominion and sovereignty. Seljuks army: their structure and functioning. Seljuks army: their structure and functioning. Midterm Exam Seljuks from light system: the military from light. Seljuks from light system: the military from light. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Seljuks military training, weapons, tactics and strategy. Seljuks military training, weapons, tactics and strategy. Seljuks military training, weapons, tactics and strategy. The relationship between liberty and civilization, the Seljuks in the development of civilization, where the free structure. Final Exam Course Book Auxiliary Sources Course Code TAE 213 Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Final Exam X 60 Osman Turan ,Selçuklular Tarihi ve Türk-İslam Medeniyeti,Ötüken yayınları. Osman Turan, Türk Cihan Hakimiyeti Mefkuresi Tarihi,Ötüken yayınları. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Friday, 15.002+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 16.00 Course tittle Ottoman History III Term Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Course Content The establishment of the Ottoman Empire after at Rumeli and Anatolia, the political, economic and cultural status have learned. The establishment of the Ottoman Empire in the military and political history and development Asst. Prof. Dr. Serkan SARI History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of XVI. XVII century. century until the Ottoman political and military developments to teach Course Learning Outcomes Learn the classical period in Ottoman history - Learn the basics of the Ottoman expansion policy - Ottoman military strategy will learn will understand the philosophy of the Ottoman conquest policy to grasp the principles of the Ottoman success Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Course objectives, content, teaching method, evaluation methods are introduced II. Bayezid Period Yavuz Selim Period (Ottoman Iran Relations) Yavuz Selim Period (OttomanMemluklu Relations) Kanuni Sultan Süleyman Cycle (Developments in the West) Kanuni Austria Relations Midterm Exam Turkish Maritime and Naval War Period of II. Selim Period of III. Murat Period of Mehmed III Period of Ahmed I Period of Osman II and Mustafa I Period of Murad IV and İbrahim I Final Exam Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Final Exam X 60 (Redaktör) Yıldız, Hakkı Dursun(1989) Doğuştan Günümüze Büyük İslam Tarihi C. 10, Çağ Yayınları, İstanbul Uzunçarşılı, İ. Hakkı, “Osmanlı Tarihi (1988). Türk Tarih Kurumu Yayınları. Ankara; JORGA, Nicolae (2005). Osmanlı İmparatorluğu Tarihi”, Yeditepe Yayınları, İstanbul. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Credit AKTS TAE 215 Course Title 2+1 2 3 COMPUTER Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory Course Content Computer identification, description of computer logic, computer components, listing, description and functions of computer hardware devices, Internet searching, mailing the attached file, theses, and articles in the search, using online databases, word editing program, paragraphs, and image properties Adding an image editing, adding tables properties, and table editing, page editing features, sub-information / Add information to the top of the cutting insert, set the properties of powerpointte presentation preparation and presentation. Lecturer Course Assistant Tamer KUTLUCA Learning Outcomes Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER The main objective of the basic computer literacy skills to students of computer hardware, operating systems, word processing program, the calculation program and presentation program aimed to gain knowledge and skills to use effectively. Computer hardware can recognize Course Content Course Content, Learning Activities Learning Activities History of computer, classification of compute Computer Hardware Computer Hardware Computer Software Computer Networks (Internet, Intranet, Extranet), Mobile Communications Windows operating system (Introduction, basic concepts and rules) Midterm Exam Windows operating system (Windows concept, Window Management) Windows operating system (file and object management, Settings) Windows operating system (Attachments and Accessories) 14. Word 2007 (Introduction, basic concepts and rules) Word 2007 (Word tools) Word 2007 (drawings, tables and other objects in Word) Power Point 2007 (Word tools) 15. Final Exam 11. 12. 13. Raring Criteria Midterm Exam Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course Attendance Others (Filing, Thesis and so forth) Final Exam Course Book Percentages(%) X 40 X Explanation 60 Her Yönüyle Bilgisayar Eğitimi, Akın Efendioğlu/Emre Sezgin, KARAHAN KİTABEVİ Auxiliary Sources Course Code TAE 217 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Course tittle Computer Labaratory Term Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 1 Obligatory History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Course Content Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes Course Content, Teaching Technics Weeks Course Content Teaching Activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Final Exam Rating Percentages (%) Criteria Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects 15 Course attendance X 10 Others (Filing, Thesis) Final Exam X 60 Explanation Course Book Auxiliary Sources Course Code TAE 219 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Course tittle Term Obligatory/ Optional Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 16.00 TURKISH EDUCATION SYSTEM AND SCHOOL MANAGEMENT 1 Obligatory History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Course Content Asst. Prof. Dr. Abidin Dağlı Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of The aims and basic principles of Turkish Education System, legal laws and arrangements related to education, structure of Turkish education Course system, Management theory and process, organization and management of school, works related to personnel, students, teaching and administration in school management, social attending to school. Learning Know the aims and the basic principles of the Turkish education Outcomes system. Know organization and management structure of Turkish Education System. Know teaching levels in Education Turkish System Know human and physical resources in the Turkish education system Know theories and processes of Management. Know concepts, principles and processes of school and school management. Know concepts, principles and processes of management of human resources Know and implement processes of student personal affairs. Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Creating Educational System Legal Foundations of the education system Organization and Management Structure of Education System Teaching Levels in Education System Teaching Levels in Education System 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Human and physical resources in the education system Debates and Projects Actual in Education Midterm Exam Theories and Processes of Management School and School Management Management of Human Resources Student personal affairs Works Related to Education and Training Administration of School Management Attending Family and Community to School Final Exam Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Course Book Final Exam X 60 Türk eğitim sistemi ve Okul Yönetimi. Mehmet ŞİŞMAN, İbrahim TAŞDEMİR, PegemA Akademi,Ankara, 2008. Türk eğitim sistemi ve Okul Yönetimi. Mehmet Auxiliary Sources Türk eğitim sistemi ve Okul Yönetimi. Kürşad YILMAZ, Hasan Basri MEMDUOĞLU, PegemA Akademi,Ankara, 2011. ŞİŞMAN, İbrahim TAŞDEMİR, PegemA Akademi,Ankara, 2008. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAE221 Course Title Course Optical Code Office Hours T+U Credit 2+0 2 TURKISH WORLD HISTORY IN THE 20th CENTURY Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 1 Elective Course Content The stategic position of Turkish World, The new Turkish states founded after the Soviet Russia, the relation between Turkey and these states. History Education Turkish IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Assist. Prof. Dr. Serdar ERKAN Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes The purpose of this course is to achieve a necessary understanding of the history of modern Turkish societies. Summarize the general characteristics of Turkish world and political events occurred after the collapse of the Soviet Union. Describe the place of the Republic of Turkey in the Türkish world and recent political and economical problems of Turkish world. Use their knowledge in their research about the topic. Course Content, Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content Teaching Activities 1. Turks, using of word of Turk, the distinctive and combining features of Turks 2. Geopolitic position and borders of Turkish World, countries and regions consisting of Turkish World 3. A General Overwiev of The former Soviet Union 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. AKTS 2 ruling a major part of Turkish World Caucasus Turks (Azerbaijan Republic and other Turkish societies of the region) Turkistan Turks (Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan Republics) Turkistan Turks (Turkmenistan and Kyrgyzstan Republics) Tajikistan and Afganistan Turks Mid-term exam Crimean Turks, Uighurs, Siberia Turks Iran, Iraq and Syria Turks Balkan Turks (West Thrace and Bulgaria Turks) Balkan Turks (Rumania, Moldovia, Kosovo and Bosnia-Herzegovina Turks) Cyprus Turks 14. Ataturk ve Turkish World 15. End-of-term exam Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources Percentages (%) Midterm Exam X 40 Quiz Homework/Term Paper Projects Course Attendance Others (Filing, Thesis and so forth). Final Exam X 60 Sebahattin Şimşir "Türk Dünyası Tarihi" Suat İlhan "Türkiye'nin ve Türk Dünyasının Jeopolitiği THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Explanation Course Code TAE 221 Course Title Midterm Compulsory/ Selective Program Title Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant The Objective of Course Learning Outcomes Course Optical Code Office Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 The History of Middle and Near East T+U 2+0 Credits 2 1 Elective Hıstory Turkish None Lecturer M. Ali YAŞAR Course Content, Teaching Activities Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Midterm Exam Quiz Homeworks/ Midterm Papers Projects Course Attendance Others (Filing,Thesis,and so forth ). Final Exam Percentages (%) X 20 X 10 X 10 X 60 AKTS 3 Course Book Auxiliary Sources HERODOTUS 2002; HERODOT TARİHİ, Çevirmen: Müntekim Ökmen, İş Bankası. Kuhrt, A. 2009; Eski Çağ'da Yakındoğu (M.Ö. 3000-330), Cilt I-II, Çeviren: D. Şendil, Türkiye İş Bankası, Kültür Yayınları, İstanbul.. Mieroop, M.V.De, 2006; Antik Yakındoğu'nun Tarihi İ.Ö.3000-323, Dost Kitabevi, Ankara Mieroop, M.V.De, 2006; Antik Yakındoğu'nun Tarihi İ.Ö.3000-323, Dost Kitabevi, Ankara İplikçioğlu, B. 1997; Eski Batı Tarihi 1: Giriş, Kaynaklar, Bibliyografya, Türk Tarih Kurumu, Ankara. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT Course Code TAE 223 Course tittle COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 THE ART HISTORY (Optional) T+U 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 1 Elective Course Content The description birth and improvement of art history as a science, and the relationship with the assistance science in art history, constructions, environment and similar subjects. Lecturer Kürşat KORKUT Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Principalities that established after the victory, political history of the other Principalities that established Anatolia, their relations with each other and their contributions in the field of culture and civilization . Learning Outcomes The political and cultural structure of the Anatolian principalities The political history of the Anatolian principalities. The importance of the Anatolian principalities for the history of Anatolia. The cultural heritage and the works of art of the Anatolian principalities. Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities The definition and importance of the subject The definition and scope of art history Art-History, Art, Culture and the relationship gy Art-community-artist relationship The emergence of the history of art as a science The emergence of the history of art as a science Branches of science benefited from the work of art history Midterm Exam 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources Benefited from the work of art history disciplines of Archaeology Branches of science benefited from the work of art history, History Peoples science disciplines available to study art history, folklore, ethnography, ethnology Branches of science studies benefited from the history of artnumismatic, Historical geography Disciplines available to study art history -Epigraphy, Mythology and History of Architecture Religions, art, and art on the effects of gaze Religions, art, and art on the effects of gaze Final Exam Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Dönem sonu sınavı X 60 Hazırlanmış ders notları Selçuk Mülayim, Sanat Tarihi Metodu, İstanbul, 1983. Oktay Aslanapa, Türk Sanatı, İstanbul, 1971. - Oluş Arık, Sanat Tarihi, Ankara, 1975. - Doğan THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY Course Code TAE 223 Course tittle Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 THE MUSIC OF TURKISH RELIGION T+U 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 1 Elective History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Course Content Asst. Prof. Dr. Kürşat GÜLBEYAZ Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course To teach the theories and the history of Turkish Religious Music. Learning Outcomes Learning basic information theory in Turkish Religious Music To know musical notes and their values To understand sound ranges of Turkish Music To have an information about Turkish Music modes and forms To study and perform musical works from Turkish Religious Music repertoire and to get them in their own repertoire Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Definition, portrait, notes, signs. Sound ranges and sound system knowledge Formation of Sound ranges and modes Modes, simple modes Modes, composed mode Modes, transposed modes Forms: Religious Music and Profane Music Mıdterm Exam Forms: Mosque Music and Dervish Music Religious Music History Famous Composers, their lives and 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources Works Methods patterns and variations Methods patterns and solfege: one example of each form Methods patterns and solfege: one example of each form Final Exam Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Final Exam X 60 “Türk Mûsikîsi Nazariyatı ve Usûlleri” İsmail Hakkı ÖZKAN, Ötüken Neşriyat, 8.b,İstanbul 2008 “Musiki Tarihi” M. Nazmi ÖZALP,M.E.B. Yay. I-II c., İstanbul 2000; DİA; “Türk Mûsikîsi Ansiklopedisi” Yılmaz Öztuna, Kült. B. Yay., I -II c., Ankara 1990. Türk din mûsikisî ders notları. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY Course Code TAE 223 Course tittle Term Obligatory/Elective Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students Course Content Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 Turkish Painting T+U 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 1 Elective History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER This class aims to discuss and inform the students by mentioning the prominent people and institutions about the stages of the development of Turkish painting from a western point of view during the period between the enunciation of Tanzimat and the enunciation of the Turkish Republic. The students taking class, are expected to have a renewed interest in studies about the recent history, comprehend the fact that historical data in a 1 field of study that nourishes the willpower of synthesis. 2 phenomenon of visual culture 3 development of Turkish society. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Union of independent painters and sculptors in the Turkish Republic Avni Çelebi Zeki Kocamemi Zeki Kocamemi Mahmud Cuda 1930’s relationship between the state and politics 1930’s relationship between the state and politics 1930’s relationship between the state and politics 1930’s relationship between the state and politics Socialist realist impressions in Turkish painting Fikret Mualla, Paris School, abstract expressionism in Turkish painting Tendencies for abstract and abstraction in Turkish painting 13. 14. Hakkı Anılı Hakkı Anılı 15. Hakkı Anılı 16. Midterm Exam Rating Criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Course Book Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Final Exam X 60 Sağlam Mümtaz, Çağdaş Türk resim sanatı/comtemporary Turkish painting from The Art Collection of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, TürkçeBoşnakça,İngilizce, (Metin ve Biyografiler: Mümtaz Sağlam), TC Merkez Bankası Yayını, İstanbul, Nisan 2011. Auxiliary Sources IV. TERM Course Code TAE 202 Course Title Term Compulsory / Elective Program Title Instruction Language precondition Disabled Students Student Responsibilities THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Office Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 Ottoman Historicial Texts II Credits 2 ACTS 3 Compulsory History Education Turkish İn case os necessity , they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course . Attending to the activies in the course . Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book Lecturer Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mehmet KARATAŞ Course Assistant Course purpose Learning Outcomes This course belongs to the Ottoman classical period of Ottoman documents are aimed at students read and evaluated by Reding and understaning of presented Ottoman Turkish writting The content of course , Teaching technics Weeks The content of course Teaching technics 1. Course review content 2. Reading and writing the example texts of Peçevi Students read the text of the history assessment the example texts in Students read the text of the assessment 3. Reading and writing Asafname of Lütfi paşa 4. Reading and writing Tevarih-i Ali Osman 5. Reading and writing the example texts Travelbook Students read the text of the of Evliya çelebi assessment 6. Reading and writing the texts about Diyarbakır in the Travelbook of Evliya çelebi 7. Reading and writing history of Naima the example texts from Students read the text of the assessment Students read the text of the assessment the example texts from Students read the text of the assessment 8. Reading and writing the example texts from history of Naima Students read the text of the assessment the example texts from Students read the text of the assessment 9. Reading and writing brochure of KoçiBey 10. Reading and writing the example texts from Kitab- Students read the text of the ı Müstetab assessment 11. Reading and writing the example texts from Tacü’t-Tevarih of Hoca Saadettin Efendi Reading and writing the example texts from Tarihi Cevdet Students read the text of the assessment Reading and writing the example texts from Tarihi Cevdet Students read the text of the assessment 12. 13. 14. Reading and writing the example texts from Students read the text of the history of Abdurrahman Şeref Bey assessment 15. Reading and writing the example texts from Tartışma ve değerlendirme history of Ahmet Refik 16. End-of-term exam Rating Criteria percentages (%) explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the course the Quiz Homework / Term Papers X 10 student to determine the projects success of his Participation to the course X 10 activities in the process will be Other (File preparation, internship given a certain reports, field work reports, thesis amount of points. preparation). End-of-term exam X 60 Kurt, Yılmaz, Osmanlı Paleografyası, Ecdat Yay. Ankara, 2002. Course Book 1. Related Chronic Auxiliary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE Course Code TAE204 Course Title ZİYA GÖKALP EDUCATION FACULTY TARİH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Office Hours T+U 2+0 Roman and History of Byzantıum II Term Compulsory/Elective Programın Adı Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Course Contents Lecturer Course Assistant Course Objective Credit 2 AKTS 3 2 Compulsory History Education Turkish None Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course . Attending to the activies in the course . Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book Foundation of Byzantine Empire affectionately known as Eastern Rome and political, military, social and economical developments of Byzantine Empire in the decadence period, The state of Anatolia during this empire until coming of the Seljukid Turks in the 11th century Instructor Kürşat KORKUT The purpose of this course is to achieve a necessary understanding of the rise and development of the Byzantine Empire, the Byzantine administrative organization, and the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire. Learning Outcomes The political-military history of the Byzantine Empire The Byzantine administrative organization The reasons of the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire Course Content, Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content Teaching Activities 1. The latest periods of the Byzantine Empire and the reading, explanation, discussion characteristics of the Byzantine synthesis reading, explanation, discussion 2. Konstantinus and the foundation of Istanbul reading, explanation, discussion 3. The period of Justinianus reading, explanation, discussion 4. The period of Herakleios Dynasty reading, explanation, discussion 5. The Iconoclast movement in Byzantine reading, explanation, discussion 6. The period of Amorium Dynasty 7. The term examination reading, explanation, discussion 8. The period of Macedonia Dynasty reading, explanation, discussion 9. Byzantine, Turks, and the crusades reading, explanation, discussion 10. The period of Komnenoslar Dynasty reading, explanation, discussion 11. The 4th Crusade and its outcomes reading, explanation, discussion 12. The Emperor of Iznik Laskaris reading, explanation, discussion 13. The period of Palaiologoslar Dynasty reading, explanation, discussion 14. The Rest of the Byzantine Empire 15. Final exam Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources Percentages (%) X 40 Midterm Exam Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course Attendance Others (Filing, thesis and so forth) Final Exam X Demirkent, I., Bizans Tarihi Yazıları, İstanbul 2005. Explanation 60 Demircioğlu, H., Roma Tarihi, TTK Yay., Ankara, 1998. Hasan Bahar, Roma ve Bizans Tarihi, Kömen Yay., Konya 2012. Ostrogorsky, G., Bizans Devleti Tarihi, TTK Yay., Ankara, 1999. Prokopius, Bizans’ın Gizli Tarihi, T.İş Bank. Yay., Ankara, 2001. Üçyiğit, E., Türk Ansiklopedisi, Roma İmparatorluğu ve Bizans Maddeleri THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAE 206 Course Optical Code Course Title History of Islam IV Term Compulsory/ Selective Program Title Instructin Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Student Responsibilities 2 Compulsory Lecturer Course Assistant Course Objective Learning Outcomes Offices Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 T+U 2+0 Credits 2 AKTS 3 Turkish None Engelli öğrenciler, ihtiyaç duymaları halinde kendi durumu ile ilgili bilgiyi öğretim elemanına ileterek gerekli kolaylıkların sağlanmasını talep edebilir. Ders içeriğini dikkate alarak, derse hazırlık yapmak. Derste yapılan etkinliklere katılmak, Derste verilen sorumlulukları (Ödev, Proje, Tartışma, İlgili bölümlerin okunması vb.) yerine getirmek. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mehmet KARATAŞ Abbasid period and the Islamic geography. The individuals who are major in their field and experienced are being grown as dependent on main principles of Republic of Turkey and convenient for the main aims of Turkish national education system. They will achieve some behaviour such as being open-minded while doing scientific investigations, being suspicious and delaying decisions in the situation of having no complete proof, and they can maintain their studies with patience and care. They will apply the modern methods writing and investigating history by being loyal to scientific ethical rules. By learning other disciplines which can be an assist to science of history, they will benefit from the branches which will help them in their investigations and studies. They will have the information of archive, library and documents. In addition, by evaluating these sources in decent way through its originality, they will present service and being of academic society. İnception until the fall of Abbasids to summarize political history. Join Abbasids of Baghdad timely to emphasize the importance Abbasid Period in the history of Turkish-Islamic time to analyze the effects on world history. Course Content, Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content Teaching Activities Abdullah b. Muhammad Es Seffah and 1. Establishment the Abbasid Caliphate 2. Period and the Islamic Caliph Mansur's new central Baghdad 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Abu Muslim Abbasid revolution's role in khorasani Mehdi and Hadi Periods Harun Rashid Period and Abbasid Amin, Mamun, Mu'tasım and Vasik periods Mutezile and Mihn Period Midterm Exam Second Semester time Abbasid caliphs of the Islamic World Attenuation of the Abbasid Caliphate of vetevaifü'l-Muluk Abbasid Samarra City Turks and Importance of Timely Of Seljuk Abbasid Relations Abbasid Period Important Riots End of the Mongol Invasion and the Baghdad Caliphate End of the Mongol Invasion and the Baghdad Caliphate 16. Final Exam Rating Criteria Midterm Exam Quiz Homeworks/Term Papers Projects Course Attendance Other (Filing, thesis and so forth). Dönem sonu sınavı Course Book Auxiliary Sources Percentages (%) X 20 X 10 X 10 X 60 Bartold, W. (çev. Fuat Koprülü), (1939) İslam Medeniyeti Tarihi, Ankara. Hitti, Philip H. (çev. Salih Tuğ),(1986) Siyasi ve Kültürel İslam Tarihi (IV Cilt), İstanbul, Boğaziçi Yayınları. Üçok, Bahriye (1968), İslam Tarihi: Emeviler ve Abbasiler Ankara.-Lewis, Bernard (çev. H.D.Yıldız) (1969), Tarihte Araplar, İstanbul.- Zeydan, Corci (çev. Z. Meganiz) (1328/19..), İslam Medeniyeti Tarihi (IV Cilt), İstanbul (Osmanlıca)Wellhausen, J. (çev. Fikret Işıltan) (1963) Arap Devleti ve Sukutu, Ankara. Course Code TAE 208 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Course tittle Turkish Cultural History II Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 2 Obligatory Course Content Uyghur Period Introduction to the Uyghur State's Foundation, Uyghur State Turks and transition to settled life, Development, with China Relations, Manichaeism Uighur his country Distribution and Uighur State Collapse of the Uighur Turks' Government Organization and Culture, Kyrgyz, Karluk and Turgish Provinces. Asst. Prof. Dr. Serkan SARI History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Being introduced the process beginning with Asian Huns B.C. 209 and economical and cultural structures of Turkish states being founded in Course that area. - The individuals who are major in their field and experienced are being Learning grown as dependent on main principles of Republic of Turkey and Outcomes convenient for the main aims of Turkish national education system. - - - Weeks 1. 2. 3. They will apply the modern methods writing and investigating history by being loyal to scientific ethical rules. By learning other disciplines which can be an assist to science of history, they will benefit from the branches which will help them in their investigations and studies. They will have the information of archive, library and documents. In addition, by evaluating these sources in decent way through its originality, they will present service and being of academic society. Accurately evaluate the Turkish state and the history of civilization to associate with the modern Turkish state structure. By making views between disciplines, seeing truly the socioeconomic and socio cultural parameters. To be dominant in scientific and occupational subjects. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Introduction to Uyghur Period Establishment of Uyghur State Uyghur State and Turks transition 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources to settled life Development of Uighur State The relationships between China and Uyghurs Spread of Manichaeism in Uyghur Country The Collapse of the Uyghur State Midterm Exam State of the Uyghur Turks and Cultural Organization State of the Uyghur Turks and Cultural Organization Kirghizs Kirghizs Kazaks Kazaks Uzbeks Final Exam Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X Midterm Exam İbrahim Kafesoğlu,Türk Milli Kültürü X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 X Bahaeddin Ögel, Hun İmparatorluğu I-II, Bahaeddin Ögel, Türk Kültürünün Gelişme Çağları, Türk Dünyası El Kitabı THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAE210 Course Title Term Compulsory/Elective Program Title Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Course Optical Code Course Content Lecturer History of Huns, Avars, Sabars, Bulgarians, Patzinaks, Uzs, Kypchaks. Assist. Prof. Dr. Tuğba KORHAN Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes Office Hours Credits AKTS 3 3 Eastern Europe Turkic History 2 Compulsory History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER The aim of this course is to enable students to learn Turkic history in eastern Europe. Enable to know European Turkic History. Enable to know Turkic migrations towards Europe. Enable to comprehend the reasons of miigrations to Europe. Enable to analyze developments and changes in Eurpe from the time when Turkic tribes appeared in Europe. Course Content, Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content Turkic migrations from east to west 1. 3. East Europe before Huns and influences of migration of Turkic tribes in European history Huns 4. Avars 5. Sabars 6. Hazars 7. 8. The term examination Ogurs – Great Bulgar state 9. Tuna Bulgar state 10. İdil Bulgar state 11. Patzinaks and Uzs 12. Kuman Kypchaks I 13. Kuman Kypchaks II 14. Macars and other Fin Ugor tribals 2. T+U 3+0 Teaching Activities reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion reading, explanation, discussion 15. Final exam Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources Percentages (%) Explanation 40 Midterm Exam Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course Attendance Other(Filing, Thesis and so forth). 60 Final Exam Kurat, Akdes Nimet, Türk Kavimleri ve Devletleri, Murat Kitabevi yay.,Ankara 1992. Ögel, Bahattin, İslamiyet ten Önce Türk Kültür Tarihi, TTK., Ankara 1988. Kafesoğlu, İbrahim, Türk Milli Kültürü, Boğaziçi Yay., Ankara 1982. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAE212 Course Title Course Optical Code Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 2 Obligatory Course Content Chronological and geopraphical size of the Seljuk civilization,Seljuks government,military,economic life,social life,freedoms,science,religion,fine arts. Asst. Prof. Dr. Serdar ERKAN Lecturer Course Assistant Course Objective Learning Outcomes Office Hours T+U 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Suljukis’ Institutions and Civilisation History II History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER To be able to learn civilization created by the Sejuks and Seljık civilization,about its place in the Tukisch-Islamic and world civilization. - To be able to learn the civilization created by the Seljuk State. - To be able to learn controbition and place of Seljuk civilization in Turk-İslam and world civiklization. -To be able to learn how Seljuk civilization origin the other following turkish States after. Course Content , Teaching Activities Weeks Course Content 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Seljuks of religion, thought, work, travel and freedom to own property. Seljuks of religion, thought, work, travel and freedom to own property. Social life of the Seljuks. Social life of the Seljuks. Social life of the Seljuks. Charitable institutions of Seljuks Charitable institutions of Seljuks Midterm Exam Economic life of Seljuks. Economic life of Seljuks. Economic life of Seljuks. Seljuks trade, trade policy. Seljuks trade, trade policy. Seljuks trade, trade policy. Final Exam Teaching Activities Rating Criteria Midterm Examination Course Book Auxiliary Sources Percentages (%) X 40 Explanation Quiz Homework/Term Paper Project Course Attendance Diğer (Dosya hazırlanması, staj raporu, arazi çalışması raporu, tez hazırlanması vb). Final Exam X 60 Osman Turan ,Selçuklular Tarihi ve Türk-İslam Medeniyeti,Ötüken yayınları. Osman Turan, Türk Cihan Hakimiyeti Mefkuresi Tarihi,Ötüken yayınları. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY Course Code TAE 214 Course tittle HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 Ottoman History IV T+U 2+0 Credit 2 AKTS 3 Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 2 Obligatory Course Content Starting with the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca, seen in the Ottoman Empire until World War I on political, social and economic developments will be discussed. Asst. Prof. Dr. Serkan SARI History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of . To evaluate of Ottoman history Modern period the political social and economic aspects. Course - The individuals who are major in their field and experienced are being Learning grown as dependent on main principles of Republic of Turkey and Outcomes convenient for the main aims of Turkish national education system. - - - - - They will achieve some behaviour such as being openminded while doing scientific investigations, being suspicious and delaying decisions in the situation of having no complete proof, and they can maintain their studies with patience and care. They will apply the modern methods writing and investigating history by being loyal to scientific ethical rules. By learning other disciplines which can be an assist to science of history, they will benefit from the branches which will help them in their investigations and studies. They will have the information of archive, library and documents. In addition, by evaluating these sources in decent way through its originality, they will present service and being of academic society. Reveals Modern Ottoman history etrays the International Relations in the Modern European History. Learns the periods of Ottoman Modernization. Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities The Ottoman Empire in the Early Modern Era Innovations and developments in the period of Selim III. Mehmet Ali Pasha and invasion of Egypt´s Emergence of Egypt problem and solution Tanzimat I. Period Tanzimat period II. Problem of the Straits and the London Agreement Midterm Exam Crimean War and the Paris Peace Conference The Ottoman Empire after the Paris Peace Conference Ottoman-Russian War of 1877-1878 Ottoman Empire in the 20. Century Colonial movements around the world in the 19. century General Evaluation 14. General Evaluation 15. 16. Final Exam Rating Criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Course Book Auxiliary Sources Percentages (%) X X X Dönem sonu sınavı X Niyazi Berkes, Türkiye’de Çağdaşlaşma Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 60 Rıfat Uçarol, Siyasi Tarih, Filiz Kitabevi, İstanbul; İlber Ortaylı, İmparatorluğun En Uzun Yüzyılı, İletişim Yayınları, İstanbul.; Donalt Quataert, Osmanlı İmparatorluğu 1700-1922, İletişim Yayınları, İstanbul. ;Erick Jan Zürcher, Moderleşen Türkiyenin Tarihi, İletişim Yayınları, İstanbul, Erhan Afyoncu, Sorularla Osmanlı İmparatorluğu Course Code TAE 216 Course tittle THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 Anatolian Principalities Credit 2 AKTS 3 Term Obligatory/ Elective Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 2 Obligatory Course Content At the end of this course, the student will learn about Principalities thar established after the Malazgirt war, Anatolian principalities that became strong after declining Otoman and their contributions to the civilization Lecturer Kürşat KORKUT Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Learning Outcomes Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Principalities that established after the victory, political history of the other Principalities that established Anatolia, their relations with each other and their contributions in the field of culture and civilization . The political and cultural structure of the Anatolian principalities The political history of the Anatolian principalities. The importance of the Anatolian principalities for the history of Anatolia. The cultural heritage and the works of art of the Anatolian principalities. