PERIODIC TRENDS - Vincent Sapone.Com
advertisement
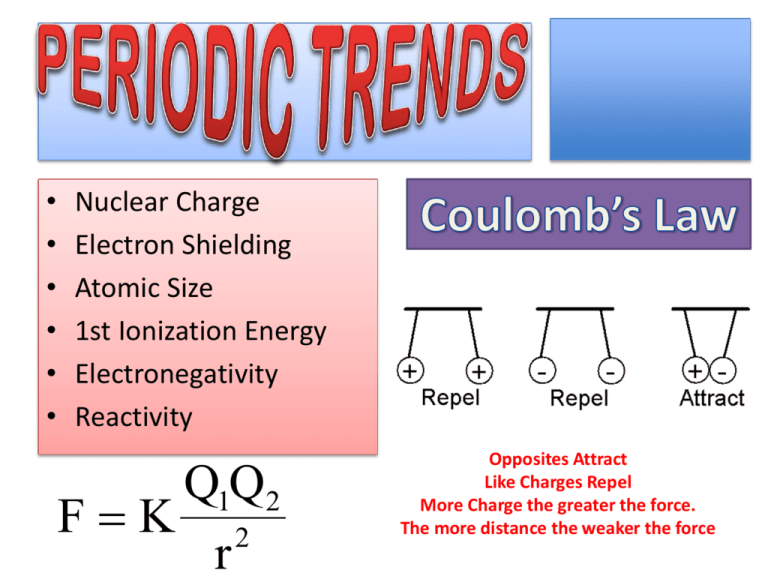
• • • • • • Nuclear Charge Electron Shielding Atomic Size 1st Ionization Energy Electronegativity Reactivity Q1Q2 FK 2 r Opposites Attract Like Charges Repel More Charge the greater the force. The more distance the weaker the force Nuclear Charge Increases Nuclear Charge Increases Total electric charge in a nucleus. It is equal to the number of protons. The Nucleus is what attracts electrons and keeps them in the atom. The more protons the stronger the nucleus can pull. 1 H Hydrogen 1 3 Li Lithium 7 11 Na Sodium 23 1 H Hydrogen 1 3 Li Lithium 7 11 Na Sodium 23 1 H Hydrogen 1 3 Li Lithium 7 11 Na Sodium 23 1 H Hydrogen 1 3 Li Lithium 7 11 Na Sodium 23 1 H Hydrogen 1 3 Li Lithium 7 11 Na Sodium 23 As you go down a group or column in the periodic table the number of energy levels increases. 1 H Hydrogen 1 3 Li Lithium 7 11 Na Sodium 23 As you go down a group or column in the periodic table the number of energy levels increases. 3 4 5 Li Be B Lithium 7 Beryllium 23 Boron 1 3 4 5 Li Be B Lithium 7 Beryllium 23 Boron 1 3 4 5 Li Be B Lithium 7 Beryllium 23 Boron 1 3 4 5 Li Be B Lithium 7 Beryllium 23 Boron 1 As you go across a period the number of energy levels remains constant. 3 4 5 Li Be B Lithium 7 Beryllium 9 Boron 11 - -- - +11 Electrons in an atom can shield each other from the pull of the nucleus. As you go down a group electron shielding increases. As you go across a period electron shielding is constant. Electron Shielding Increases Nuclear Charge Increases Electron Shielding Remains Constant Nuclear Charge Increases