Naming Molecular Compounds
advertisement

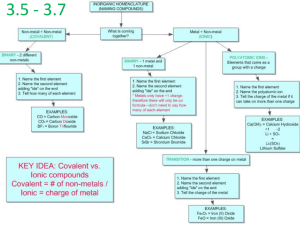
The anatomy of the periodic table Get out your periodic tables Know where the following are on your periodic table (p.t) Group A Group B Metals Nonmetals Metalloids (Semimetals) Note - aluminum is not considered a metalloid The anatomy of the periodic table Know where the following are on your periodic table (p.t) continued Transition metals Inner transition metals Alkali metals Alkaline metals Halogens Noble gases QuickTime™ and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Naming Compounds Ionic Molecular i.e. covalent Naming Molecular Compounds Molecules are made up of nonmetals Prefixes are used to represent numbers of atoms. See your text for prefixes Binary compounds end in -ide Examples Name? - Cl2O8 and OF2 Formula for? - dinitrogen tetroxide Answers - dichlorine octoxide, oxygen difluoride, N2O4 Naming Molecular Compounds Your turn. Try these. Name or write the formula for: Boron trichloride Dinitrogen tetrahydride N 2 O5 PF5 S4N2 CCl4 SO3 H2O Answers BCl3 N2H4 dinitrogen pentoxide Phosphorus pentafluoride Tetrasulfur dinitride Carbon tetrachloride Sulfur Trioxide Dihydrogen Monoxide Take ten minutes and work a few problems on the “Naming covalent compounds” side of your worksheet. Ions An atom that carries a charge The charge on the ion is called the Oxidation state or Oxidation Number Cation - positively charged atom Metals form cations CATions are PAWsitive Anion - negatively charged atom Nonmetals form anions Naming Cations Name the metal followed by the word ion Example Na - sodium - neutral element Na1+- sodium ion - cation of the element Another example: Mg - magnesium Mg2+ - Magnesium ion Naming Anions Ending changes are used for Anions Elemental anions will end in -ide Example Cl2 - chlorine - neutral element Cl1- - chloride - anion of the element Another example O2 - oxygen O2- Oxide Writing Formulas for Binary Ionic Compounds The periodic table tells you the charge for group A (aka - the representative elements) Group 1A - 1+ Group 2A - 2+ Group 3A - 3+ Group 4 - depends Group 5A - 3- Group 6A - 2 Group 7A - 1- Group 8A or (0) - does not form ions Naming Your turn: Name or write the symbol for the following: Aluminum Calcium Ion Ga3+ K Phosphide Iodine Nitrogen Sulfide Naming Binary Ionic Compounds Name the metal then the nonmetal with the ending changing to -ide The -ide tells the person it is a binary compound and the anion portion. Examples: MgCl2 K2S Magnesium Chloride Potassium Sulfide Writing Formulas for Binary Ionic Compounds All compounds are electrically neutral To write the formula, figure out how many cations and anions are needed so that the number of positives and negatives are equal. Find the least common multiple to figure out the total number of +’s and -’s. Then divide by the charge to find out how many of each atom is needed! If X1+ and Y2-, what would be the formula? X2Y - Charges total 2 +’s and 2 -’s Writing Formulas for Binary Ionic Compounds If X3+ and Y2-, what would be the formula? X2Y3 - Charges total 6 +’s and 6 -’s Find the formula for the following pairs of ions: Na1+ , P3- Answers: Na3P Sr2+ , N3- Sr3N2 Now: Finish side 1 of worksheet Work sections 1 - 4 on back of worksheet Work homework problems Naming Compounds Is there a metal? Yes No Ionic Molecular Does the compound contain a multivalent ion aka - transition metal or group B element Use prefixes to represent the number of atoms. Example: H2O Dihydrogen Monoxide CO2 Cabon Dioxide No Yes Name the cation first then name the anion Example: Lithium Fuoride Magnesium Carbonate Name the cation first Place a roman numeral Name the anion Example: Iron (II) Sulfate