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities The conquest of Anatolian by Turkish The political history of Danişmend’s, The culture and art in Danişmend’s Mengucek Artuklular Saltuklular Ahlatşahlar Midterm Exam 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources Germiyanoğulları Menteşeoğulları Saruhanoğulları Candaroğulları Karamanoğulları Ramazanoğulları Dulkadiroğulları Final Exam Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Dönem sonu sınavı X 60 İ. H. Uzunçarşılı, Anadolu Beylikleri, Akkoyunlu-Karakoyunlı Devletleri, Ankara 1969. İ. H. Uzunçarşılı, Anadolu Beylikleri, Akkoyunlu-Karakoyunlı Devletleri, Ankara 1969. M. Çetin Varlık, Germiyanoğulları Tarihi, Ankara 1980 Merçil, Erdoğan, Müslüman Türk Devletleri Tarihi , İstanbul, 1985 Course Code TAE 254 Course tittle THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 SPECIAL TEACHING METHODS –I Credit 2 AKTS 3 Term Obligatory/Elective Program Title Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 2 Compulsory History Education Turkish Course Content 1 Aims, content and resources of Special Teaching Methods I, Analysis on examples of general teaching methods adapted in teaching of a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (I) 2 History of teaching of Religion and Ethics in Turkey Analysis on examples of general teaching methods adapted in teaching of a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (II) 3 Psychological, social and legal grounds and of teaching Analysis on examples of general teaching methods adapted in teaching of a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (III) 4 Models of Religious educational in contemporary world and teaching religion in Turkey Analysis on examples of general teaching methods adapted in teaching of a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (IV) 5 Main approaches of religious education curriculum development, and curriculum development process in religious education. Analysis on examples of general teaching methods adapted in teaching of a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (V) 6 Essential components of Religion and Ethics (faith-worship, and morals) and developmental stages of individual. Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (I) 7 An analysis of the curriculum of Religion and Ethics regarding learning areas Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (II) 8 An analysis of the curriculum of Religion and Ethics regarding learning outcomes and assessment processes. Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (III) 9 An analysis of the curriculum of Religion and Ethics regarding comments and evaluations on the curriculum of Religion and Ethics Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (IV) 10 Analysis of textbooks of Religion and Ethics I Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (V) 11 Analysis of textbooks of Religion and Ethics II Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (VI) 12 Teaching methods and techniques in Pre-school Childhood (Ages 2 to 6) Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (VII) 13 Teaching methods and techniques in Childhood (Ages 7 to 12) Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course matter in Religion and Ethics (VIII) 14 Teaching methods and techniques in Adolescence (Ages 13 to 18) Presentations of teaching methods and techniques in a subject matter in Religion and Ethics (IX) Lecturer Seyit Ahmet ATAK The objective of the course is to: motivate students to get knowledge and skills of how to teach religion to the primary and secondary school students, and discuss the fundamental teaching strategies, learning theories, teaching and learning methods and techniques. . Learning Outcomes - Being able to prepare yearly, daily and activity plans regarding objectives and acquisitions Being able to prepare yearly, daily and activity plans regarding objectives and acquisitions - Being able to implement yearly, daily and activity plans into curriculum regarding objectives and acquisitions - Being able to arrange physical conditions in classroom environment according to criteria - Being able to explain features of methods and techniques used in preschool teaching Being able to implement models used in preschool education into daily plan Being volunteer to use different methods and techniques in daily plan - Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Course Content, Teaching Technics Course Content Teaching Activities Introduction of the course: Content, significance, rules and requirements Objectives and acquisitions in preschool curriculum Classroom arrangement and learning corners Types of plans; yearly and daily plans, important issues Types of plans; working on sample yearly and daily plans Expository instruction and related methods in preschool education Discovery instruction and related 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria Course Book Auxiliary Sources methods in preschool education Midterm Exam Inquiry based instruction and related methods in preschool education Instructional techniques in preschool education Sample activities by using instructional techniques in preschool education Active learning by sample activities Active learning by sample activities Classroom management, strategies, parent involvement Assessment in terms of child, program, and teacher Final Exam Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Course attendance Others (Filing, Thesis) Percentages (%) X X X Explanation 20 05 10 15 10 Dönem sonu sınavı X 60 Demirel, Ö.(2003). Planlamadan Değerlendirmeye Öğretme Sanatı, Ankara: Pegem A Yayıncılık. Goffin, S.G., & Wilson, C. (2001). Curriculum Models and Early Childhood Education: Appraising The Relationship (2nd Ed.) New Jersey: Prentice Hall Inc. Ün Açıkgöz, K. (2003). Aktif Öğrenme, İzmir: Eğitim Dünyası Yayınları. MEB Okul Öncesi Eğitimi Genel Müdürlüğü (2006) 36-72 Aylık Çocuklar için Okul Öncesi Eğitim Programı, Ankara: Devlet Kitapları Müdürlüğü. MEB Okul Öncesi Eğitimi Genel Müdürlüğü (2006)Okul Öncesi Eğitim Kılavuz Kitabı Etkinlik Örnekleri, Ankara: Devlet Kitapları Müdürlüğü V. YARIYIL THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code Course Optic Code TAE 301 Consultation Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 T+U Credit ECTS 2+0 2 3 Course Name Ottoman ArchiveText I Semester Compulsory / Optional Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 5 Optional Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Asst. Prof.Mehmet KARATAŞ, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com, Tel:8832 Week 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Teacher Training Program All Programs Turkish None The language used in the documents of the Ottoman period , concepts, terms , and to learn the information . Ottoman writing and understanding of the read and write The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities The introduction of the Ottoman archives and Course content review introducing diplomacy Domestic and overseas Ottoman archives Investigation of Ottoman documents To read the Turkish Ottoman archival documents, specifications and grammar rules Turkish Ottoman archival documents, specifications and grammar rules to read 6. 7. 8. 9. Turkish properties Ottoman documents to read and grammar rules Correspondence diplomatic language used in Visa Cater to foreign kings and emperors ; Appealto the Sultan ; appeal to queen 10. Guys 10 and addressed to the commander ; Shaykh al-Islam , women soldiers, judges and ulema appeal 11. Archival documents written in different techniques reading techniques ( Nesih and Rica) 12. Archival documents written in different techniques reading techniques ( Talika and Divani ) 13. Archival documents written in different techniques reading techniques ( Siyaat ) 14. The interpretation of Ottoman documents 15. The interpretation of Ottoman documents 16. Overall Rating Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Kurt Y., Osmanlıca Dersleri I-II, İstanbul 1989 Textbook Osmanlıca Okumaya Giriş, A.Ü. Yay., Ankara, 1972. 13. Ergin, M., Helpful resources Osmanlıca Dersleri, Boğaziçi Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 14. Muallim Naci, Lugat-ı Naci, Çağrı Yay., İstanbul, 1987. 15. Şemseddin Sami, Kâmûs-ı Türkî, Enderun Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 16. Hacı Mustafa Dervişi ve Ahmet Hulusi, Ahder-i Kebir, Osmanlı Yay. 17. Yazır, M., Eski yazıları Okuma Anahtarı, Vakıflar Genel Müd. Yay., Ankara, 1983. 18. Gökbilgin, T., Osmanlı Paleografya Ve Diplomatik İlmi, Enderun Kitabevi, İstanbul, 1992. 19. Kurt, Y., Osmanlıca Dersleri-I ve II, Akçağ Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 20. Kütükoğlu, M., Osmanlı Belgelerinin Dili, Kubbealtı Neşr., İstanbul, 1994. 21. Osmanlı Paleografyasına Giriş, Elhan Kitabevi, 22. Günday, D., Arşiv Belgelerinde Siyakat Yazısı ve Divan Rakamları, TTK Yay., Ankara, 1974. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAE 303 Course Title Term Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites Disabled Student Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant The aim of the course Course Optic Code Consultation Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 Ottoman History V (1699-1908) T+U Credit ECTS 2+0 2 3 5 Compulsory Department of History Education Turkish None In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Kürşat KORKUT The students about the reasons for the decline of the Ottoman Empire pause and to inform. Conduct studies at an advanced level in the field independently. Share the ideas and solution proposals to problems on issues in the field with professionals and non-professionals by the support of qualitative and q Know and use the historical method. Have notions, knowledges, abilities and values of history and education of history. Explain theories, models, principles and generalisations of the sc Obey ethic and professional rules and takes charge in collusive practices. Use of advanced theoretical and practical knowledge within the field. The course content , learning activities Week Topic Course Learning Activity Activities Ahmet III Period Active Learning 1. First Mahmoud Period Active Learning 2. First Mahmoud Period Active Learning 3. Learning Outcomes 4. Osman III Period Active Learning 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Evaluation criteria Third Period Mustafa Third Period Mustafa First Abdulhamid Period Visa First Abdulhamid Period First Abdulhamid Period First Abdulhamid Period First Abdulhamid Period First Abdulhamid Period First Abdulhamid Period First Abdulhamid Period General Review Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Evaluation criteria (X ) mark as X Percent (%) Textbook Midterm Exams Quiz X Homework Projects X Term Paper Laboratory Other X Final Exam Doğuştan Günümüze Osmanlı Tarihi c. XI Helpful resources İsmail Hakkı Uzun çarşılı ve Enver Ziya Karal’ın Osmanlı Tarihi Course Code TAR 305 Course Name THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Hours Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 History of Europe in the middle age and modern times Credit ECTS 2 3 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 5 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Structor Mehmet Ali YAŞAR Week 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Department of History Education Turkish None mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Course objective understanding of the fundamental issues of Medieval European History. Understanding of the political, social and religious structure of Medieval Europe The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities Course objectives, content, teaching methods, Course content review introducing assessment methods Medieval Concept The process of disintegration of the Roman Empire . The emergence of Christianity , spread and Rome to stiffen Migration of Peoples causes and consequences of migration of tribes Teutonic state established as a result of migration of tribes and features The institutionalization of the emergence of Feudalism Feudalism Midterm Exam The institutionalization of the emergence of Feudalism Feudalism 9. Crusades Crusades Influences 10. The results of the Crusades 11. Two universal roof of the Middle Ages ( the church with the crown of the Holy Roman - German Empire ), and the clash of these two forces 12. two universal roof of the Middle Ages ( the church with the crown of the Holy Roman - German Empire ), and the clash of these two forces 13. Century Wars and the War of the Roses 14. Of the cities in the late Middle Ages the increase of political power , the disintegration of the feudal order and phase out state territoryal national kingdoms began to emerge 15. Of the cities in the late Middle Ages the increase of political power , the disintegration of the feudal order and phase out state territoryal national kingdoms began to emerge 16. Review Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Jacques Le Goff, Ortaçağ Batı Uygarlığı, Textbook Henri Pirene, Ortaçağ Avrupası’nın Ekonomik ve Siyasi Tarihi. Helpful resources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE Course Code TAR 307 Course Name ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Hours Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 History of the Ottoman Organization I Credit ECTS 2 3 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 5 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Asst. Dr. . Serkan SARI, e-mail: serkan.sari@dicle.edu.t Tel: 8931 This course Ottoman Establishment Period is intended to teach the organization and functions of government agencies. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Week 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Department of History Education Turkish None Acquiring the information about the the administrative and province organization of Ottoman Empire from the foundation of Ottoman to the beginning of XVI. Century The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities Course objectives , content, teaching methods , Course content review introducing assessment methods Group discussion, question -andOttoman state management answer Student presentations , question -andDivan-i Humayun's structure and function answer The members of Divan-ı Hümayun and their Comparison between their tasks , responsibilities questions and answers Grand vizier and other viziers , Qazasker Question-answer, expression Student presentations , question -andTreasurer , Nişancı , other members answer Ottoman Bureaucracy İtems 8. 9. 10. 11. Ottoman Bureaucracy Ottoman Bureaucracy Palas Organizations Enderun Comparisons between these items and discussion Group work student presentations , question -andanswer Student presentations , question -andanswer 12. Midterm Exam 13. White and Black eunuch network Lecture and slide show 14. Biru and the notables of the subject of documentary Lecture and slide show 15. General evaluation of the course Question -and-answer 16. End-of -term exam Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the course the Quiz Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to determine the Projects success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Ünal, Mehmet Ali, Osmanlı Müesseseleri Tarihi, Fakülte Kitabevi, Isparta Textbook 2003. Helpful resources 1. Halaçoğlu, Y., “XIV-XVII Yüzyıllarda Osmanlılarda Devlet Teşkilatı ve Sosyal 2. Yapı”, TTK 1991 3. İpşirli, M., “Klasik Dönem Osmanlı Devlet Teşkilatı” Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 4. MEB, İA ve DİA İlgili Maddeler 5. Pakalın, M. Z., “Tarih Deyimleri ve Terimleri Sözlüğü” İstanbul 1983 6. Özcan, A., “Osmanlı Askeri Teşkilatı”, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 7. Kütükoğlu, M., “Osmanlı Belgelerinin Dili (Diplomatika)”, İstanbul 1994 8. Genç, M., “Osmanlı İmparatorluğunda Devlet ve Ekonomi”, İstanbul 2000 9. Öz, M., Osmanlı’da “Çözülme” ve Gelenekçi Yorumlar, İstanbul 1997 10. Barkan, Ö. L., “Tımar”, İA, C. 12 11. Yediyıldız, B., Osmanlı Toplumu, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: 12. Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 13. Aydın, A., “Osmanlı Hukukunun Genel Yapısı ve İşleyişi” Türkler (Yeni Türkiye Yay.) c: 10 14. Tabakoğlu, A.,”Osmanlı İktisadî Yapısının Ana Hatları”, Osmanlı, c: 3 15. Kurt, Y., “Osmanlı toprak Yönetimi” Osmanlı c: 3 Course Code TAE 309 Course Name THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Credit Hours Tuesday, 15.002+0 2 16.00 History of the Turkish State in the New and Modern times I. ECTS 2 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 5 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes intructor Mehmet Ali YAŞAR Week 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Department of History Education Turkish None mayasar@dicle.edu.tr XVI- XX. Centuries of Turkish Ottoman Empire outside world outlined to provide information about turkish state. Acquiring the theoretical basics of history of Turks living in Balkans, north of Black sea, Persia, Central Asia and India. Knowing the way to reach information and using effectively them about in Turkish archives, libraries and museum Having a protection and development consciousness about international and national cultural heritage in Turkish World from 1453 to the present Following the relevant international and national agendas and evaluating historical perspective. The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities XVI.Century Turkish world views the overall Course content review introducing After the collapse of the Golden Horde Khanate Group discussion, question-and-answer Turkish presence in the north of the Black Sea Crimean Khanate Lecture, Question and Answer Russian Domination Turkish communities under expression the federal Lecture, Question and Answer Russian Domination Turkish communities under the federal Iran and Turkishness 6. expression 7. Midterm Exam Student presentation 8. Uzbek and Uzbek Khanate expression 9. Kazakh and Kazakh Khanate expression 10. East Turkestan Turkishness expression 11. Baburshahs and India Turkishness Discussions, question and answer 12. Turkish presence in the Caucasus and history expression 13. Middle East History of Turkishness Lecture, Question and Answer 14. Balkan Turkishness Lecture, Question and Answer 15. Baburshahs and India Turkishness expression 16. Overall rating Discussions, question and answer Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Togan, Z. V., Bugünkü Türk İli (Türkistan) ve Yakın Tarihi, İstanbul, 1942 Textbook 1. Hayıt B. M., Türkistan Rusya ile Çin Arasında, İstanbul,1975. Helpful resources 2. Togan, Z. V., Bugünkü Türk İli (Türkistan) ve Yakın Tarihi, İstanbul, 1942 3. Togan, Z. V., Hatıralar, Türkistan ve Diğer Müslüman Doğu Türklerinin Millî Varlık ve Kültür Mücadeleleri, İstanbul, 1969. 