the great war chapter 29
advertisement

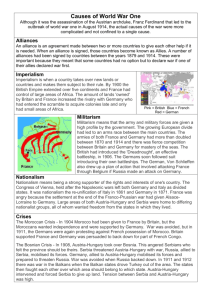
UNIT 10 – THE GREAT WAR CHAPTER 29 THE GREAT WAR The Great War, 1914–1918 Several factors lead to World War I, a conflict that devastates Europe and has a major impact on the world. Allied soldiers climbing over trenches on first day of the costly Battle of the Somme (July 1, 1916). SECTION 1 Marching Toward War SECTION 2 Europe Plunges into War SECTION 3 A Global Conflict SECTION 4 A Flawed Peace OBJECTIVES CORE OBJECTIVE: Analyze the causes and effects of World War I. Objective 10.1: Summarize the events that set World War I in motion. Objective 10.2: Describe the military events that developed on the Western and Eastern fronts. Objective 10.3: Analyze the how the conflict goes global and the Allies push to victory. Objective 10.4: Identify the effects of the Versailles treaty on European powers. THEME: At the beginning of the 20th century, a terrible war begins in Europe that will claim over 8 million lives. Chapter 29 SECTION 1 – MARCHING TOWARD WAR In Europe, military buildup, nationalistic feelings, and rival alliances set the stage for a continental war. CAUSES OF WWI Imperialism Competition for colonies stirs mistrust among European nations Militarism Mutual animosity spurs European countries to engage in arms race Militarism — policy of glorifying military power, preparing army Nationalism One type of nationalism inspired the great powers of Europe to act in their own interests. EX: gaining land to feel powerful Another emerged as ethnic minorities within larger nations sought selfgovernment. EX: Serbia wants to merge with Bosnia for an empire. Alliances In a complicated system of alliances, different groups of European nations had pledged to come to one another’s aid in the event of attack. RISING TENSIONS The Rise of Nationalism Europe enjoys peace in late 1800s but problems lie below surface Growing nationalism leads to competition among nations Nationalism in the Balkans leads many groups to demand independence Germany Under Otto von Bismark the 25 German states were united into the German Empire in 1871 after the Franco-Prussian War. Germany takes land from France. The ‘Iron Chancellor’ Otto von Bismarck focused on maintaining cordial relations with the other European powers. THE TRIPLE ENTENTE Germany’s Otto von Bismarck works to keep peace in Europe after 1871 Believes France wants revenge for loss in 1870 Franco-Prussian War Kaiser Wilhelm II becomes German ruler in 1888; Bismarck was replaced and policy shifted to aggressive expansion. Foreign policy changes begin in 1890 with dismissal of Bismarck alliance with Russia dropped; Russia then allies with France effort to strengthen German navy, which alarms Britain In response: Britain, France, Russia form Triple Entente alliance in 1907 •Austrian-Hungarian Empire controlled several ethic groups. •Many groups in Balkans win independence during early 1900s Saravejo •New nation of Serbia made up largely of Slavs •Serbian nationalists wanted to unite Serbs who lived in the Austrian-Hungarian Empire with Serbia. •Austria-Hungary annexes Slavic region Bosnia and Herzegovina (1908) •Serbia outraged, sees itself as rightful ruler of these Slavic lands FRANZ FERDINAND The immediate event sparking the Great War was the assassination of Archduke Francis Ferdinand in Sarajevo, Bosnia, on June 28, 1914. Member of the Black Hand, a Serbian nationalists group Garvillo Princip, a Serbian nationalist assassinated the Archduke. He was trying to gain allowances for his fellow Serbs who lived under Austrian rule. Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his family. Archduke was heir to the throne in the Austrian Hungarian Empire. His assassination June 28, 1914 eventually led to WWI. THE ASSASSINATION https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BCTIaiiGB4o GREAT WAR SPARKED At the time of his assassination, Francis Ferdinand, heir to the throne of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, had been visiting Bosnia, a new AustroHungarian province. Convinced that Serbia was behind the Archduke’s assassination, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia on July 28, 1914. Russia, as Serbia’s protector, began mobilization, or the readying of troops for war. Germany, an ally of Austria declares war on Russia on August 1. France, Russia’s ally will join the war a few days later. Britain will join by the end of August. Germany and Austria-Hungary formed the Central Powers Russia, France, Serbia, and Great Britain were called the Allies. The War in Europe, 1914–1918 When Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, the complex alliance system in Europe drew much of the continent into the conflict. THE CAUSES OF WWI Causes and the Assassination of the Archduke https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=njINCi9iIrA Causes of wwi History.com video http://www.history.com/videos/causes-of-world-war-i The Road to War—Assessment Which of the following was a cause of World War I? (A) Rising nationalism in European nations (B) Decrease in militarism among European powers (C) Pro-German propaganda in Britain (D) United States support of the Central Powers Why did the United States proclaim its neutrality in August 1914? (A) To please supporters of both sides (B) To protect its overseas investments (C) To allow time for preparedness (D) To aid Great Britain The Road to War—Assessment Which of the following was a cause of World War I? (A) (B) (C) (D) Rising nationalism in European nations Decrease in militarism among European powers Pro-German propaganda in Britain United States support of the Central Powers Why did the United States proclaim its neutrality in August 1914? (A) To please supporters of both sides (B) To protect its overseas investments (C) To allow time for preparedness (D) To aid Great Britain