Document
advertisement

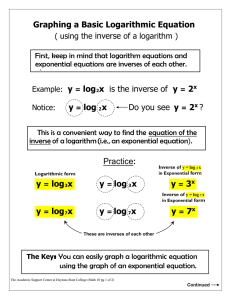
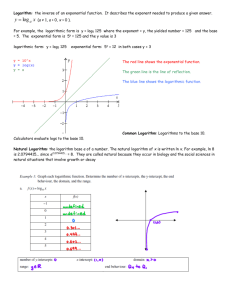
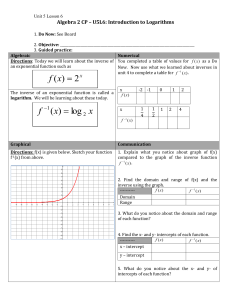
x 2 =4 X=2 y 2 =8 y=3 z 2 =6 Z=? Mathematicians use a LOGARITHM to find z and we will study logarithmic functions this unit A logarithm is the inverse of an ______________ Exponential function X Inverses Y X Y -3 1/8 1/8 -3 -2 1/4 1/4 -2 -1 1/2 0 1 1 2 2 4 3 8 Note exp fcn has H.A. and log fcn has V.A. 1/2 -1 1 0 2 1 4 2 8 3 These 2 graphs are reflections over the line _________ y=x If x = b y log b x = y then ________ Look at the log function graph: x is ____________________ always greater than 0 domain is _________ x>0 Value of asymptote Convert the Exponential Equations to Logarithms If x = y b log b x = y then ________ 1. 16 2 4 log 2 16 = 4 2. 100 10 2 log 10 100 = 2 3. 32 = 9 log 3 9 = 2 Note that we are changing form …. not solving Convert the Exponential Equations to Logarithms If x = y b log b x = y then ________ 4. 4 log 2 1 4 16 1 16 = -2 5. 10 1 0.1 log 10 0.1 = -1 6. 1 = 50 log 5 1 = 0 Write the Logarithmic Equations in Exponential Form If x = y b log b x = y then ________ 7. log 8 64 = 2 8 64 2 8. log 2 8 = 3 2 8 3 9. log 100 = 2 When no base is written ….it is a common log with base 10 10 100 2 Evaluate each Logarithm If x = y b Now we are solving for x y = log b x then ________ 1. log3 27 = x 3 27 x 3 3 x x3 3 2. 1 log6 6 =x 10 x 1000 1 6 6 x 6 6 x 3. log1000 = x 1 x 1 10 10 x x3 3 Evaluate each Logarithm If x = y b y = log b x then ________ 4. log 9 27 = x 9 27 x 3 3 2x 3 3 x 2 2x 3 5. log½ 1 8 =x 6. log816 =x 8 x 16 x 1 1 2 8 2 1x 2 3 1x 3 x3 2 2 3x 4 3x 4 4 x 3 Special Logarithm Values logb1=_____ 0 b x= 1 1 logbb=_____ b x= b x logbbx=_____ b x= b x Why are these good rules to know: (not on your notes) Find the y-intercept of (0,4) y log 7 ( x 7) 3 Substitute 0 for x y log 7 7 3 y 1 3 10 For example: log10x (The log key on the log x = _____________ calc. is the common log) 2 6 z Use the change of base Formula: Example: log x log 10 x log b x = log b log 10 b log 7 2.807 log 2 7 = log 2 log 2 6 z log 6 z log 2 z 2.585 not log 3 Parent Function: y log b x Vertical Shift: y a log b ( x h) k The k Horizontal Shift: y a log b ( x h) k The h Stretch/Compress: Reflection in x-axis: a 1 a0 0 a 1 On an earlier slide we graphed an exponential function and its inverse. This current slide is not in your notes – but lets prove why y=2x and y = log 2x are inverses. y = log 2 x x = log 2 y y2 x Switch variables to find inverse equations Convert from log to exp. form y log 2 ( x 1) 4 Look above at the parent function of y = log2x 4 1 1 1 x 16 15 x 16 Parent Function Y=log2x Horiz shift ________ Left 1 X Y Vert Shift = _______ Up 4 1/4 -2 1/2 -1 V Asymptote: ______ x = -1 Domain: __________ x > -1 1 0 15 ,0) 16 X-intercept:______ 2 1 4 2 0 = log 2 (x+1) +4 8 3 ( – 4 = log 2 (x+1) 2 -4 = x+1 Activity: Now lets see what you know. I will show you some problems. When I ask for the answer, please show the color of the matching correct answer. HW : WS 8.2 – which is is due next class. We will also be taking a quiz next class on these concepts. A. log24=16 B. log216=4 C. log416=2 D. log164=2 A. logbc=a B. logcb=a C. logab=c D. logac=b A. c b =a B. c a =b D. a b =c C. b a =c A. 9 3 =2 B. 3 2 =9 D. 2 9 =3 C. 2 3 =9 A. 3 B. 4 C. 16 D. 256 1 2 A. -4 B. -3 C. 3 D. 4 1 3 A. -4 B. -27 C. 27 D. 243 f ( x) log 3 x A. Translated down 1 and left 5 B. Translated up 1 and left 5 C. Translated left 1 and down 5 D. Translated right 1 and down 5 A. B. C. D. X 1 X1 X -1 X -1 A. B. C. D. (7,0) (8,0) (9,0) (10,0) 1 3 9 x A. B. C. D. X=1/3 X=27 X=-2 X=-27 2 A. B. C. D. X=-5 X=-3 X=3 X=7 x 1 1 16 3 27 x A. B. C. D. X=1.5 X=5 X=6 X=9 2 2 A. B. C. D. X=10/3 X=4 X=16 X=64 8x 32 x2 x A. B. C. D. X=-81 X=9 X=2/3 X=3/2 3 3 8 27 x 27 1 8 3 x 2 3 3 x 2 3 A. B. C. D. 1 3 X=-27 X=-9 X=-4 X=27 x 81 3 1 x 3 1x 4 x 4 4 Like HW 8.2