acid rain by dylon gookin and todd ramsey
advertisement

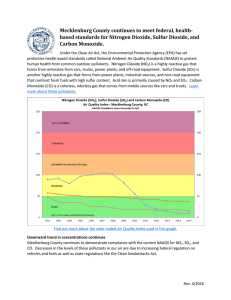
ACID RAIN BY DYLON GOOKIN AND TODD RAMSEY ACID RAIN DEFINITION • Precipitation, as rain, snow, or sleet, containing relatively high concentrations of acid-forming chemicals, as the pollutants from coal smoke, chemical manufacturing, and smelting, that have been released into the atmosphere and combined with water vapor: harmful to the environment. SERIES OF EQUATIONS • S (in coal) + O2 SO2 • These equations show the step-by-step process • 2 SO2 + O2 2 SO3 from the burning of coal to the forming of acid • SO3 +H20 H2SO4 rain, or sulfuric acid in aqueous form. • 2 NO2 + H2O HNO2 + HNO3 • This Reaction shows how Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water to give a mixture of nitrous acid and nitric acid. VEHICLE NITROGEN OXIDE EMISSIONS • At the high temperatures found in the gasoline and diesel engines of cars and trucks, N2 and O2 react to form a small quantity of NO which can be oxidized in the air to form NO2. The NO2 absorbs energy from the sunlight, and then decomposes into Nitric Oxide and Oxygen atoms. These atoms react with O2 to form O3. The ozone then decomposes into O2 and O. The O then reacts with water to form hydroxyl radicals. These hydroxyl radicals (OH) react with NO2 (emission) to form HNO3. INDUSTRY SULFUR OUTPUT • Coal burnt in industrial plants for energy often contains sulfur. Due to petroleum shortage, coal is being used more and more often and with higher sulfur concentrations. The sulfur in the coal reacts with O2 to form SO2 which further reacts with Oxygen gas again, to form SO3. The sulfur trioxide, being highly reactive, reacts with water to form Sulfuric acid. EFFECTS OF ACID RAIN • Acid rain reacts with – man-made substances such as • Marble / Limestone Structures – CaCO3 + H2SO4 Ca + SO4 + H2O + CO2 – Organic Structures • Forested ecosystems • Natural Wildlife (Aqueous) PREVENTION • Lower sulfur dioxide emissions from power plants: – Use a scrubber to blow powdered limestone (CaCO3) into the combustion chamber, where it is decomposed to lime and carbon dioxide. – CaCO3 CaO + CO2 – The lime then combines with the sulfur dioxide to form calcium sulfite: – CaO + SO2 CaSO3