MCQ UNIT IV
advertisement

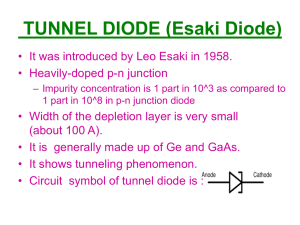
1. Which of the following is (are) diodes? A. Schottky B. Varactor C. Tunnel D. All of the above 2. Which of the following metals is (are) used in the fabrication of Schottky diodes? A. Molybdenum B. Platinum C. Tungsten D. All of the above 3. What are the typical ranges of reverse-bias current levels IS for low-power and high-power Schottky diodes at room temperature? A. Picoamperes, nanoamperes B. Nanoamperes, microamperes C. Microamperes, milliamperes D. Milliamperes, amperes 4. What is the voltage drop across Schottky diodes? A. 0 V to 0.2 V B. 0.7 V to 0.8 V C. 0.8 V to 1.0 V D. 1.0 V to 1.5 V 5. What metal(s) is(are) used in the construction of Schottky diodes? A. Molybdenum B. Platinum C. Tungsten D. Silicon E. Any of the above 6. For a 50-A unit, the PIV of the Schottky is about _____ compared to 150 V for the p-n junction variety. A. 25 B 50 C. 75 D. 100 7. Schottky diodes are very effective at frequencies approaching _____. A. 20 GHz B. 10 MHz C. 100 MHz D. 1 MHz 8. This is an approximate equivalent circuit for the _____ diode. A. Schottky B. varicap C. tunnel 9. What is the range of the varying capacitor CT in varactor diodes? A. 0 pF to 5 pF B. 2 pF to 100 µF C. 2 µF to 100 µF D. 2 pF to 100 pF 10. Which of the following areas is (are) applications of varactor diodes? A. FM modulators B. Automatic-frequency control devices C. Adjustable bandpass filters D. All of the above 11. The tuning diode is a _____-dependent, variable _____. A. voltage, resistor B. current, capacitor C. voltage, capacitor D. current, inductor 12. This is an equivalent circuit for the _____ diode. A. Schottky B. varicap C. tunnel 13. The varicap diode has a transition capacitance sensitive to the applied reverse-bias potential that is a maximum at zero volts and decreases _____ with increasing reverse-bias potentials. A. logarithmically B. parabolically C. exponentially 14. The majority of power diodes are constructed using _____. A. molybdenum B. platinum C. tungsten D. silicon 15. The current capability of power diodes can be increased by placing two or more in series. A. True B. False 16. The PIV rating of power diodes can be increased by stacking the diodes in series. A. True B. False 17. Which of the following diodes has a negative-resistance region? A. Schottky B. Varactor C. Tunnel D. Power 18. Which of the following semiconductor materials is (are) used in the manufacturing of tunnel diodes? A. Germanium B. Gallium C. Both germanium and gallium arsenide D. Silicon 19. What is the ratio IP / IV for gallium arsenide? A. 1:1 B. 5:1 C. 10:1 D. 20:1 20. What is the limit of peak current IP in tunnel diodes? A. A few microamperes to several hundred amperes B. A few microamperes to several amperes C. A few microamperes to several milliamperes D. A few microamperes to several hundred microamperes 21. What is the maximum peak voltage for tunnel diodes? A. 50 mV B. 100 mV C. 250 mV D. 600 mV 22. In which region is the operating point stable in tunnel diodes? A. Negative-resistance B. Positive-resistance C. Both negative- and positive-resistance D. Neither negative- nor positive-resistance 23. Which of the following diodes is limited to the reverse-bias region in its region of operation? A. Schottky B. Tunnel C. Photodiode D. Rectifier 24. Schottky diodes have _____. A. quick response time B. a lower noise figure C. both quick response time and a lower noise figure D. None of the above 25. Schottky diode construction results in a _____ uniform junction region and a _____ level of ruggedness. A. more, high B. less, high C. more, low D. less, low 26. In both n-type and p-type silicon materials, the _____ is the majority carrier in a Schottky diode. A. hole B. electron C. proton C. neutron 27. The barrier at the junction for a Schottky diode is _____ that of the p-n junction device in both the forward- and reverse-bias regions. A. the same as B. more than C. less than D. None of the above 28. A Schottky diode has _____ level of current at the same applied bias compared to that of the p-n junction at both the forward- and reverse-bias regions. A. a lower B. a higher C. the same D. None of the above 29. The PIV of Schottky diodes is usually _____ that of a comparable p-n junction unit. A. 1/2 B. 1/3 C. 1/4 D. 1/5 30. Varactor diodes are _____. A. semiconductor devices B. voltage-dependent C. variable capacitors D. All of the above 31. In varactor diodes, as the reverse-bias