1 Inheritance 1

To Start: Turn to p99-101
1. What is a locus?
2. Why is the fruit fly often used in genetics?
3. Why are certain characteristics more likely to be inherited together?
4. How did geneticists determine which genes were closer together?
5. What do we mean by “cross over value”?
6. What do geneticists use as symbols for the short arm of the chromosome and for the long?
To Start: Turn to p99-101
1. What is a locus? Position of a gene on a chromosome
2. Why is the fruit fly often used in genetics?
Short life cycle, defined phenotypes, easy to culture, only 4 chromosomes.
3. Why are certain characteristics more likely to be inherited together? If they are located close together on a chromosome.
4. How did geneticists determine which genes were closer together? Carrying out crosses and determining how frequently genes were separated by crossing over.
5. What do we mean by “cross over value”? High cross over value – genes are far away, low – genes are close and less likely to be separated at crossing over.
6. What do geneticists use as symbols for the short arm of the chromosome and for the long? p – short, q - long
3 of 45 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
4 of 45 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
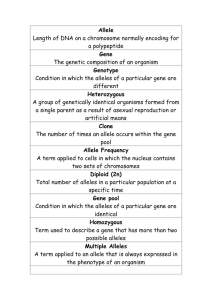
Genetics Terms
Write the word on one side of the card and the definition on the other.
Gene
Diploid
Allele
Haploid
Locus
Dominant
Recessive Genotype Phenotype
Homozygous Heterozygous Gamete
Zygote Homologous chromosomes
© Boardworks Ltd 2009 5 of 45
Key terms
Alleles are different forms of a gene. A gene is a sequence of bases on a DNA molecule that codes for a polypeptide.
Within a cell, there may be pairs of homologous chromosomes, which have the same genes at the same locus . The cell is diploid . The zygote (fertilised egg) and other somatic (body) cells are diploid.
If a cell contains one chromosome from each homologous pair , the cell is haploid . The gametes (sex cells) are haploid.
© Boardworks Ltd 2009 6 of 45
Key terms
If the alleles for a characteristic are the same, the organism is said to be homozygous for that characteristic. The organism is a homozygote .
If the alleles for a characteristic are different, the organism is said to be heterozygous for that characteristic. The organism is a heterozygote .
An allele is dominant if it is always expressed in the phenotype, even if the organism is heterozygous.
An allele is recessive if it is only expressed in the phenotype when the organism is homozygous.
© Boardworks Ltd 2009 7 of 45
Key terms
The genotype of an organism is determined by the combination of alleles it has.
The phenotype of an organism is determined by the genotype and the environment.
© Boardworks Ltd 2009 8 of 45
Representing alleles
A gene can be represented using a letter: upper case for the dominant allele, and lower case for the recessive allele.
For example, the allele for wing length in Drosophila can be either long (L) or short (l).
Genotype
LL
Ll ll
Phenotype homozygous dominant long wings heterozygous long wings homozygous recessive short wings
© Boardworks Ltd 2009 9 of 45
Task
Working in pairs:
- 1 person places their cards with the word facing up
- 1 person places their cards with the definition facing up
Time each other to see how quickly you can match the words to the correct definitions.
© Boardworks Ltd 2009 10 of 45