Internal Carotid Artery Beginning
advertisement

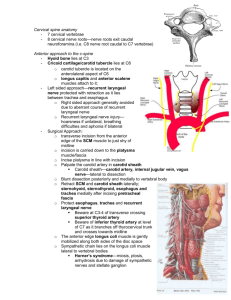
VESSELS AND NERVES OF THE NECK Main Arteries of the neck 1. Common Carotid Artery. 2. External Carotid Artery. 3. Internal Carotid Artery. 4. Subclavian Artery. Main Veins of the neck 1. Internal Jugular vein. 2. Subclavian vein. Main Nerves of the neck Vagus nerve. Accessory nerve. Hypoglossal nerve. Cervical part of sympathetic trunk. 5. Cervical plexus. 6. Phrenic nerve. 1. 2. 3. 4. Common Carotid Artery Beginning: the right from the brachiocephalic trunk behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left arises directly from the arch of aorta in the superior mediastinum of thorax. End: at the level of the upper border of thyroid cartilage (3rd cervical vertebra) by dividing into internal and external carotid arteries. At its end (or beginning of internal carotid) there is a dilatation called carotid sinus which is sensitive to blood pressure changes. It has pressoreceptors which are innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve. Course and Relations It ascends in the neck, enclosed in the carotid sheath with internal jugular vein and vagus nerve. Anterolateral relations: Skin, superficial fascia, investing fascia, sternocleidomastoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid and superior belly of omohyoid. Posterior relation: Transverse processes of lower 4 cervical vertebra, prevertebral muscles and sympathetic trunk. Medial relations: larynx, pharynx, thyroid gland, trachea and esophagus. Lateral relation: Internal jugular vein and (posterolaterally) vagus nerve External Carotid Artery Beginning: One of the two terminal branches of the common carotid artery. It begins at the level of the upper border of thyroid cartilage (3rd cervical vertebra). End: behind the neck of the mandible, within the substance of parotid gland by dividing into maxillary and superficial temporal arteries. At is beginning, the artery lies medial to the internal carotid artery but as it ascends in the neck passes backward and laterally. It is crossed by the posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid muscles. Relations Anterolateral relations: At its beginning, it is overlapped by sternocleidomastoid. Above, it is covered by skin, superficial fascia, investing deep fascia. It is crossed by hypoglossal nerve, posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid. Within parotid gland, it is crossed by facial nerve. Internal jugular vein first lies lateral then posterior to the artery. Medial relations: pharynx, internal carotid artery. Structures passing between external and internal carotid arteries: Styloid process, stylopharyngeus muscle, glossopharyngeal nerve, pharyngeal branch of vagus and parotid gland. Branches: 1. 2. 3. Superior thyroid artery: It arises from the anterior aspect and gives muscular branch to the sternocleidomastoid and superior laryngeal artery, it supplies the thyroid gland. Ascending pharyngeal artery: It emerges from the medial side of the artery. It ascends on the wall of the pharynx and supplies it. Lingual artery: It arises from the anterior aspect opposite the tip of greater horn of hyoid bone. It makes a loop which is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve, then it supplies the tongue. Branches: 4. 5. 6. Facial artery: It arises from the anterior aspect just above the lingual artery (may arise in one common trunk with lingual) & supplies the face. Occipital artery: It emerges from the posterior aspect of the artery. It ascends on the lower border of the posterior belly of digastric and accompanies greater occipital nerve to be distributed on the back of the scalp. Posterior auricular artery: It arises from the posterior aspect and runs on the upper border of posterior belly of digastric and reaches the auricle. Branches: 7. Superficial temporal artery: One of the two terminal branches of the ext. car. artery. It arises within the substances of the parotid gland and supplies the temporal region and scalp. 8. Maxillary artery: The other terminal branch of the ext. car. artery. It arises within the substances of the parotid gland and supplies many regions (later). Internal Carotid Artery Beginning: One of the two terminal branches of the common carotid artery. It begins at the level of the upper border of thyroid cartilage (3rd cervical vertebra). The artery enters the cranial cavity through the carotid canal to be distributed to the brain, eye, forehead and part of the nose. It ascends in the neck enclosed in the carotid sheath with the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve. It is crossed by the posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid muscles. It gives off NO BRANCHES in the neck. Relations A. B. Anterolateral relations: Below the digastric muscle: At its beginning, it is overlapped by sternocleidomastoid. Above, it is covered by skin, superficial fascia, investing deep fascia. It is crossed by hypoglossal nerve, Above the digastric: stylohyoid, stylopharyngeus muscle, glossopharyngeal nerve, pharyngeal branch of vagus, parotid gland and external carotid artery. Posterior relations: Sympathetic trunk, longus capitis and transverse processes of the upper 3 cervical vertebrae. Medial relations: pharynx and superior laryngeal nerve. Structures passing between external and internal carotid arteries: Styloid process, stylopharyngeus muscle, glossopharyngeal nerve, pharyngeal branch of vagus and parotid gland. Subclavian artery Beginning: the right from the brachiocephalic trunk behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left arises directly from the arch of aorta in the superior mediastinum of thorax. End: At the outer border of the first rib where it continues as the axillary artery. The scalenus anterior muscle when passing in front of the artery divides it into 3 parts; 1st, 2nd and 3rd. First part of Subclavian artery 1. 2. 3. Relations: Anterior: common carotid artery, vagus nerve and internal jugular vein. Posterior: Dome of pleura, apex of the lung and on right the right recurrent laryngeal n. Branches: Vertebral artery. Thyrocervical trunk. Internal thoracic artery. Second part of Subclavian artery Relations: Anterior: scalenus anterior muscle. Posterior: Dome of pleura, apex of the lung. Branches: Costocervical trunk, which gives 1. Superior intercostal artery. 2. Deep cervical artery Third Part of Subclavian Artery Course: enters the anteroinferior angle of posterior triangle and disappears behind the middle of the clavicle. Together with the brachial plexus, it is surrounded by extension from prevertebral fascia called axillary sheath. Branches: No branches, but sometimes the transverse cervical artery arises from it. Third Part of Subclavian Artery Relations: Anteriorly: Skin, superficial fascia, external jugular vein and investing deep cervical fascia. At its beginning it is partially covered by sternomastoid, and at its end it is covered by clavicle. Posteriorly: Lower trunk of brachial plexus and scalenus medius. Superiorly: Upper and middle trunks of brachial plexus. Inferiorly: Upper surface of the first rib. Internal jugular vein Beginning: at the jugular foramen as a continuation of the sigmoid sinus. End: by uniting with the subclavian vein behind the medial end of clavicle to form the brachiocephalic vein. The vein has two dilatation; at its beginning (superior bulb) and at its end (inferior bulb). It descends in the neck within the carotid Tributaries of Internal jugular vein 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Inferior petrosal sinus. Facial vein. Pharyngeal veins. Lingual vein. Superior thyroid vein. Middle thyroid vein. Occipital vein (occasionally).