4. Kurat, A. N., Türkiye ve İdil Boyu, Ankara, 1966. 5. Saray, M., Kazak Türkleri Tarihi, Ankara, 1992. 6. Saray, M., Rus İşgali Devrinde Osmanlı Devleti ile Türkistan Hanları Arasındaki Siyasî Münasebetler, 1775-1875, İstanbul, 1984. 7. Sümer, F., Safevî Devleti’nin Kuruluşu ve Gelişmesinde Anadolu Türklerinin Rolü, Ankara, 1976. 8. Arat, R.R., Baburnâme, Ankara, 1985. 9. Baddeley, J.F., Rusların Kafkasya’yı İstilası ve Şeyh Şamil, (çev.)S. Özden, İstanbul,1989. 10. Yakubovsky, A. Yu., Altınordu ve Çöküşü, çev: H. Eren, Ankara, 1992. 11. Kurban, İ., Doğu Türkistan İçin Savaş, Ankara, 1995. 12. İnalcık, H., “Osmanlı-Rus rekabetinin Menşei ve Don-Volga Kanalı Teşebbüsü, 1569”, Belleten, c: 12, sa: 46, Ankara, 1948. COURSE CODE TAE 313 The Name of Course THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION C ourse Optical Code Office Hours T+U Credit Tuesday, 15.002+0 2 16.00 The History of Turkish Education I. AKTS 2 Midterm Obligatory/ Optional Program Name Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 5 Obligatory Responsibility of the Students Responsibilities Course Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Mehmet Ali YASAR mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Learning outcomes Understanding about leading persons and events about Turkish education History. History Education Turkish None In case of necessity, they can demand facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer Giving information about education and teaching activities in the Turkish history from beginning to today. Content of course, Teaching activities Weeks Content of course Teaching activities 1. Examination of course content Introducing the methods of course content, aim, teaching style 2. Introducing the field aand method of course 3. Education of Turks in the past (Khuns, Gokturks, Uighurs) 4. Education in the Karahans and the state of Ghazni 5. Education in the Suljukis and domains 6. Education in the Suljukis and domains 7. Midterm Exam 8. Education in the Ottoman State 9. The feaures of education of the period 10. Sahn-ı Seman and Suleymaniye Madrasahs 11. Madrasahs’ activities in the society 12. 13. 14. 15. Teaching institutes in the palace in the Ottomans Innovation period in the education Basic features of the peried Military schools, which were opened in the innovation period 16. Public schools, which were opened in the innovation period Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects 15 Attending to the course X 10 Other (File, internship report, thesis, etc.). Final Exam X 60 Çelebi, A., İslam'da Eğitim Öğretim Tarihi, İstanbul, 1976. Course Book Akyüz, Y. Türk Eğitim Tarihi, Auxiliary Sources Explanation Course Code TAE 315 Course Name THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Credit Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 Special Teaching Methods-II 2+2 3 ECTS 4 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 5 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Structor S.Ahmet ATAK Learning Outcomes Week 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Department of History Education Turkish None nice1971@hotmail.com Social Sciences , in particular information concerning the process of teaching and learning history be the way to becoming a good teacher in the field provided and the application of the modified Possess advanced level theoretical and practical knowledge supported by textbooks with updated information, practice equipments and other resources. Use of advanced theoretical and practical knowledge within the field. Conduct studies at an advanced level in the field independently. The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities Course objectives, content, teaching methods, Course content review introducing assessment methods Detection time and place in history teaching skills Concept based on history teaching History teaching problem solving and critical thinking skills History teaching methods and techniques (eg event simulation , lectures . Group work and individual study Midterm Exam 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Out of school history teachin Oral history Local and family history Computer and history teaching Historical novels and stories of history teaching Questions to ask in history teaching skills History teachers in teaching approaches, roles expected of a good history teacher 15. The teaching of history in the assessment and evaluation 16. Evaluation of the course and students' opinions Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 1. Baymur, F., Tarih Öğretimi, İnkılap Yay., İstanbul, 1949. Textbook 2. Dilek, D., Tarih Derslerinde Öğrenme ve Düşünme Gelişimi, 3. Türkiye’de Tarih Eğitimi, Felsefe Kurumu Semirnerleri, 1977. 4. İlköğretim Sosyal Bilgiler Öğretimi, YÖK/Dünya Bankası Ö.E.P., 5. Kısakürek, M.A ve Paykoç, F., Sosyal Bilgiler Öğretimi, 6. Köstüklü, N., Sosyal Bilimler ve Tarih Öğretimi, 7. Levent, T., Eğitimde Drama: Genel Yaklaşımlar, Seminer Notları. 8. Moffatt, M., Sosyal Bilgiler Öğreitmi, 9. Nichol, J., Tarih Öğretimi, (çev. M. Safran), 10. Oğuzkan, A. F., Öğretmenliğin Üç Yönü, 11. Orta Öğretim Kurumlarında Sosyal Bilimler Öğretimi ve Sorunları, 12. Özbaran, S., Tarih ve Öğretimi, 13. Özbaran, S., Tarih, Tarihçi ve Toplum, 14. Özçelik, A. DE., Test Hazırlama Kılavuzu. 15. Paykoç, F., Tarih Öğretimi, 16. Sosyal Bilimler Öğretimi, YÖK/Dünya Bankası Ö.E.P., 17. Tarih Eğitim Ve Tarihte "Öteki" Sorunu, Yurt Yay., İstanbul, 1998. 18. Thompson, P., Geçmişin Sesi: Sözlü tarih, (çev. Ş. Layıkel), 19. 20.Yüzyıl Avrupa Tarihi Nasıl Öğretilmeli, Tarih Vakfı Yay., İstanbul, 2003. 20. Türkiye’de Tarih Eğitimi ve Ders Kitapları: Buca Sempozyumu, Tarih Vakfı Yurt. Helpful resources DICLEUNIVERSITY ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SCIENCE COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code: TAE 317 Course Title: Year/Semester Status Name of the Programme Prerequisites Disable Students Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant Language of instruction Course Objectives Learning Outcomes Week 1. 2. 3. Optic Code: Consultation Hours: Wed 1500-1600 T-A-C: 3-0-3 ECTS: 4 Guidance 5 Compulsory All the 4th year programmes that train teachers None Disable students, if they need, can demand that necessary eases be provided carrying information about their situations to the instructors Making preparations for the course considering the content of the unit to be taught. Participating the activities during the course, doing the given responsibilities Inst. Mahmut ARİKAN, e-mail: marikan@dicle.edu.tr, Tel: 8822 Turkish To get student teacher experience and information about guidance service at school At the end of this course, the student; - Explains the basic concepts about guidance - Explains aims of student personality service - Explains general rules of guidance - Recognizes students, - Applies guiding rules to students, - Explains gathering information, - explains psychological guidance, - explains counseling - choices rules to help to the students need private education Contents, learning activities Topic Learning Activities Introduction of the goal, content, teaching Searching of the goal, content, style and evaluation of the course teaching methods and techniques, teaching materials and evaluation techniques Student personality service and guidance Expression, question-answer, discussion Services at Psychological information and Expression, question-answer, guidance discussion, sample applications 4. R.A.M Guidance services at school 5. Type teory and learning types and styles 6. Intelligence and intelligences types 7. Career guidance 8 9. Mid-term Personal guidance and Psychological guidance 10. Recognizing a person and its rtecniques 11. Private education 12. Anger and control of anger 13. Rebellion and intensity at school 14. Skills of control of stress and prevent 15. Improvement of programs of school psychological information and guidance Organization and staff in guidance 16. Assessment criteria Textbook / Material Recommended Reading Midterm Exams Quizzes Homeworks Projects Term Paper Lab Work Final Exam Psikolojik Danışma ve Rehberlik, Kaya A; Psikolojik Danışma ve Rehberlik, Deniz M.E; Eğitimde Çoklu Zeka, Demirel Ö; Önleyici Rehberlik, Korkut F Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications from schools. Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications Expression, question-answer, discussion, sample applications If any, mark as (X) X X X Percent (%) 20 10 10 X 10 X 50 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code Course Optical Code TAE 319 Offices Hours T+U Credit AKTS Salı 15.00-16.00 2+0 2 3 The Name of Course Sociology Midterm 5 Compulsory/ Optional Compulsory The Name of Program History Education Instruction Language Turkish Prerequisite None Disabled Students IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Responcibilities of Students Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Lecturer Seyit Ahmet Atak Course Assistant - The aim of course Learning and using of sociological concept and knowledge Learning Outcome Students learn basic concepts andknowledge of sociology and understand the rising of sociological idea, as well. The Content of Course, Teaching Activities Week s The Content of Course Teaching Activities Examination of the content of course 1. 2. Sociology’s topic and field Discussing in group, Questions and answers 3. The first theorists of Sociological idea (A. Comte ve E. Durkheim) Student Presentation, Questions and Answers 4. The first theorists of Sociological idea (K. Marx ve M. Weber) Student Presentation, Questions and answers 5. Female sociologist (H. Martineau) Questionq-answers, discuss in group 6. Globalisation and its affects Questionq-answers, discuss in group 7. Stratification in society, category and status Questionq-answers, discuss in group 8. Mowement in society Questionq-answers, discuss in group 9. Education, inequality, Questionq-answers, discuss in group 10. Globalisation and education, gender and education Questionq-answers, discuss in group 11. Urban and urbanisation Questionq-answers, discuss in group 12. Globalisation and urban Questionq-answers, discuss in group 13. Work and economy, Taylorizm, Fordizm, Questionq-answers, discuss in group 14. Post-Fordist production, career, gender, unemployment and changing roles. Questionq-answers, discuss in group 15. Poverty, wealth Questionq-answers, discuss in group 16. Globalisation and poverty, emigration and poverty Questionq-answers, discuss in group Rating Criteria Explanati on Percentages (%) Midterm Exam X 25 X 20 X 15 Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Attending to the course Other(File, Internship report, Thesis, and so forth). Final Exam X 40 Course Book Giddens, Anthony (2005) Sosyoloji, İkinci Baskı, Ankara: Ayraç Yayınevi. Auxiliary Sources - Bottomore, Tom& Nisbet, Robert (2002) Sosyolojik Çözümlemenin Tarihi, Haz. Mete Tuncay&Aydın Uğur, Ankara: Ayraç Yayınevi - Özkalp, Enver (2005). Sosyolojiye Giriş. 13. Baskı, Bursa: Ekin Kitabevi. - Bilton, T.&Bonett, K.&Jones, P.&Lawson, T.&Skinner, M.&Stanworth, M.&Webster, A.(2008). Sosyoloji. Ankara: Siyasal Kitabevi. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code Course Optical Code TAE 321 Offices Hours T+U Credit AKTS Salı 15.00-16.00 2+0 2 2 The Name of Course Philosophy of History Midterm 5 Compulsory/ Optional Compulsory The Name of Program History Education Instruction Language Turkish Prerequisite None Disabled Students IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Responcibilities of Students Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Lecturer Doç Dr. Mehmet KARATAŞ Course Assistant - The aim of course The aim of the course in the historical process and the properties of the evolution of the teaching of Turkish thoughts Learning Outcome Turkey and in different periods of evolutionary aspects of the idea of the features shown Understanding The Content of Course, Teaching Activities Week s 1. 2. 3. The Content of Course Definition of History and Philosophy of History Sources of Turkish Culture in the Philosophy of History The Concept of Time Teaching Activities Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Concepts of Space People Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Human Questionq-answers, discuss in group Historical Events and Cause-and-effect relationship Visa Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Relationship with Other Sciences History of Relations with Other Sciences Relationship between Geography History General Characteristics of some regions General Characteristics of some regions Mainstreaming body of law Spiritual Laws Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Questionq-answers, discuss in group Overall Rating Questionq-answers, discuss in group Rating Criteria Explanati on Percentages (%) Midterm Exam X 25 X 20 X 15 Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Attending to the course Other(File, Internship report, Thesis, and so forth). Final Exam X 40 Course Book . 1. Ülken H. Ziya, İslam Felsefesi, Ülken Yayınları, İstanbul, 2004 Auxiliary Sources 1. Ülken H. Ziya, İslam Felsefesi, Ülken Yayınları, İstanbul, 2004 2. Ülken H. Ziya, Türkiye’de Çağdaş Düşünce Tarihi, Ülken Yayınları, İst, 2002 VI. YARIYIL THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code Course Optic Code TAE 302 Consultation Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 T+U Credit ECTS 2+2 2 3 Course Name Ottoman ArchiveText II Semester Compulsory / Optional Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 6 Optional Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Asst. Prof.Mehmet KARATAŞ, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com, Tel:8832 Teacher Training Program All Programs Turkish None The language used in the documents of the Ottoman period , concepts, terms , and to learn the information . Ottoman writing and understanding of the read and write Outcomes Week 1. The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities Of classified documents and books are located in the Course content review introducing Prime Ministry Ottoman Archives. 2. classification of documents and books are located in the Prime Ministry Ottoman Archives Course content review introducing 3. 4. Hatt-i Humayun text reading from regimentation sorting text reading from Cevdet Course content review introducing Course content review introducing 5. Will read from text classification Course content review introducing 6. classification of text reading from the grand vizier Course content review introducing 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. reading from the Ministry of Interior to classify text Stars from reading text classification Stars from reading text classification Course content review introducing Course content review introducing Course content review introducing Course content review introducing Course content review introducing Course content review introducing 13. 14. Sicill-i Ahval text reading from classification Finance from the reading text classification Course content review introducing Course content review introducing 15. classified text reading from the Ministry of Education Course content review introducing Midterm Exam External sorting text reading of Awqaf reading text classification Year Final Exam 16. Course content review introducing Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Kurt Y., Osmanlıca Dersleri I-II, İstanbul 1989 Textbook Osmanlıca Okumaya Giriş, A.Ü. Yay., Ankara, 1972. 13. Ergin, M., Helpful resources Osmanlıca Dersleri, Boğaziçi Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 14. Muallim Naci, Lugat-ı Naci, Çağrı Yay., İstanbul, 1987. 15. Şemseddin Sami, Kâmûs-ı Türkî, Enderun Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 16. Hacı Mustafa Dervişi ve Ahmet Hulusi, Ahder-i Kebir, Osmanlı Yay. 17. Yazır, M., Eski yazıları Okuma Anahtarı, Vakıflar Genel Müd. Yay., Ankara, 1983. 18. Gökbilgin, T., Osmanlı Paleografya Ve Diplomatik İlmi, Enderun Kitabevi, İstanbul, 1992. 19. Kurt, Y., Osmanlıca Dersleri-I ve II, Akçağ Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 20. Kütükoğlu, M., Osmanlı Belgelerinin Dili, Kubbealtı Neşr., İstanbul, 1994. 21. Osmanlı Paleografyasına Giriş, Elhan Kitabevi, 22. Günday, D., Arşiv Belgelerinde Siyakat Yazısı ve Divan Rakamları, TTK Yay., Ankara, 1974. