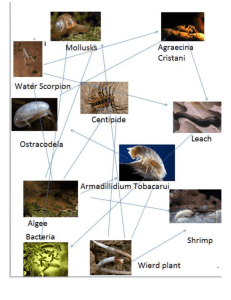
Food Webs
advertisement

Trophic Levels Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers Food Web Components • Producer (ex. plankton) • Consumer (ex. fish) • Decomposer (ex. bacteria) Food Chain vs. Food Web • Food Chain: path of energy from one organism to the next • Food Web: interconnected food chains Producers • A photosynthetic plant (use sun) or chemosynthetic bacterium (use chemical reactions) • Constituting the first trophic level in a food chain • An autotrophic organism (can produce its own food) Producers • Most producers use water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight to produce food for themselves and oxygen for other marine life. Ocean Plants: Producers - Producers make up the largest biomass of the ocean Producers help sustain marine ecosystems by providing oxygen and food for marine life Includes: phytoplankton, diatoms, and dinoflagellates, algal films, and seaweed What is a Consumer? • A heterotrophic organism that ingests other organisms or organic matter in a food chain. – – – – Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Detritivore Consumers - Herbivores • Animals that feeds mainly on plants/plankton Consumers - Carnivores • Flesh eating animals. Consumers - Omnivores • Organisms that eats both plants and animals Consumers - Detritovores • Organisms that feeds on dead plant or animal matter Consumer Levels Marine Primary Consumers • Filter Feeders • Grazers • Browsers Filter Feeders • Eat diatoms • Convert plant material into animal tissue • Ex. Barnaclesextend feathers into water Grazers • Eat algal films on rocks and surfaces • Most grazers are classified as Molluscs • Ex. Sea Slugs, Snails, Limpids Browsers • Eat algae • Browsers are an important element of coral reef ecology Marine Secondary Consumers • Cnidarians • Comb Jellyfish • Echinoderms • Arthropods • Molluscs • Vertebrates Cnidarians • Great abundance in the ocean • Corals, Sea Jellies, Anemones • Have stinging tentacles that stun prey and move them into the gut of the cnidarian • Feed by predation Comb Sea Jellies • Classified as Ctenophora • Hydroid in early stages of life then grow to become a free floater • Use cilia for movement • Tentacles are used for capturing food • Transparency helps with protection - makes them nearly invisible Echinoderm • • • • Organisms with bilateral symmetry Spiny skinned and have tube feet Water Vascular System Ex. Sea Stars, Sea Cucumbers, Sea Urchin Arthropod • Jointed legged invertebrate • Segmented body with hard exoskeleton • Eat by predation, browsing seaweed, scavengers • Ex. crabs, shrimps, sea spiders Molluscs • • • • Body without cavity, bilateral symmetry Wide range of feeding (primary grazers) Ex. Snails, Slugs, Squid, Bivalves Largest Mollusc: Octopus Vertebrates • • • • Internal skeleton, nerve chord, and backbone Mostly predators Largest predatory vertebrate: whale Ex. dolphins, seals, sea turtles Decomposers • An organism, often a bacterium, that feeds on and breaks down dead plant or animal matter, thus making organic nutrients available to the ecosystem • Puts nutrients back into the water in their elemental form to be used by producers as fertilizer Review • Producers (algae, sea weed, phytoplankton) • Primary Consumers (grazers, browsers, filter feeders) eat producers • Secondary consumers eat primary consumers • Scavengers (ex. crabs) eat dead plants and animals • Decomposers (ex. bacteria and fungi) eat the last bit of usable energy for organic matter