Bertillionage and Anthropometry
advertisement

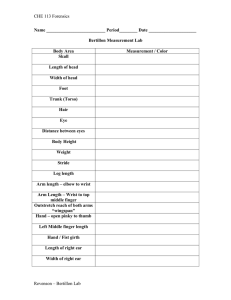
Bertillon and Anthropometry Anthropometry • Anthropometry refers to the measurement of the human individual for the purposes of understanding human physical variation. • This was used by Alphonse Bertillon to set up one of the first biometrics systems. Anthropometry • During the early 20th century, anthropometry was used extensively by anthropologists in the United States and Europe. One uses became the attempted differentiation between differences in the races of man, and it was often employed to show ways in which races were "inferior" to others. • Today, anthropometry plays an important role in industrial design, clothing design, ergonomics and architecture where statistical data about the distribution of body dimensions in the population are used to optimize products. Bertillon and Criminology • In 1883 Bertillon developed a system of identification depending on the unchanging character of certain measurements of parts of the human frame. • He concluded that if these measurements were made and recorded systematically every single individual would be found to be perfectly distinguishable from others. • The French adopted the Bertillon method into their criminal system, while the English was adopting the use of fingerprinting for identification Bertillon and Criminology • The system included 11 different measurements collected on over 100,00 cards, one for each individual. • Francis Galton was a key contributor as well, and it was in showing the redundancy of Bertillon's measurements that he developed the statistical concept of correlation. Galton however would eventually advocate for the use of the fingerprint as a form of identification. Bertillon and Criminology • Bertillon’s method was discredited in the case of the stolen Mona Lisa. – His system of measurements failed to identify the perpetrator. – Fingerprints where used to solve this case.