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Code TAE 304 Course Title Term Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Course Optic Code Consultation Hours Tuesday, 15.0016.00 Ottoman History VI (1699-1908) 86 Compulsory Department of History Education Turkish T+U Credit ECTS 2+0 2 3 Pre-requisites Disabled Student Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant The aim of the course None In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Kürşat KORKUT The students about the reasons for the decline of the Ottoman Empire pause and to inform. Conduct studies at an advanced level in the field independently. Share the ideas and solution proposals to problems on issues in the field with professionals and non-professionals by the support of qualitative and q Know and use the historical method. Have notions, knowledges, abilities and values of history and education of history. Explain theories, models, principles and generalisations of the sc Obey ethic and professional rules and takes charge in collusive practices. Use of advanced theoretical and practical knowledge within the field. The course content , learning activities Week Topic Course Learning Activity Activities 1. Selim III Period Active Learning 2. Selim III Period Active Learning 3. Mahmut II Period Active Learning Learning Outcomes 4. Mahmut II Period Active Learning 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Evaluation criteria Mahmut II Period Mahmut II Period Abdülmecit Period Visa Abdülmecit Period Fifth Murat Period Second Abdulhamid Period Second Abdulhamid Period Second Abdulhamid Period Second Abdulhamid Period Second Abdulhamid Period General Review Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Active Learning Evaluation criteria (X ) mark as X Midterm Exams Quiz Homework Projects Term Paper Laboratory Other X X Percent (%) Textbook Final Exam X Doğuştan Günümüze Osmanlı Tarihi c. XI Helpful resources İsmail Hakkı Uzunçarşılı ve Enver Ziya Karal’ın Osmanlı Tarihi Course Code TAE 306 Course Name THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Hours Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 History of Europe in the Modern times Credit ECTS 2 3 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 6 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Structor Mehmet Ali YAŞAR Week 1. Department of History Education Turkish None mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Course objective understanding of the fundamental issues of Medieval European History. Understanding of the political, social and religious structure of Medieval Europe The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities Course objectives, content, teaching methods, Course content review introducing assessment methods, introduction 2. New and modern period of European history resource 3. The European Concept, at the end of the Middle Ages as a European Political and Cultural 4. Competition between European States at the beginning of the new age European Expansion and Geographical Discoveries; Political and Economic Consequences of discovery; Reformation and Counter-Reformation, the Renaissance, 5. 6. 7. 8. Midterm Exam 9. XVI. Century Europe's population, Cities and Rural Areas 10. XVII. Century Europe 11. XVIII. Century Europe, the Industrial Revolution 12. Absolute Monarchy and statism; Formation of the Concept of National Government; XIX. Century Europe 13. European Culture and Civilization 14. European Culture and Civilization Evaluation of New and Modern European history 15. 16. FINAL Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Jacques Le Goff, Ortaçağ Batı Uygarlığı, Textbook Henri Pirene, Ortaçağ Avrupası’nın Ekonomik ve Siyasi Tarihi. Helpful resources Course Code TAR 308 Course Name THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Hours Tuesday, 15.002+0 16.00 History of the Ottoman Organization II Credit ECTS 2 4 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 6 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Asst. Prof . Serkan SARI, e-mail: serkan.sari@dicle.edu.t Tel: 8931 This course Ottoman Establishment Period is intended to teach the organization and functions of government agencies. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Department of History Education Turkish None Acquiring the information about the the administrative and province organization of Ottoman Empire from the foundation of Ottoman to the beginning of XVI. century The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities Learning Activities 1. Course objectives , content, teaching methods , Course content review introducing assessment methods 2. Group discussion, question -andOttoman military organization answer 3. Student presentations , question -andThe Period of the Ottoman army foundatıon answer 4. Kapıkulu system and Soldiers Expression 5. İnductee soldiers, janissaries , cebeci Question-answer, expression 6. Cannon unions, kapıkulu Cavalry Student presentations , discussion 7. State military organization Expression 8. Tımarlı sipahi Cavalries soil functions within the 9. 10. 11. Back service unions Leading forces and forces the castle Ottoman Navy system of evaluation Group discussion, question -andanswer Student presentations , question -andanswer Student presentations , question -andanswer 12. Midterm Exam 13. Ottoman finances Lecture and slide show 14. Ottoman budgets Subject of documentary 15. Form the Ministry of Finance Question -and-answer 16. End-of -term exam Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the course the Quiz Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to determine the Projects success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Ünal, Mehmet Ali, Osmanlı Müesseseleri Tarihi, Fakülte Kitabevi, Isparta Textbook 2002. Helpful resources 1. Halaçoğlu, Y., “XIV-XVII Yüzyıllarda Osmanlılarda Devlet Teşkilatı ve SosyalYapı”, TTK 1991 2. İpşirli, M., “Klasik Dönem Osmanlı Devlet Teşkilatı” Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 3. MEB, İA ve DİA İlgili Maddeler 4. Pakalın, M. Z., “Tarih Deyimleri ve Terimleri Sözlüğü” İstanbul 1983 5. Özcan, A., “Osmanlı Askeri Teşkilatı”, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 6. Kütükoğlu, M., “Osmanlı Belgelerinin Dili (Diplomatika)”, İstanbul 1994 7. Genç, M., “Osmanlı İmparatorluğunda Devlet ve Ekonomi”, İstanbul 2000 8. Öz, M., Osmanlı’da “Çözülme” ve Gelenekçi Yorumlar, İstanbul 1997 9. Barkan, Ö. L., “Tımar”, İA, C. 12 10. Yediyıldız, B., Osmanlı Toplumu, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: 11. Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 12. Aydın, A., “Osmanlı Hukukunun Genel Yapısı ve İşleyişi” Türkler (Yeni Türkiye Yay.) c: 10 13. Taneri, Aydın, Kuruluş Dönemi Osmanlı Deniz Kuvvetleri, Kültür Bak. Yay. Ankara, 1998. 14. Kurt, Y., “Osmanlı toprak Yönetimi” Osmanlı c: 3 Course Code TAE 310 Course Name THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Credit Hours Tuesday, 15.002+0 2 16.00 History of the Turkish State in the New and Modern times II. ECTS 2 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 6 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes intructor Mehmet Ali YAŞAR Week 1. 2. Department of History Education Turkish None mayasar@dicle.edu.tr XVI- XX. Centuries of Turkish Ottoman Empire outside world outlined to provide information about turkish state. Acquiring the theoretical basics of history of Turks living in Balkans, north of Black sea, Persia, Central Asia and India. Knowing the way to reach information and using effectively them about in Turkish archives, libraries and museum Having a protection and development consciousness about international and national cultural heritage in Turkish World from 1453 to the present Following the relevant international and national agendas and evaluating historical perspective. The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities Historical developments in the world in the near term Course content review introducing (summary) Turkish state in the history of the world (political, economic, geographical features as well as a summary Group discussion, question-and-answer 3. 4. Turkish states 5. Turkey's history -2 (political, economic, geographical features as well as a summary) Lecture, Question and Answer 6. The history of the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (political, economic, geographical features, as well as a summary) expression 7. History of Azerbaijan in the Caucasus (political, economic, geographical features also in summary) Student presentation 8. Midterm exam and course evaluation expression 9. Join Uzbekistan (political, economic, geographical features as well as a summary) expression 10. Join Turkmenistan (political, economic, geographical features, as well as a summary) expression 11. Join Kyrgyzstan (political, economic, geographical features, as well as a summary) Discussions, question and answer 12. History of the Turks in other states of the region (political, economic, geographical features, as well as a summary expression 13. The history of the Autonomous Republic of Turkey (political, economic, geographical features, as well as a summary) Lecture, Question and Answer 14. The history of the Autonomous Republic of Turkey (political, economic, geographical features, as well as a summary) Lecture, Question and Answer 15. Overall the recent history of Turkish World expression History of Turkey-II (political, economic, geographical features as well as a summary of Lecture, Question and Answer expression Year Final Exam 16. Discussions, question and answer Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) amount of points. End-of-term exam. X 60 Togan, Z. V., Bugünkü Türk İli (Türkistan) ve Yakın Tarihi, İstanbul, 1942 Textbook 1. Hayıt B. M., Türkistan Rusya ile Çin Arasında, İstanbul,1975. Helpful resources 2. Togan, Z. V., Bugünkü Türk İli (Türkistan) ve Yakın Tarihi, İstanbul, 1942 3. Togan, Z. V., Hatıralar, Türkistan ve Diğer Müslüman Doğu Türklerinin Millî Varlık ve Kültür Mücadeleleri, İstanbul, 1969. 4. Kurat, A. N., Türkiye ve İdil Boyu, Ankara, 1966. 5. Saray, M., Kazak Türkleri Tarihi, Ankara, 1992. 6. Saray, M., Rus İşgali Devrinde Osmanlı Devleti ile Türkistan Hanları Arasındaki Siyasî Münasebetler, 1775-1875, İstanbul, 1984. 7. Sümer, F., Safevî Devleti’nin Kuruluşu ve Gelişmesinde Anadolu Türklerinin Rolü, Ankara, 1976. 8. Arat, R.R., Baburnâme, Ankara, 1985. 9. Baddeley, J.F., Rusların Kafkasya’yı İstilası ve Şeyh Şamil, (çev.)S. Özden, İstanbul,1989. 10. Yakubovsky, A. Yu., Altınordu ve Çöküşü, çev: H. Eren, Ankara, 1992. 11. Kurban, İ., Doğu Türkistan İçin Savaş, Ankara, 1995. 12. İnalcık, H., “Osmanlı-Rus rekabetinin Menşei ve Don-Volga Kanalı Teşebbüsü, 1569”, Belleten, c: 12, sa: 46, Ankara, 1948. COURSE CODE TAE 314 The Name of Course THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION C ourse Optical Code Office Hours T+U Credit Tuesday, 15.002+0 2 16.00 The History of Turkish Education II. AKTS 2 Midterm Obligatory/ Optional Program Name Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students 6 Obligatory Responsibility of the Students Responsibilities Course Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Mehmet Ali YASAR mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Learning outcomes Understanding about leading persons and events about Turkish education History. History Education Turkish None In case of necessity, they can demand facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer Giving information about education and teaching activities in the Turkish history from beginning to today. Content of course, Teaching activities Weeks Content of course Teaching activities Constitutional period 2 primary, secondary and higher 1. Examination of course content education innovation 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Constitutional period 2 primary, secondary and higher education innovation Constitutional period 2 primary, secondary and higher education innovation During the War of Independence Education Examination of course content During the War of Independence Education Examination of course content Examination of course content During the War of Independence status of minority and foreign schools Republic of the training period features Midterm Exam Atatürk's place in the history of Turkish education Atatürk's place in the history of Turkish education Republic during the primary, secondary and higher Examination of course content Examination of course content Examination of course content Examination of course content Examination of course content Examination of course content Examination of course content 12. education, innovations in Republic during the primary, secondary and higher education, innovations in Examination of course content 13. Special education during the Republican period, the status of minority and foreign schools Examination of course content 14. Special education during the Republican period, the status of minority and foreign schools Examination of course content 15. Republic in the field of training during the administrative restructuring Examination of course content 16. Republican era in the development process of education and teacher issues Examination of course content Rating Criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Homeworks/Term Paper Projects Attending to the course Other (File, internship report, thesis, etc.). Final Exam Course Book Percentages (%) X 20 05 X 10 15 X 10 X Explanation 60 Çelebi, A., İslam'da Eğitim Öğretim Tarihi, İstanbul, 1976. Akyüz, Y. Türk Eğitim Tarihi, Auxiliary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 316 Course Title Course Optic Code Term VI. Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Office Hours History of Turkish İnnovation I Department of History Education Turkish T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 2 Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Lecturer Mehmet Ali Yasar is mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Instructor Lecturer Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes The aim of the course in the Ottoman Empire XVII. XXI century onwards . Century until the beginning of the reform movement and related sources of basic information related to the investigation of Revolutionary movements in Europe, with Turkey as a comparative understanding of developments The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. Course objectives , content, teaching methods , course content review introducing assessment methods, course content review introducing 2. course content review introducing Innovation examination of historical sources course content review introducing 3. 4. 5. XVII. century of reform and reformer Tulip Era reform movements I. Mahmut era reform movements course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing 6. III. Mustafa era of reform movements course content review introducing 7. Midterm Exam course content review introducing 8. Abdulhamid era reform movements course content review introducing 9. III. Selim era of reform movements course content review introducing 10. II. Mahmoud era reform movements 11. Tanzimat period of reform movements ( speed Abdulmecit ) 12. Tanzimat period of reform movements ( Sultan Abdul Aziz speed ) 13. II. Abdulhamid era reform movements 14. II. Age of Constitutional Monarchy reform movements 15. II. Age of Constitutional Monarchy reform movements 16. Overall Rating Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Description Per (%) X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . Course book by Kemal Karpat, Osmanlı Modernleşmesi, Ankara N.Hayta-U.Ünal,Osmanlı Devleti’nde Yenileşme Hareketleri, İstanbul İlber Ortaylı, Osmanlı’da Değişim ve Anayasal Rejim Sorunu Enver Ziya Karal, Osmanlı Tarihi, V- IX. Şerif Mardin, Yeni Osmanlı Düşüncesinin Doğuşu Şerif Mardin, Jön Türklerin Siyasi Fikirleri Feroz Ahmed, İttihat ve Terakki ( 1908- 1914) Feroz Ahmed, İttihatçılıktan Kemalizme İlber Ortaylı, İmparatorluğun En Uzun Yüzyılı, Ankara Auxilary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code: Optic Code: TAE 352 Consultation Hours: T-A-C: ECTS: Friday, 09.00- 10:00 2+2 - 3 6 Course Title: Education Technologies and Material Projects Year/Semester 6 Status Compulsory Name of the Programme All the programmes which educate a teacher Prerequisites None Disable Students If the disable students need information about their situations, they can ask lecturers. Student Responsibilities Prepare for the lesson, be active in the lesson activities, make the responsibilities ( homework, project, reading, discussion ) Lecturer Yrd.Doç.Dr. Bayram AŞILIOĞLU, e-mail: bayrama@dicle.edu.tr , 8906 Course Assistant Language of instruction Turkish Course Objectives Acquire the students’ main information, principles and ability for performances deal with education technology. Learning Outcomes At the end of the lesson, the student: explains the main concepts about education technologies. makes different meanings of education technologies. explains the relationship with education and communication. explains the relationship with education and classing materials. explains main material preparations. explains the superior and weak sides of materials. classes the seminar materials. prepares seminar materials deal with his/ her department. uses communication technologies which is suitable of lesson’s aim. knows internet’s properties. uses internet deal with his/ her department. Contents, learning activities Week Topic Learning Activities 1. Introduce the target, index, type of education, revaluations methods of the lesson. Examine the lesson 2. Education technologies and communication process and education explain the education, technologies and communication. Discuss about educational communication handicaps in class. 3. Classing the material and connection with education. Seminar, question-answer and discussions 4. Main material preparations. Give information about preparation of material and studying with students on example situations. 5. The principles of preparation education material. Seminar, question-answer and discussions 6. Preparation of seminar materials Explain the main points on preparation material, ask questions to students and discussions 7. Preparation of viewer and using it make students prepare viewer papers, control student’s studies, discuss with them. 8. Improving alternative lesson material Seminar, question-answer and discussions 9. Selecting and ordering education materials make students performance with selecting education materials and ordering them about their departments. 10. Midterm exam 11. visual , auditory materials Explaining the visual and auditory materials and explain their superior and weak points, asking questions and discussions 12. Using visual , auditory materials in education making students performance about using visual and auditory materials. 13. Using visual , auditory materials in education making students performance about using visual and auditory materials. 14. Computer and internet in education using computer in education, and it’s advantages and disadvantages, and studying on them. 15. Performances computer and internet in education studying of students on computer supported education , e- education examples. 