Nectria perithecia
advertisement
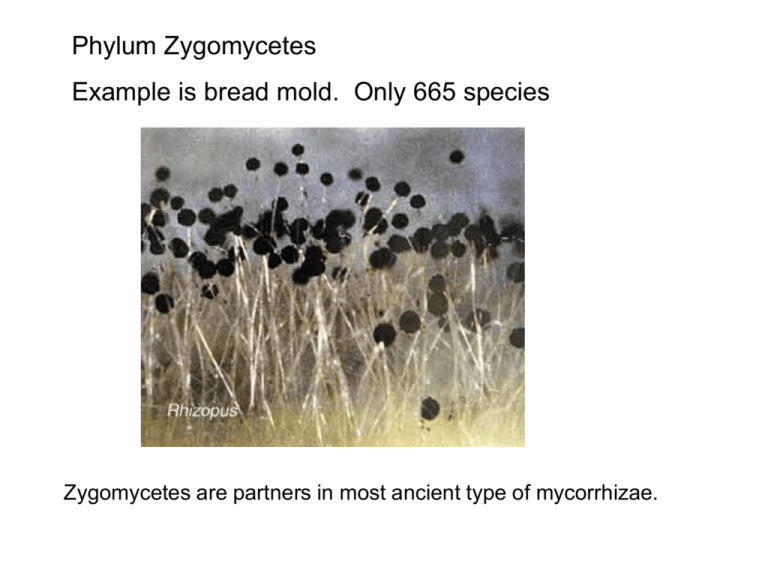
Phylum Zygomycetes Example is bread mold. Only 665 species Zygomycetes are partners in most ancient type of mycorrhizae. Phylum Ascomycetes, spores in sacs, 30,000 species. Nectria perithecia A species in this genus causes Beech Bark Disease http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/332/Ascomycota/ Black knot of cherry is caused by an Ascomycete fungus. Morels are ascomycete fungi Basidiomycetes carry spores on clubs; 16,000 species Agaricus sylvicola http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/332/Basidiomycota/Hymenomycetes/Agaricales/ Amanita muscaria http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/332/Basidiomycota/Hymenomycetes/Agaricales/ Pleurotus dryinus http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/332/Basidiomycota/Hymenomycetes/Agaricales/ Go to Tom Volk’s website for pictures of: Ganoderma (shelf fungus) Fomes fomentarius (carried by the ice man) Cladonia cristatella (lichen forming fungus) Tuber gibbosum (important mycorrhizal fungus) http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/toms_fungi/ Douglas fir and White pine seedlings with & without mycorrhizae Review of Mycorrhizal Types Type Morphology Fungus Plants Major Benefits Endo- VesiclesArbuscles In cell walls Zygos 80% of all Inorganic P Ecto- Btw cells. Mantle/sheath Basidios Ascos High-lat woodies Organic N, P H2O Ericoid Proliferate inside of cell walls; membrane envelopes hyphae. Ascos Some Ericaceae Organic N, P Endomycorrhizae-- ancient, widespread, and non-specific A stained arbuscule of Glomus mosseae in a leek root cell (a superb photomicrograph by Mark Brundrett see Fig 17 in Brundrett et al. 1984 Can. J. Bot. 62: 2128) A leek root packed with vesicles of its endomycorrhizal fungal partner. Colonization of a root by an endomycorrhizal fungus. Note hyphae, arbuscules and vesicles. (see Fig 21 in Brundrett et al. 1985 Can. J. Bot 63: 184) These structures in the "roots:" of early land plants fossilized in the Rhynie Chert (350 MYBP) are regarded as vesicles of an early endomycorrhizal fungus. http://www.mycolog.com/chapter17.htm Ectomycorrhizas of Laccaria bicolor with Populus tremuloides. http://www.mycolog.com/chapter17.htm Ectomycorrhizae Section of outer layers of an ectomycorrhizal root of Pinus strobus, showing some of the mantle and the Hartig net the latter formed by hyphae of the mycobiont, Pisolithus tinctorius, penetrating between the cortical cells of the root. Transverse section of an ectomycorrhiza of Pseudotsuga menziesii with Rhizopogon colossus showing the fungal mantle (brown in this example). Ericoid mycorrhizae help ericaceous plants survive on sites with slow decomposition (bogs, arctic, sand, etc.) Ericoid mycorrhiza of salal, Gaultheria shallon. Dark blobs are masses of fungal hyphae in cortical cells of root. Hyphae up to 80% of mass of root, but do not penetrate cell membrane.





