7.4 Notes
advertisement

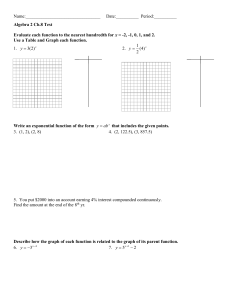
Logarithm: the inverse of an exponential function. It describes the exponent needed to produce a given answer. y log a x (a ≠ 1, a > 0, x > 0 ). For example, the logarithmic form is y = log5 125 where the exponent = y, the yielded number = 125 and the base = 5. The exponential form is 5y = 125 and the y value is 3 logarithmic form: y = log5 125 exponential form: 5y = 12 in both cases y = 3 The red line shows the exponential function. The green line is the line of reflection. The blue line shows the logarithmic function. Common Logarithm: Logarithms to the base 10. Calculators evaluate logs to the base 10. Natural Logarithm: the logarithm base e of a number. The natural logarithm of x is written ln x. For example, ln 8 is 2.0794415... since e2.0794415... = 8. They are called natural because they occur in biology and the social sciences in natural situations that involve growth or decay