16. general evaluation of lesson Discussion Assessment criteria If any, mark as (X) Percent (%) Midterm Exams X 20 Quizzes X 05 Homeworks X 10 Projects X 15 Term Paper X 10 X 40 Lab Work Other Final Exam Textbook / Material Özcan Demirel, Doç. Dr. Eralp Altun (Editör) (2009). Öğretim Teknolojileri ve Materyal Tasarımı, 3. Baskı, Pegem Akademi Yayıncılık, Ankara.. Recommended Reading Seferoğlu, S. Sadi (2009). Öğretim Teknolojileri ve Materyal Tasarımı, 4. Baskı, Pegem Akademi Yayıncılık, Ankara. Selvi Kıymet (Edit). (2008). Öğretim Teknolojileri ve Materyal Tasarımı, Anı Yayıncılık, Ankara Yanpar, Tuğba Ş. (2007). Öğretim Teknolojileri ve Materyal Tasarımı, Anı Yayıncılık, Ankara THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 318 Course Title Course Optic Code Term 6 Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Disabled Student Student Responsibilities Instructor Lecturer Office Hours T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 3 General Geography Department of History Education Turkish In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Asst. Assoc. Dr.. Aydogan question, e-mail: ameseli@dicle.edu.tr Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes The purpose of the general principles of geography lessons, teach fundamental concepts and methodology Knows the general principles of geography, basic concepts in geography judge, knows the natural environment of human interaction, is aware of the processes that are causing problems The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities Definition of geography review course content 1. course content review introducing 2. Department of Geography, group discussion, questionand-answer course content review introducing course content review introducing 3. Methods in Geography Lecture course content review introducing 4. 5. 6. 7. Students who take advantage of the geographer is which data presentation, ask questions, answer questions Map, projections Lecture Sections, diagrams, charts Ööğrenc presentation, ask questions, answer questions course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing Midterm Exam 8. Introduction to Physical environment (lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere and biosphere) Lecture course content review introducing 9. Expression shape of the earth course content review introducing 10. Expression of earth movements Plate tectonics-the internal forces 11. Epirorejenez, Orogeny student presentation 12. Of volcanism, earthquakes 13. Lithology impact on the environment 14. Lithology impact on the environment 15. Final Exam 16. Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Description Per (%) Course book by Şahin C., Coğrafyaya Giriş, Auxilary Sources Atalay İ., Genel Fiziki Coğrafya, Atalay İ., Toprak Coğrafyası, Atalay İ., Uygulamalı Klimatoloji Atalay İ., Türkiye Vejetasyon Coğrafyası Akkuş A., Genel Fiziki Coğrafya . X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 320 Course Title Course Optic Code Term 6 Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Disabled Student Student Responsibilities Instructor Lecturer Office Hours T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 3 History of the Turkish Freedom War Department of History Education Turkish In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Asst. Prof. Tuğba KORHAN Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Course objective Turkish War of Independence and the revolutionary Movements of results and Cons of both the place and importance in the history disclosure At the end of this course the student; - Opening of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey and the understanding of the activities - The Lausanne Peace Conference to grasp the importance of the Turkish War of Independence The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. T.B.M.M. 's Opening and Activities course content review introducing - Opening Preparation - Parliament's Studies 2. The first Grand National Assembly Features - Be a national council - Idealistic and democratic assemblies to be - Assembly of a State of Emergency to be - Hero is a parliamentary group discussion, question -and-answer After the armistice Entente on Turkey New Projects - Paris Peace Conference - London Conference - San - Remo Conference Speech course content review introducing course content review introducing 4. Treaty of Sèvres - Articles of the Treaty Student presentation, ask questions , answer questions course content review introducing 5. course content review introducing 8. Treaty of Sevres Evaluation of the Turkish War of Independence Lecture South Front and the French and Challenges - Maras Defense - Urfa Defense - Pistachio Defense - Adana Defense Ööğrenc presentation , ask questions , answer questions Midterm Exam Lecture battles on the Eastern Front and Armenians 9. Battle of the Western Front course content review introducing 10. II. Battle of the -Kütahya- Eskişehir battles Lecture Battle of Sakarya and Results - Preparations for War - Beginning of War and Its Consequences Lecture, Question and Answer 3. 6. 7. 11. 12. of the Treaty of Kars - Ankara name of the Entente - New Diplomacy Initiatives Student presentation 13. The Great Raid and the Great Victory - Lecture Mudanya and Results 14. Lausanne Peace Negotiations and Results - Treaty of situation? - Signing of the Treaty of Peace Lecture 15. Lausanne Peace Treaty and Decisions - Limits - Straits - Capitulations course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing - Minorities - Debt Speech 16. Overall Rating Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Description Per (%) X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . Course book by Baykara, T. ; Türk Devrim Tarihi, Ankara 1980. Auxilary Sources 1. Akyüz, Y.; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Fransız Kamuoyu, Ankara 1988. 2. Atatürk’ün Söylev Ve Demeçleri, C. I-Iı-Iıı, Tite Yay., Ankara 1981. 3. Armaoğlu, F.; Siyasi Tarih 1789-1960, Ankara 1964. 4. Atatürk, M. K., Nutuk (1919-1927) Bugünkü Dille, (yay. haz.) Z. Korkmaz, Atatürk Araştırma Merkezi Yay., Ankara, 1999. 5. Aybars, E.; Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Tarihi I, Ankara 1990. 6. Baykal, B. S.;Heyet-İ Temsiliye Kararları, Ankara 1989. 7. Baykara, T. ; Türk Devrim Tarihi, Ankara 1980. 8. Bayur, Y. H.; Türk İnkılabı Tarihi, C.Iıı, Ankara 1983. 9. Belen, F.; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı, Ankara 1983. 10. Cebesoy, A. F.; Milli Mücadele Hatıraları, İstanbul 1953. 11. Eroğlu, H.; Türk İnkılap Tarihi, İstanbul 1982. 12. Gökbilgin, T.; Milli Mücadele Başlarken, C.I, Ankara 1959. 13. Gül, M.; Türk İnkılap Tarihi, Ankara 1995. 14. Gürün, K.; Ermeni Dosyası, Ankara 1983. 15. Karal, E. Z.; Atatürk’ten Düşünceler, İstanbul 1986. 16. Kazım Karabekir; Enver Paşa Ve İttihat Terakki Erkanı, İstanbul 1967. 17. Kazım Karabekir; İstikbal Harbimiz, C. I, İstanbul 1995. 18. Koçak, C.; Türk-Alman İlişkileri (1923-1939), Ankara 1991. 19. Okyar, O.; Milli Mücadele Dönemi Türk-Rus İlişkilerinde Mustafa Kemal, Ankara 1998. 20. Öke, M. K.; Ermeni Sorunu, Ankara 1991. 21. Özkaya, Y.; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Cumhuriyet Tarihi, Ankara 1981. 22. Sonyel, S. R.; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Dış Politika, C. I-Iı, Ankara 1986 23. Soysal, İ.; Türkiye’nin Siyasal Antlaşmaları (1920-1945), Ankara 1983 24. Süslü, A.; Ermeniler Ve 1915 Tehcir Kanunu, Ankara 1990. 25. Şahin, M.; Milli Mücadele’de Doğu Trakya, Ankara 1992. 26. Şahingöz, Mehmet; İzmir, İstanbul Ve Maraş’ın İşgali Üzerine Yapılan Protesto ve Mitingler, Ankara 1986. 27. Şıvgın, H.; Trablusgarp Savaşı Ve 1911-1912 Türk İtalyan İlişkileri, Ankara 1989. 28. Şimşir, B.; Lozan Telgrafları I (1922-23), Ankara 1990. 29. Tansel, S.; Atatürk Ve Kurtuluş Savaşı, Ankara 1965. 30. Tunaya, T. Z.; Türkiye’de Siyasi Partiler, İstanbul 1952. 31. Turan, R. Ve Diğerleri; Atatürk İlkeleri Ve İnkılap Tarihi, Ankara 1999. 32. Turan, Ş.; Türk Devrim Tarihi I, Ankara 1991. 33. Uras, E.; Tarihte Ermeniler Ve Ermeni Meselesi, İstanbul 1950 34. Ünal, T.; 1700’den 1958’e Kadar Türk Siyasi Tarihi, Ankara 1974. 35. Yalçın, E. S., Atatürk’ün Milli Dış Siyaseti, Ankara 2000. 36. Yalman, A. E.; Gördüklerim Ve Geçirdiklerim, C. Iı, İstanbul 1970. 37. Yavuz, Ü.; İmparatorluktan Milli Devlete, Ankara 1990. VII. YARIYIL THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAR 401 Course Title Course Optic Code Office Hours T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 4 History of Ottoman Organization III Term Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition VIII. Compulsory Department of History Education Turkish Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Lecturer Course Assistant Asst. Proff. Serkan SARI,serkan.sari@dicle.edu.tr tel:8931 The aim of the This course Ottoman Establishment Period is intended to teach the organization course and functions of government agencies. Learning Outcomes Acquiring the information about the the administrative and province organization of Ottoman Empire from the foundation of Ottoman to the beginning of XVI. century The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. Course objectives , content, teaching methods , course content review introducing assessment methods, course content review introducing 2. Sheykhulislamate , kadıaskerlik group discussion, question -and-answer course content review introducing course content review introducing 3. Müderris the Nakibü'l notables , Sultan teacher Student presentations , question -and-answer course content review introducing 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Kadje institutions Scientific employment areas of the class , lecture Madrasa Organization Lecture course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing The first Ottoman School student presentations , discussion Classification and grading of Madrasa education, language teaching and training style discussion of the structure of Ottoman society course content review introducing Madraisah degradation of the teaching staff and school group work foundations in the Ottoman Empire and evaluation of student presentations course content review introducing course content review introducing The functions of the Foundation and perception of student presentations , question -and-answer Midterm Exam Question and Answer Social institutions Inter-institutional relations and conflicts with the subject of documentary Evaluation of the course Lecture and slide show 16. Overall Rating Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Description Per (%) X X X X 20 05 10 15 . determines the success of the course the student to pass Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Course book by X 10 X 60 his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . Ünal, Mehmet Ali, Osmanlı Müesseseleri Tarihi, Fakülte Kitabevi, Isparta 200 Auxilary Sources 1. Halaçoğlu, Y., “XIV-XVII Yüzyıllarda Osmanlılarda Devlet Teşkilatı ve Sosyal Yapı”, TTK 1991 2. Faruqhi, S., “Osmanlı’da Kentler ve Kentliler, Tarih Vakfı Yurt Yayınları, İstanbul 1998. 3. MEB, İA ve DİA İlgili Maddeler 4. Akgündüz, A., Osmanlı Kanunnameleri, OSAV, İstanbul 1996. 5. Özcan, A., “Osmanlı Askeri Teşkilatı”, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 6. Genç, M., “Osmanlı İmparatorluğunda Devlet ve Ekonomi”, İstanbul 2000 7. Öz, M., Osmanlı’da “Çözülme” ve Gelenekçi Yorumlar, İstanbul 1997 8. Barkan, Ö. L., “Tımar”, İA, C. 12 9. Yediyıldız, B., Osmanlı Toplumu, Osmanlı Devleti ve Medeniyeti Tarihi, Editör: 10. Ekmeleddin İhsanoğlu, İstanbul 1994 11. Aydın, A., “Osmanlı Hukukunun Genel Yapısı ve İşleyişi” Türkler (Yeni Türkiye Yay.) c: 10 Kurt, Y., “Osmanlı toprak Yönetimi” Osmanlı c: 3 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 403 Course Title Course Optic Code Office Hours World History in the 20th Century I Term Compulsory / Elective IX. Compulsory T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 4 Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Department of History Education Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Assist. Prof. Tuğba KORHAN Student Responsibilities Instructor Lecturer Turkish Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes The aim of the course of world history that shaped developments to understand the causes and consequences Join the world 's major developments of the 20th century , the historical foundations of these developments and to know the cause and effect relationship The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. Course objectives , content, teaching methods , course content review introducing assessment methods, course content review 2. in the world and the Great Powers in the 20th course content review introducing Century course content review introducing Formation of the Postwar Order And Problems Arising 3. On the Eve of World War I , the Great Powers course content review introducing 4. Historical Foundations of the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance World War I course content review introducing 5. Russian Revolution , the War of the United States to participate War Strengths and Weaknesses Affecting Results course content review introducing 6. Turkey's Foreign Policy ( 1919-1939 ) course content review introducing 7. Midterm Exam course content review introducing 8. Lausanne . And the issues and Drop course content review introducing solutions 9. course content review introducing Turkey of Depression 10. Cooperation in the Balkans , the Balkan Entente 11. In the interwar period and Anti- Revisionists The Revisionists 12. Nazism and Fascism , Fundamentals and Objectives 13. Formation of World War Conditions 14. Beginning of World War II , Developments and Causes 15. Turkey in World War II 16. Overall Rating Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Description Per (%) X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . Course book by Paul Kennedy, Büyük Güçlerin Yükseliş ve Çöküşleri Fahir Armaoğlu: 20. Yüzyıl Siyasi Tarihi, İş Bankası yay. Hanry Kissenger: Diplomasi Oral Sander, Siyasi Tarih, I-II Mehmet Gönlübol, Olaylarla Türk Dış Politikası Auxilary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code Course Optic Code Office Hours T Credit ECTS 2+0 2 4 TAE407 Course Title History of Turkish Renovation II Term VIII. Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Lecturer Department of History Education Turkish Lecturer, Mehmet Ali Yasar mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Course Assistant The aim of the course Objective of the Course Innovation and modernization philosophical roots in accordance with the Turkish reform process since breaking points , the innovation of the concept of modernization and modernization concepts identified with the grounds and of innovation nowadays the point where the detection Learning Outcomes The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. Course objectives , content, teaching methods , course content review introducing assessment methods, course content review introducing 2. Intellectual Foundations of Westernization -I course content review introducing course content review introducing 3. Westernization Intellectual Fundamentals- II course content review introducing 4. Westernization Corporate Fundamentals- I course content review introducing 5. Westernization Corporate Fundamentals- II course content review introducing 6. Integration with intellectual Westernization of Innovation course content review introducing 7. Midterm Exam course content review introducing 8. 18th century Reformation Movement course content review introducing 9. 19th century Reformation : Tanzimat Edict of Reform course content review introducing 10. 11. Modernleşms and II. Constitutional Monarchy Current Opinion in of Westernization 12. Current Opinion in of Westernization 13. Post-Ottoman and Republic of Innovation 14. Post-Ottoman and Republic of Innovation 15. Republican era of modernization 16. Overall Rating Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Description Per (%) X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 Course book by Kemal Karpat, Osmanlı Modernleşmesi, İlber Ortaylı, Osmanlı’da Değişim ve Anayasal Rejim Sorunu İlber Ortaylı, Batılılaşma Yolunda, Ali Akyıldız, Osmanlı Bürokrasisi ve Modernleşme, Enver Ziya Karal, Osmanlı Tarihi, V- IX. Şerif Mardin, Yeni Osmanlı Düşüncesinin Doğuşu Şerif Mardin, Jön Türklerin Siyasi Fikirleri Feroz Ahmed, İttihat ve Terakki ( 1908- 1914) Feroz Ahmed, İttihatçılıktan Kemalizme İlber Ortaylı, İmparatorluğun en uzun yılı Abdurrahman Şeref, Tarih Musahebeleri, . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . Ahmet Cevdet Paşa, Tarih-i Cevdet, Berkes, N., Türkiye’de Çağdaşlaşma, Davison, R., Osmanlı İmparatorluğunda Reform, Mardin, Ş., Türk Modernleşmesi, Shaw, S., Osmanlı İmparatorluğu ve Modern Türkiye, Tunaya, T. Z., Türkiye’nin Siyasî Hayatında Batılılaşma Hareketleri, Auxilary Sources THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 409 Course Title Course Optic Code Term VIII. Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Asst. Prof . Tuğba KORHAN Course Assistant Office Hours T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 4 History of Turkish Thought Department of History Education Turkish The aim of the course Learning Outcomes The aim of the course in the historical process and the properties of the evolution of the teaching of Turkish thoughts At different periods of evolutionary aspects of Turkish thought and Understanding of features revealed The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. Thought, History , Culture course content review introducing 2. Introduction to Turkish Thought course content review introducing course content review introducing 3. Turkish Cosmogony and Asian nations course content review introducing 4. Oguz Turkish mythology and epic course content review introducing 5. Place in Turkish Wisdom and Thoughts course content review introducing 6. Place in Turkish Wisdom and Thoughts course content review introducing 7. Technical Contemplation in Turkey course content review introducing 8. Visa course content review introducing 9. of the Hindu neighborhood Turks and interaction with Avrulı course content review introducing 10. Introduction to Islamic Turkey contemplation 11. 12. Islamic Thought and Civilization Islamic Thought and Civilization 13. 