potential increases, the width of the depletion region _____, which in turn _____ the transition capacitance. A. increases, increases B. decreases, reduces C. increases, reduces D. decreases, increases 32. The normal range of reverse-bias voltage VR for varactor diodes is limited to about _____. A. 15 V B. 20 V C. 25 V D. 40 V 33. In the reverse-bias region of varactor diodes, the resistance RR in parallel with the varying capacitor is _____ and the series resistance RS is _____. A. very large, very small B. very large, very large C. very small, very large D. very small, very small 34. The majority of power diodes are constructed using silicon because of its higher _____ rating(s). A. current B. temperature C. PIV D. All of the above 35. The current capability of power diodes can be increased by placing two or more of the diodes in _____, and the PIV rating can be increased by stacking the diodes in _____. A. parallel, parallel B. series, parallel C. parallel, series D. series, series 36. In the negative-resistance region of tunnel diodes, as the terminal voltage increases, the diode current _____. A. remains the same B. decreases C. increases D. is undefined 37. The p-n junction of a tunnel diode is doped at a level from _____ to _____ times that of a typical semiconductor diode. A. one, several B. several, ten C. more than ten, several hundred D. one hundred, several thousand 38. The negative-resistance region of tunnel diodes can be used in the design of _____. A. oscillators B. switching networks C. pulse generators D. All of the above 39. The wavelength is usually measured in _____. A. angstrom units B. micrometers C. both angstrom units and micrometers D. None of the above 40. A photodiode which conducts current only when forward biased and is exposed to light. A. LAD B. LED C. PIN D. Photoconductor 41. What is the most commonly used color of an LED? A. Orange B. Blue C. Red D. Green 42. If the temperature of a semiconductor material increases, the number of free electrons A. Decreases B. Increases C. Remains the same D. Becomes zero 43. Varactor diode’s transition capacitance is directly proportional to the product of the permittivity of the semiconductor material and PN junction area but inversely proportional to its A. Resistance B. Voltage C. Depletion width D. Threshold voltage 44. A ________ is a light-sensitive device whose number of free electrons generated is proportional to the intensity of the incident light. A. Varicap B. Photodiode C. Schottky diode D. LED 45. Which of the following is NOT one of the three distinct regions in the characteristic curve of a diode? A. Forward bias region B. Reverse bias region C. Breakdown region D. Saturation region 46. Another name for saturation current in a diode, which arises from the fact that it is directly proportional to the cross-sectional are of the diode. A. Steady-state current B. Constant current C. Thermal current D. Scale current 47. How much voltage would you measure across the base-emitter junction of a silicon transistor at class A? A. 0 V B. 0.3 V C. 3.6 V D. 0.7 V 48. In an amplifier, the emitter junction is A. Forward biased B. Reverse biased C. Grounded D. Shorted 49. A manufacturer quotes in his specifications that a germanium diode conducts 50 mA at 1 volt. Determine the bulk resistance. A. 100 ohms B. 60 ohms C. 14 ohms D. 20 ohms 50. How many terminals does a programmable unijunction transistor (PUT) have? A. 4 B. 3 C. 2 D. 1 ANSWERS 1. D. All of the above 2. D. All of the above 3. C. Microamperes, milliamperes 4. A. 0 V to 0.2 V 5. E. Any of the above 6. B 50 7. A. 20 GHz 8. A. Schottky 9. D. 2 pF to 100 pF 10. D. All of the above 11. C. voltage, capacitor 12. B. varicap 13. C. exponentially 14. D. silicon 15. B. False 16. A. True 17. C. Tunnel 18. C. Both germanium and gallium arsenide 19. D. 20:1 20. A. A few microamperes to several hundred amperes 21. D. 600 mV 22. B. Positive-resistance 23. C. Photodiode 24. C. both quick response time and a lower noise figure 25. A. more, high 26. B. electron 27. C. less than 28. B. a higher 29. B. 1/3 30. D. All of the above 31. C. increases, reduces 32. B. 20 V 33. A. very large, very small 34. D. All of the above 35. C. parallel, series 36. B. decreases 37. D. one hundred, several thousand 38. D. All of the above 39. C. both angstrom units and micrometers 40. LAD 41. Red 42. Increases 43. Depletion width 44. Photodiode 45. Saturation region 46. Scale current 47. 0.7 V 48. Forward biased 49. 14 ohms 50.B.3