Content Management in Nursing Education Curricula - the ADN
advertisement

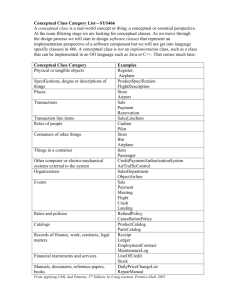
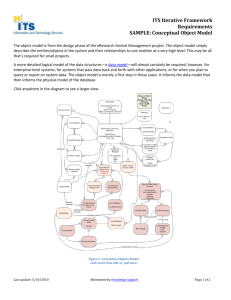
Understanding Concepts and the Conceptual Approach Infusing Conceptual Learning Into the Classroom North Carolina Associate Degree Nursing Council Fall Conference October 23, 2007 Jean Foret Giddens, PhD APRN-BC, Associate Professor College of Nursing , University of New Mexico jgiddens@salud.unm.edu Overview Foundations in Concepts Conceptual Approach in Nursing Conceptual Teaching and Learning Concept Based Curriculum What is a Concept? What is a Concept? A concept is an organizing principle or a unifying classification of information. Concepts are “mental constructions representing categories of information that contain defining attributes” (Walker & Advant, 1988) Humans begin conceptual thinking at an early age. Defining Attributes These are the “rules” or “parameters” used to identify, define and recognize a concept. These are important because these rules help all individuals or groups of individuals universally recognize the concept. Example: Concepts as Categories What concepts do the shapes below represent? What other concepts can you identify? Example: Concepts as Categories Concepts for Nursing Education Clarity Useful What are the Concepts for Nursing Practice? Concepts vs. Exemplars Concepts vs. Medical Diagnoses Concept Definition and Exemplars Concept: Intracranial Regulation Definition: Mechanisms that impact intracranial processing and function Exemplars: Traumatic brain injury Seizures Stroke Concept Development & Presentation Develop concepts according to template for consistency Types of/Categories Populations at risk/personal risk factors Assessment Nursing Care Primary Prevention Secondary Prevention Collaborative Care Interrelated Concepts Conceptual Learning What is Conceptual Learning? Process by which students learn how to organize information in logical mental structures. Focuses on organizing principles – the “cubby holes” in which the mind organizes facts into ideas. The difference between concept and content focused learning is… “the difference between facts of the Alaska oil spill and an understanding of the importance of environmental sustainability” (Erickson, 1998 p. 50). Promoting Conceptual Learning Means…… Focusing on big ideas – students anchor to specifics. Fostering deep learning, and deep understanding through connections and reflection (as opposed to surface learning). Developing student-centered learning with a purpose. Teaching Conceptually Focus is on Concept Exemplars provide content knowledge Application of content to interrelated concepts Application of other content to the concept Pulmonary Edema Anemia RDS Pnuemothorax PE AMI Pneumonia RSV COPD Asthma Oxygenation Example #1: Respiratory Failure Case Study Child – RF with Asthma Adult – RF with COPD Risk Factors Risk Factors Clinical Onset Clinical Onset Presenting Clinical Presenting Clinical Manifestations Collaborative Management Outcome Interrelated Concepts Manifestations Collaborative Management Outcome Interrelated Concepts Example #2 Long-term complications of DM Hypertension ASHD Renal Failure Diabetic Retinopathy Peripheral Neuropathy Peripheral Artery Disease Students struggle to grasp the long-term complications associated with DM. Tendency is to focus on each complication as separate entity What underlying concept or concepts could explain this? Example #3 Skill Acquisition: Securing an IV Catheter After starting an IV, what steps are necessary to properly secure the IV? What concept(s) apply? Example #4 Cause and Effect Model Motion Sensory Perceptual Oxygenation Perfusion Elimination Nutrition Skin Integrity Pain Other Teaching Strategies: Experiential Learning Games Jigsaw Role Play Virtual Experiential Learning (Neighborhood) Simulation Learning Rounds Concept Analysis Case Writing Clinical Judgment Model (Tanner, 2006) Linking to Nursing Research oNoticing oInterpreting oResponding oReflecting Final Thoughts on Conceptual Learning A focus on concepts in itself does not guarantee conceptual learning. Faculty must adopt active learning strategies to enhance conceptual learning. Ideally, concepts are woven through all courses and incorporated into clinical learning as well as didactic courses. Benefits of Conceptual Learning Content Management Concepts addressed across disease categories and populations. Fosters systematic observations about events or conditions that influence a problem. Emphasis on interrelated concepts Catalyst for challenging students to think at more advanced levels. Meets the needs of diverse learners Drawbacks It is different, thus faculty lack understanding Faculty resistant to changes Requires a different level of organization Lack of literature detailing steps What about NCLEX?