14. transplants and mental sciences in Islam Sufism in Islam 15. The Turkish-Islamic Thinkers 16. Overall Rating Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship Description Per (%) X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 X 60 be given a certain amount of points . Course book by 1. Ülken H. Ziya, İslam Felsefesi, Ülken Yayınları, İstanbul, 2004 Auxilary Sources 1. Ülken H. Ziya, İslam Felsefesi, Ülken Yayınları, İstanbul, 2004 2. Ülken H. Ziya, Türkiye’de Çağdaş Düşünce Tarihi, Ülken Yayınları, İst, 2002 Course Code TAE 413 Course Title THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Office Hours T+U Çarşamba, 15.00- 2+0 16.00 Arabic Credit 2 AKTS 3 Halfterm Compulsory/ Optional Programın Title Instruction Language Prerequisite Disabled Students Spring Optional Students Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Associate Prof. Mehmet KARATAS, e-mail:mkaratasksu@mynet.com, Tel:89 33 Lecturer History Education Arabic None In case of necessity, they may request facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Giving informatıon in theory and practise about Arabic . Learning Outposts Weeks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Writing, understanding and reading texts in Arabic. Course Content, Teaching Activities Course Content Teaching Activities Third leson in Third unite Forth lesson in Third unite Fifth lesson in Third unite First lesson in Forth unite Second lesson in Forth unite Third lesson in Forth unite Forth lesson in Forth unite Midterm Exam Fifth lesson in Forth unite First Lesson in Fifth unite Second Lesson in Fifth unite Third Lesson in Fifth unite 13. Forth Lesson in Fifth unite 14. Fifth Lesson in Fifth unite 15. Text Reading 16. General Consideration Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Explanation Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz X 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects X 15 Course Attendance X 10 Other(Filing, Internship Report, Thesis and so forth). Final Exam X 40 Altun Ahmet-Meydan Ahmet-Erkul İhsan, Modern Arapça Öğretimi Course Book Auxiliary Sources 1. Beken, S., Osmanlıca Okumaya Giriş, A.Ü. Yay., Ankara, 1972. 2. Ergin, M., Osmanlıca Dersleri, Boğaziçi Yay., İstanbul, 1989. 3. Gökbilgin, T., Osmanlı Paleografya Ve Diplomatik İlmi, Enderun Kitabevi, İstanbul, 1992. 4. Kütükoğlu, M., Osmanlı Belgelerinin Dili, Kubbealtı Neşr., İstanbul, 1994. 5. Osmanlı Paleografyasına Giriş, Elhan Kitabevi, 6. Timurtaş, F., Osmanlı Türkçesine Giriş, Alfa Yay., İstanbul, 2000 DICLE UNIVERSITY ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SCIENCE COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code: TAE 451 Optic Code: Course Title: Year/Semester Status Name of the Programme Prerequisites Disable Students Classroom Management Spring Compulsory All the programmes that train teachers Student Responsibilities Lecturer Course Assistant Language of instruction Course Objectives Consultation Hours: Tuesday 15:00-16:00 T-A-C: 2-0-2 ECTS: 2 None Disable students, if they need, can demand that necessary eases be provided carrying information about their situations to the instructors. Making preparations for the course considering the content of the unit to be taught. Participating the activities during the course, doing the given responsibilities. Asst. Prof. Dr.Hasan ŞENTÜRK, e-mail: h-senturk@dicle.edu.tr, Tlf: 8851 --Turkish Teacher candicates acquiring necessray information, skills, values about classroom management. Learning Outcomes At the end of tfis course a student can; - Knows the basic concepts related to the classroom management and epress them correctly. - Analyse the classroom management at different dimensions - Acquires the true senses about the classroom management’s models and uses the most convenientest of the situation. - Creates a good communication order the learning atmospheres - Administrates the learning process well and use time effectively. - Prevents the undesired behaviours and even if they occur he/sehe can change them. - Controls and assess the classroom activities according to goals. Contents, learning activities Week Topic Learning Activities 1. Introduction 2. Basics of classroom management Factors affecting classroom management Dimensions of classroom Determine the objectives of the lesson and examine its content. Investigate basic concepts and principles about classroom management Introduce factors have roles on shaping activities of classroom management Discuss on the dimensions of the classroom management, 3. 4. 7. management Models of classroom management The physical characteristics of Classroom Time management ask and answer questions Investigate the basic principles and approaches about shaping models of classroom management Student presentment on the physical characteristics and orders of classroom Investigate the relationship between the given time 8. Introduction management Student presentment, ask and answer questions, do model practices 9. Classroom management and communication Midterm exam Investigate the relationship between the Classroom Management and Communication Classroom management and motivation Developing rules and provide discipline Prevent the undesired behaviours Change the undesired behaviours Provide a positive classroom atmosphere convenient to learning Check control and asses the activity done during the term Investigating the motivation approaches and apply them to classroom management Make students comprehend the importance and necessity of rules and discipline, discuss some rules in practice Determine the undesired behaviours, discuss what can be done to prevent them before occur Discuss on how to change the undesired behaviours when they occur whatever done Define a positive classroom atmosphere convenient to learning according to the classroom atmosphere of now. 5. 6. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Check the activities done during the term and determine their achievement level according to this suggest offers to develop this process. If any, mark as (X) X Assessment criteria Textbook / Material Recommended Reading Percent (%) Midterm Exams 20 Quizzes Homeworks X 10 Projects X 10 Attendance to the lesson X 10 Lab Work Other Final Exam X 50 Kıran. Hüseyin, ve Diğerleri; Etkili Sınıf Yönetimi (2008), Pegem A Yay., Ankara Aydın, Ayhan. (2008) Sınıf Yönetimi, Ankara: Pegem Yayınları Başar, Hüseyin. (2008) Sınıf Yönetimi. Ankara: Pegem Yayınları. Celep, Cevat. (2007) Sınıf Yönetimi ve Disiplin. Anı Yayıncılık, Ankara 2007 Erden, Münire (2005). Sınıf Yönetimi. Alkım Yayınları, İst. Özyürek, Mehmet.(2004) Sınıfta Davranış Yönetimi 1, 2.Baskı, Karatepe Yayınları, Ankara Karip, Emin. (2005) Sınıf Yönetimi PegemA Yayıncılık Ankara. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 417 Course Title Course Optic Code Term IX. Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Assist. Prof. Tuğba KORHAN Student Responsibilities Instructor Lecturer Office Hours T 2+0 Turkish Foreign Policy in The Period of Republic Credit 2 ECTS 4 Department of History Education Turkish Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Course objectives National Struggle and the Republic of Turkey's foreign policy in the period to be told Period of the Republic of Turkey 's National Struggle understanding of foreign policy - Lausanne Peace Conference, Turkey's understanding of the solutions to the issues brought - 1923-32 and 1932-38 period, Turkey's comprehension of the relations with other states The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. Armistice Period in Turkish Foreign Policy review course content review introducing course content 2. delegation of Turkish Foreign Policy in the Era group discussion, question -and-answer course content review introducing course content review introducing 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Period of First Assembly of Turkish Foreign Policy Speech National Pact Student presentation, ask questions , answer questions of the Lausanne Peace Conference Speech course content review introducing Turkish Foreign Policy in the Period 1923-32 Student presentation, ask questions , answer questions course content review introducing Midterm Exam Mosul Problem expression Greek-Turkish , Turkish-Soviet relations; expression Turkish-Italian , Turkish-French Relations Lecture 11. 1932-38 Period Turkish Foreign Policy Lecture, Question and Answer 12. Introduction to the League of Nations of student presentations Turkey's Relations with the Balkan States and the Islamic Countries Lecture Turkish - Soviet, Turkish , Italian, German-Turkish , Turkish-British Relations Lecture 13. 14. 15. course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing Montreux Straits Convention Speech 16. Hatay Problem Lecture Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Description Per (%) X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . Course book by Yalçın, E. Semih, Atatürk’ün Milli Dış Siyaseti, Ankara 2000. Auxilary Sources Akyüz, Yahya; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Fransız Kamuoyu, Ankara 1988. 2. Atatürk’ün Söylev Ve Demeçleri, C. I-Iı-Iıı, Tite Yay., Ankara 1981. 3. Atatürk, M. K., Nutuk (1919-1927) Bugünkü Dille, (yay. haz.) Z. Korkmaz, Atatürk Araştırma Merkezi Yay., Ankara, 1999. 4. Armaoğlu, Fahir; Siyasi Tarih 1789–1960, Ankara 1964. 5. Aybars, Ergün; Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Tarihi I, Ankara 1990. 6. Baykal, Bekir Sıtkı; Heyet-İ Temsiliye Kararları, Ankara 1989. 7. Baykara, Tuncer; Türk Devrim Tarihi, Ankara 1980. 8. Bayur, Y. Hikmet; Türk İnkılâbı Tarihi, C.III, Ankara 1983. 9. Cebesoy, Ali Fuat; Milli Mücadele Hatıraları, İstanbul 1953. 10. Eroğlu, Hamza; Türk İnkılâp Tarihi, İstanbul 1982. 11. Gökbilgin, Tayyip; Milli Mücadele Başlarken, C.I, Ankara 1959. 12. Gül, Muhittin; Türk İnkılâp Tarihi, Ankara 1995. 13. Gürün, Kamuran; Ermeni Dosyası, Ankara 1983. 14. Karal, Enver Ziya; Atatürk’ten Düşünceler, İstanbul 1986. 15. Kazım Karabekir; Enver Paşa Ve İttihat Terakki Erkanı, İstanbul 1967. 16. Kazım Karabekir; İstikbal Harbimiz, C. I, İstanbul 1995. 17. Koçak, Cemil; Türk-Alman İlişkileri (1923-1939), Ankara 1991. 18. Okyar, Osman; Milli Mücadele Dönemi Türk-Rus İlişkilerinde Mustafa Kemal, Ankara 1998. 19. Öke, M. Kemal; Ermeni Sorunu, Ankara 1991. 20. Özkaya, Yücel; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Cumhuriyet Tarihi, Ankara 1981. 21. Sonyel, Salahi R.; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Dış Politika, C. I-Iı, Ankara 1986 22. Soysal, İsmail; Türkiye’nin Siyasal Antlaşmaları (1920-1945), Ankara 1983 23. Süslü, Azmi; Ermeniler Ve 1915 Tehcir Kanunu, Ankara 1990. 24. Şahingöz, Mehmet; İzmir, İstanbul Ve Maraş’ın İşgali Üzerine Yapılan Protesto ve Mitingler, Ankara 1986. 25. Şıvgın, Hale; Trablusgarp Savaşı Ve 1911–1912 Türk İtalyan İlişkileri, Ankara 1989. 26. Şimşir, Bilal; Lozan Telgrafları I (1922–23), Ankara 1990. 27. Tansel, Selahattin; Atatürk Ve Kurtuluş Savaşı, Ankara 1965. 28. Tunaya, Tarık Zafer; Türkiye’de Siyasi Partiler, İstanbul 1952. 29. Turan, Refik Ve Diğerleri; Atatürk İlkeleri Ve İnkılâp Tarihi, Ankara 1999. 30. Turan, Şerafettin; Türk Devrim Tarihi I, Ankara 1991. 31. Uras, Esat; Tarihte Ermeniler Ve Ermeni Meselesi, İstanbul 1950 32. Ünal, Tahsin; 1700’den 1958’e Kadar Türk Siyasi Tarihi, Ankara 1974. 33. Yalçın, E. Semih, Atatürk’ün Milli Dış Siyaseti, Ankara 2000. 34. Yalman, Ahmet Emin; Gördüklerim Ve Geçirdiklerim, C. II, İstanbul 1970 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 419 Course Title Course Optic Code Term IX. Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Lecturer Course Assistant Asst. Proff. Serkan SARI The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Office Hours T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 4 School of Experiment Department of History Education Turkish In this course , student teachers develop their professional competence , occupations that require theoretical knowledge infrastructure , gain the ability to apply to the educational environment and teaching are intended to assume a positive attitude about the profession . learning Outcomes knowledge of the area and plan activities to ensure the development of skills . Prepared implement the activities in the classroom . Course management is effective. Activities during the implementation of the class provides the control . Student responses and evaluates the work . Learning and development recognizes individual differences between students in terms The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. course content review introducing General information about the plan period . 2. teachers in the school day as a result of this observation , monitoring and reporting of the notes to report 3. İn the school day of student as a result of this observation , monitoring and reporting of grades to report 4. course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing course content review introducing Course of the observation skills of the students to ask questions following the topic discussed with teachers reporting. 5. course content review introducing teaching methods , teaching materials and methods to keep the observation report 6. course content review introducing making lesson plans and activities related to the selection of topics and report observations of eclipses. 7. course content review introducing Course management and control of the activities of the class track and report 8. course content review introducing school issues discussed with school authorities , social and cultural characteristics of the school environment and school-parent relationships to be reported 9. course content review introducing of teacher candidates in their industry consultants prepare and teach a one-hour lesson plan form of the method of construction of this plan , however , on issues such as choice of materials and tools for evaluation 10. says, explaining one hour of teacher candidates related to this course consultants make a report, with the teacher evaluations 11. activities to meet the requirements in the subject area 12. activities to meet the requirements in the subject area 13. activities to meet the requirements in the subject area 14. activities to meet the requirements in the subject area 15. Overall rating 16. End-of -term exam Percentages of evaluation criteria Per (%) Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Course book by Auxilary Sources X X X X X X Description . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will 100 be given a certain amount of points . Ziya Selçuk, Okul Deneyimi ve Uygulama: Öğretmen ve Öğrenci Çalışmalarının Gözlenmesi, Ankara 2000; Barbaros Güncer, Okullarda Uygulama Çalışmaları-İlköğretim, YÖK/DB. Milli Eğitimi – Geliştirme Projesi Hizmet Öncesi Öğretmen Eğitimi, Ankara 1997; Sönmez Veysel, Yaratıcı Okul, Öğretmen Öğrenci, Yaratıcılık ve Eğitim, Ankara 1993; Fakülte-Okul İşbirliği, YÖK / Dünya Bankası Milli Eğitimi Geliştirme Projesi Hizmet Öncesi Öğretmen Eğitimi, Ankara 1998 VIII. YARIYIL Course Code TAE 402 Course Title Term Compulsory / optional Programme name Language of instruction precondition Disabled Students Student Responsibilities THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Office Hours T+U Salı, 15.00-16.00 2+0 Turkish Social and Economic History Credits 2 ACTS 3 Compulsory History Education Turkish İn case os necessity , they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course . Attending to the activies in the course . Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book Lecturer Asst.Prof.Mehmet KARATAŞ Course Assistant Course purpose Learning Outcomes Turkey in the issues of Social veal thoughts and suggestions for solutions to problems by supporting qualitative and quantitative data with experts and nonSocial rights, social justice, quality and cultural values, preservation of culture, environmental protection, occupational health and safety issues to Knows and uses historical methods Concepts related to history and history education, knowledge, skills and values will have. Date of theories about the science, the model explains the principles and generalizations have Related to the field to conduct an independent study in advanced. Turkey in the issues of Social veal thoughts and suggestions for solutions to problems by supporting qualitative and quantitative data with experts and nonSocial rights, social justice, quality and cultural values, preservation of culture, environmental protection, occupational health and safety issues to Knows and uses historical methods Concepts related to history and history education, knowledge, skills and values will have. Date of theories about the science, the model explains the principles and generalizations have Related to the field to conduct an independent study in advanced. The content of course , Teaching technics Weeks The content of course Teaching technics 1. Economic Life in Ancient Turkey Course review content Students read the text of the assessment 2. Anatolia Economic Facilities 3. Anatolian Seljuk Period of Islamic Economics and Students read the text of the Economic and Social Structure assessment 4. Organisation and the Classical Period of the Students read the text of the Ottoman Economy assessment 5. Sources of Ottoman Economic History Students read the text of the assessment 6. Ottoman Central Administration Students read the text of the assessment 7. Ottoman Financial Management and Grooming Students read the text of the System assessment 8. Visa Students read the text of the assessment 9. Merchant Guild Ottoman Cities Students read the text of the assessment 10. 17 10th and 18th century Ottoman Economy Students read the text of the assessment 11. Before the Tanzimat Period of Economic Development, Economic Developments in Ottoman Tanzimat Period Ottoman Industrialization Enterprises 12. 13. 14. Application of Economic Policy in the Early Years of the Republic Atatürk period and after the (Second World War up to) Economic Applications 15. Atatürk period and after the (Second World War up to) Economic Applications 16. End-of-term exam Rating Criteria Midterm exams Quiz Homework / Term Papers projects Participation to the course Other (File preparation, internship reports, field work reports, thesis Students read the text of the assessment Students read the text of the assessment Students read the text of the assessment Tartışma ve değerlendirme percentages (%) X 20 X 10 X 10 explanation To pass the course the student to determine the success of his activities in the process will be given a certain Textbook Auxiliary preparation). amount of points. End-of-term exam X 60 Tabakoğlu, Ahmet (1994), Türk İktisat Tarihi, İstanbul, dergah yayınları Karamursal, Ziya (1989), Osmanlı Mali tarihi Hakkında Tetkikler, Ankara, Ata Tabakoğlu, Ahmet (1994), Türk İktisat Tarihi, İstanbul, dergah yayınları Karamursal, Ziya (1989), Osmanlı Mali tarihi Hakkında Tetkikler, Ankara, Ata UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 404 Course Title Course Optic Code Term X. Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Precondition Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Assist. Prof. Tuğba KORHAN Student Responsibilities Instructor Lecturer Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Office Hours T 2+0 Credit 2 ECTS 4 World History in the 20th Century II Department of History Education Turkish The aim of the course of world history that shaped developments to understand the causes and consequences Join the world 's major developments of the 20th century , the historical foundations of these developments and to know the cause and effect relationship The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities 1. Course objectives , content, teaching methods , course content review introducing assessment methods, 2. II. At the end of World War II Cold War Era (1945- course content review introducing 1960) course content review introducing 3. 4. revival of the Soviet empire , the Soviet superiority in Europe Establishment of the socialist bloc in Europe course content review introducing course content review introducing 5. Balance Setting in Europe for Westerners course content review introducing 6. Far East Conflict 1950-1954 course content review introducing 7. Midterm Exam course content review introducing 8. Middle East Conflict 1955-1959 course content review introducing 9. Turkey after World War 1945-1960 course content review introducing 10. Changes in the Structure of Block 11. 12. Developments in the Eastern Bloc Developments in the Western Bloc 13. 14. II. After World War II in Asia Developments in the Middle East from 1960 to 1980 in World Politics 15. Turkish Foreign Policy 1960-1980 16. Overall Rating Percentages of evaluation criteria Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) Final Exam X 60 Description Per (%) X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 60 Course book by Paul Kennedy, Büyük Güçlerin Yükseliş ve Çöküşleri Fahir Armaoğlu: 20. Yüzyıl Siyasi Tarihi, İş Bankası yay. Hanry Kissenger: Diplomasi Oral Sander, Siyasi Tarih, I-II Mehmet Gönlübol, Olaylarla Türk Dış Politikası . determines the success of the course the student to pass his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZİYA GÖKALP FACULTY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY COURSE INFORMATION PACKAGE Course Code TAE 410 Course Title Course Optic Code Term VII Compulsory / Elective Programme Name Language of instruction Pre-requisites Students with Disabilities Compulsory Student Responsibilities Office Hours T+U 3+0 Kredisi 2 AKTS 4 Research Project İn The Field of Study Teacher Training Program All Programs Turkish None Students with disabilities need, with information about their own status submitted to the faculty may request the provision of necessary convenience Taking into account the content of the course , to prepare for the course . To participate in the activities carried out in the course , course given responsibilities ( homework, projects , discussion, reading of relevant sections , etc.). Fulfill . Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Asst. Proff. Serkan SARI, 8931 Learning Outcomes Concepts related to history and history education , knowledge, skills and values will have. Theories about the science of history , the model explains the principles and generalizations and generalizations are made. Student has acquired in the field of advanced theoretical and practical knowledge to comprehend. The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning 1. World government of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century to become a qualitative and quantitative research , Oral Presentation. 2. of Tsarist Russia and the Central Asian Turkic invasion of Central Asia 's independence movement Activities Presentation. Presentation. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 18th and 19th century. Qualitative and quantitative research in the Ottoman-Russian relations At the beginning of the new epoch of international and Turkish world of qualitative and quantitative research Of the 20th century to the beginning of the Turkish world an overview of qualitative and quantitative research Movement of the Renaissance and Reformation Visa The Eastern Question / Armenian Issue Blocs in Europe and World War qualitative and quantitative research studies The Nationalists and the National Pact of qualitative and quantitative research II. Middle East from World War I to the present qualitative and quantitative research Of the world during the Cold War and Turkey The transition to a multiparty political developments in the Turkish domestic politics ( 1946-1980 ) Atatürk era of Turkish foreign policy in the death of Atatürk and Turkish foreign policy today OTHER TOPICS İn the death of Atatürk and Turkish foreign policy today OTHER TOPICS OF qualitative and quantitative research Overall Rating Percentage of evaluation criteria Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Presentation. Description Per (%) Midterm Exams Quiz Assignments / Term Paper Project Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship reports , field work reports , thesis preparation , etc. ) . Final Exam X X X X X 20 05 10 15 10 X 40 Textbook Berkes, N., Türkiye’de Çağdaşlaşma, Auxilary Sources Paul Kennedy, Büyük Güçlerin Yükseliş ve Çöküşleri Fahir Armaoğlu: 20. Yüzyıl Siyasi Tarihi, İş Bankası yay. Hanry Kissenger: Diplomasi Oral Sander, Siyasi Tarih, I-II Mehmet Gönlübol, Olaylarla Türk Dış Politikası Determine the success of the student to pass the course of his activities in the process will be given a certain amount of points . . Enver Ziya Karal, Osmanlı Tarihi, V- IX. Şerif Mardin, Yeni Osmanlı Düşüncesinin Doğuşu Şerif Mardin, Jön Türklerin Siyasi Fikirleri Feroz Ahmed, İttihat ve Terakki ( 1908- 1914) Feroz Ahmed, İttihatçılıktan Kemalizme İlber Ortaylı, İmparatorluğun en uzun yılı Abdurrahman Şeref, Tarih Musahebeleri, Ahmet Cevdet Paşa, Tarih-i Cevdet, Berkes, N., Türkiye’de Çağdaşlaşma, Davison, R., Osmanlı İmparatorluğunda Reform, Mardin, Ş., Türk Modernleşmesi, Shaw, S., Osmanlı İmparatorluğu ve Modern Türkiye, Tunaya, T. Z., Türkiye’nin Siyasî Hayatında Batılılaşma Hareketleri, Öke, M. K.; Ermeni Sorunu, Ankara 1991. Özkaya, Y.; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Cumhuriyet Tarihi, Ankara 1981. Sonyel, S. R.; Türk Kurtuluş Savaşı Ve Dış Politika, C. I-Iı, Ankara 1986 Soysal, İ.; Türkiye’nin Siyasal Antlaşmaları (1920-1945), Ankara 1983 Süslü, A.; Ermeniler Ve 1915 Tehcir Kanunu, Ankara 1990. Course Code TAE 412 Course Name THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Hours Frday, 15.002+0 16.00 HISTORY OF TURKISH DEMOCRACY Credit ECTS 2 3 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 6 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the Department of History Education Turkish None course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Learning Outcomes Week 1. 2. Assistant Professor Doctor Tuğba KORHAN email: ttugbadogan@hotmail.com The aim of this course is to provide history teacher candidates to learn Turkish democracy history from Ottoman time to Turkish Rebuplic and developments in this period. 1. Discuss the concept of democracy 2. Explain the basic transformation stages of Ottomanism thought 3. Compare the basic features of constitutions in Turkish history 4. Analyze the effects of military coups to democracy in history of Turkish Republic 5. Comment on the developments for democracy in present-day Turkey and in the World. The course content , learning activities Course Learning Activities Learning Activities Introduction to the History of Democracy and Reading, explanation and discussion Resources Reading, explanation and discussion Evolution of the Idea of Ottomanism: Authoritarian Centralist Politics and the New Ottoman Opposition 3. Evolution of the Idea of Ottomanism: Young Turk Opposition and The Commitee of Union and Progress; II. Constitutional Era 4. "Üç Tarz-ı" Politics 5. Bab-ı Ali Raid ve ITC(The Commitee of Union and Progress) Power 6. 1921 Constitution and Legal Base of Independence War 7. 1924 Constitution and Single Party Period / 19451950 The Period of Transition to Multi-party System 8. Midterm Exam 9. 1950-1960 DP Power 10. 27 Mayıs Revolution 11. 1961 Constitution and New Institutions 12. 12th March Period 13. 12th September Period 14. 1982 Constitution 15. Developments in Turkey and in the World From 1990 to present 16. Final Exam Evaluation criteria Midterm exams Quiz Assignments / Term Papers Projects Attendance and Participation Other (File preparation, internship Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Reading, explanation and discussion Percentiles (%) X 20 05 X 10 15 X 10 Explanation To pass the course the student to determine the success of his activities in the Textbook Helpful resources Course Code TAE 418 The Name of Course reports, field work reports, thesis process will be preparation, etc.) given a certain End-of-term exam. X 60 amount of points. 1. Tanör, Bülent (2011). Osmanlı-Türk Anayasal Gelişmeleri (1789-1980). Istanbul: Yapı Kredi Yayınları 2. Çavdar, Tevfik (2008). Türkiye'nin Demokrasi Tarihi, 1839-1950. Ankara: Imge Kitabevi Yayınları. 1. Çavdar, Tevfik (2008). Türkiye'nin Demokrasi Tarihi, 1950'den Günümüze. Ankara: Imge Kitabevi Yayınları 2. Modern Türkiye'de Siyasi Düşünce (9 Cilt). Istanbul: Iletişim Yayınları 3. Ahmad, Feroz (2010). Bir Kimlik Peşinde Türkiye. Istanbul: Bilgi Üniversitesi Yayınları 4. Karpat, Kemal H. -Der. (2004). Osmanlı Geçmişi ve Bugünün Türkiye'si. Istanbul: Bilgi Üniversitesi Yayınları 5. Ortaylı, Ilber (2008). Osmanlı'da Değişim ve Anayasal Rejim Sorunu. Istanbul: Iş Bankası Kültür Yayınları ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Tuesday, 15.0016.00 Subject Area Textbook Review 2+0 Credit AKTS 2 3 Midterm 8 Compulsory/ Optional The Name of Program Language of Instruction Prerequisite Compulsory Disabled Students IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Responsibility of the Students Lecturer Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Mehmet Ali YASAR mayasar@dicle.edu.tr Course Assistant - The Aim of course Teacher candidates use textbooks used in the teaching of history in terms of form and content, examining concepts, theory and practice of learning and assessment History Turkish None books this information, they can ear in the development and adaptation. . Learning outcomes The content of course, Teaching technics Weeks 1. The content of course Introduction and organization Teaching technics The Examination of teaching technics 2. The concept of the textbook Expression, questions and Answers 3. in place of textbooks in the curriculum Expression, questions and Answers 4. in the textbook review and selection work in the catalog Questions and Answers 5. overall in textbook evaluation criteria Discussion 6. styles of textbook approaches in curriculum Discussion, Questions and Answers 7. Midterm Exam 8. styles of textbook approaches in curriculum Presentation 9. of the content of the textbook approaches in curriculum of the content of the textbook approaches in curriculum of the content of the textbook approaches in curriculum of the content of the textbook approaches in curriculum of the content of the textbook approaches in curriculum methodical flow of activities in the textbook and in this flow connections between events methodical flow of activities in the textbook and in this flow connections between events Presentation, questions and answers Review Presentation, questions and answers 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Rating Criteria questions and answers Practice Practise Presentation, questions and answers Presentation, questions and answers Presentation, questions and answers Percentages (%) Midterm Exams X Quiz Homework/term paper 20 05 X 10 Explanation Projects 15 Attending to the course X 10 Other (File, Internship report, Thesis and so forth). Final Exam X 60 • Course Book Auxiliary Sources Course Code TAe 452 THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optical Code Offices Hours T+U Salı, 15.00-16.00 2+0 Course tittle Educational Measurement and Evaluation Term Obligatory/ Optional The Name of Program Instruction Language Pre-requisite Disabled Students 8 Obligatory Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Öğr.Gör.Yunus AVANOĞLU, e-mail: yunusavanoglu@yahoo.com , Tel: 8958 Lecturer Course Assistant The Aim of Course Credit 2 AKTS 3 History Education Turkish None IN CASE OF NECESSITY, THEY CAN DEMAND SOME FACILITIES BY GIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THEMSELVES TO THE LECTURER Measuring and evaluating the basic knowledge, concepts, principles and skills to . Learning Outcomes At the end of this course the student; importance of the place. ropriate statistical methods. Course Content, Teaching Technics Weeks Course Content Teaching Activities 1. Course objectives, content, teaching methods, assessment 2. Measurement and Evaluation of the basic concepts 3. Qualifications required for measurement tools (Reliability) 4. Qualifications required for measurement tools (validity) 5. Measurement of Conduct 6. Classification of measuring instruments 7. Traditional approaches to assessment and evaluation (written exams and the oral examinations) 8. Exam 9. Traditional approaches to assessment and evaluation (short-answer-Correct WrongMatching) 10. Traditional approaches to assessment and evaluation (multiple choice tests) 11. Alternative assessment and evaluation approaches 12. Alternative measurement and assessment techniques 13. Measurement results on the statistical operations (basic concepts of statistics) 14. Measurement results on the statistical procedures (central tendency and dispersion measures) 15. Measurement results on the statistical procedures (standard scores and correlation) 16. General Consideration Rating Criteria Percentages (%) Explanation Midterm Exams X 20 Quiz 05 Homeworks/Term Paper X 10 Projects 15 Course attendance X 10 Diğer (Dosya hazırlanması, staj raporu, arazi çalışması raporu, tez hazırlanması vb). Dönem sonu sınavı X 60 Course Book Auxiliary Sources Tan, Şeref (2009). Öğretimde Ölçme ve Değerlendirme KPSS El Kitabı, 2.Baskı, Pegem Yay., Ankara - Course Code TAE 454 Course Name Atılgan, Hakan (Ed.) (2009). Eğitimde Ölçme ve Değerlendirme. 3.Baskı, Pegem Yay., Ankara. Tekindal, Satılmış vd.(2008).Eğitimde Ölçme ve Değerlendirme, Pegem Yay., Ankara. Atılgan, Hakan (Ed.) (2007). Eğitimde Ölçme ve Değerlendirme. Pegem Yay., Ankara. Erkan, Serdar ve Müfit Gömleksiz (2008). Eğitimde Ölçme ve Değerlendirme. Pegem Yay., Ankara Karip, Emin. Ölçme ve Değerlendirme. Pegem Yay., Ankara Nartgün, Zekeriya vd(2000). Ölçme ve Değerlendirme. Pegem Yay., Ankara Erkuş, Adnan. Sınıf Öğretmenleri İçin Ölçme ve Değerlendirme Kavramlar ve Uygulamalar, Pegem Yay., Ankara. THE UNIVERSITY OF DICLE ZIYA GOKALP EDUCATION FACULTY HISTORY DEPARTMENT COURSE INFORMATION Course Optic Code Consultation T+U Hours 2+0 TEACHING PRACTICE Credit ECTS 2 3 Semester Compulsory / Elective Program Code Language of instruction Pre-requisites 6 Compulsory Disabled Student In case of necessity, they can demand some facilities by giving information about themselves to the lecturer. Student Responsibilities Making provision to the course with regard to the content of course. Attending to the activities in the course. Being responsible for making Project, doing homework discussing and reading the some part of the course book. Instructor Course Assistant The aim of the course Department of History Education Turkish None The main purpose of this course is to provide the students with the opportunity that they are well–informed about educational field and about the basic methods Learning Outcomes and strategies and to ease their adaptation to teaching profession Organizes materials and learning environments in line with the Social Studies curriculum. Gives students the awareness of their responsibilities to humanity. Plans and organizes the curriculum in line with the process of teaching- learning environment. The course content , learning activities Week Course Learning Activities Learning Activities 1. Resources, Lesson and Practice in Information on Observation and Analysis-Face to face Schools. interview 2. Course description, objectives, syllabus and Observation and Analysis-Face to face Teaching Practice Photo File Information on the interview process. 3. Activity to be followed in the implementation Observation and Analysis-Face to face process, the preparation of the chart shows the interview distribution of observations and assessments by weeks 4. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 5. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 6. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 7. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 8. Midterm Exam 9. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 10. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 11. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 12. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 13. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 14. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 15. Advice on the assessment of the studies made in Observation and Analysis-Face to face practice school. interview 16. Final Exam Evaluation criteria Percentiles (%) Explanation Midterm exams X 20 To pass the Quiz 05 course the Assignments / Term Papers X 10 student to Projects 15 determine the success of his Attendance and Participation X 10 activities in the Other (File preparation, internship process will be reports, field work reports, thesis given a certain preparation, etc.) Textbook Helpful resources End-of-term exam. X 60 amount of points. Sands, M.-D.A. Özçelik (1997): Okullarda Uygulama Çalışmaları, YÖK/Dünya Bankası MEGP (1998): Fakülte-Okul İşbirliği, Öğretmen Eğitimi Dizisi, Ankara Selçuk, Z. (2000). Okul Deneyimi ve Uygulama,Ankara.