Midterm Review by Student
advertisement

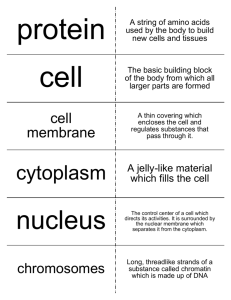
MIDTERM ClickBRANDON BY: to edit Master WILSON subtitle style Directory • • • • • • Midterm review and Chapter 1 pages 3-132 Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life 133-199 Chapter 3 Cell Structure 200-286 Chapter 4 Cells and Energy 287-335 Chapter 5 Cell growth Chapter 8 DNA to Proteins 1.Name this molecule which has a polar head and two non-polar tails and is used to make cell membranes. Phospholipid 2.Molecules (like lipids) that are “water fearing” and try to stay away from water and other polar molecules are called ___________________. Hydrophobic 3.Organisms like green plants that can make their own food are called ________________. Autotrophs 4.A “living thing” can also be called a(n) ____________________. Organism 5. Name this molecule Glycoprotien (protein with a sugar attached) 6. Tell the function of the molecule in previous question. Cell to cell recognition 7.The nitrogen base that is NOT found in RNA is _______________. Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Uracil Thymine 8.The process in which cells change as they grow to become different kinds of cells with different functions is called _________________. Differentiation 9.The name of the type of reproduction in which genetic material from two parents is combined to produce offspring. Sexual 10.The sum of all the chemical reactions that build up and break down molecules in cells is called _____________________. Metabolism 11. Cells always try to maintain a stable internal environment. This is called ____________________. Homeostasis 12. Which of the following molecules could you join together to make a polysaccharide? A B C D D 13. A molecule with an uneven distribution of electric charges (more positive on one side and more negative on the other) is called ____________. Polar 14.Which of the molecules below is an amino acid? A B C D B 15. The monomers (subunits) used to make proteins are ________________. amino acids nucleic acids sugars lipids nitrogen bases Amino acids (transfer RNA drops off) 16. Which of the following molecules could you use to build a DNA molecule? A B C D B- it’s a nucleotide 17.Animal cells store glucose in our tissues in the form of ________________. Starch glycogen cellulose glycoproteins ATP Glycogen 18. DNA and RNA are both _________________________. Amino acids nucleic acids carbohydrates lipids proteins Nucleic acids 19. The branch of science that studies all living things is called ___________. Biology 20. Water is a ________ molecule. Polar non-‐polar Polar – gives water properties like cohesion adhesion and capillary action 21. This type of chemical reaction is called ________________. Condensation/ dehydration reaction 22. Humans are _____ and _____. Unicellular Autotrophs Or Or Multicellular Heterotrophs Multicellular + Heterotrophs 23 , 24, 25. Name 3 characteristics shared by all living things. Demonstrates heridity (DNA) Made of cells Responds to stimuli Metabolism (require energy) Maintain homeostasis Reproduce (asexual or sexual) Grow/evolve/adapt 26. List the three parts of the Cell Theory ____________, ______________, & _____________. Cell is smallest unit of life, all living things made of cells, and all cells come from other cells. 27. Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the ______________ Activation energy 28. A substance that has a pH of 2 is ___________ times more/less acidic/basic than a substance with a pH of 5. 1000x, more acidic 29. Name D in this diagram showing an enzyme catalyzed reaction. Enzyme substrate complex 30. If this molecule was a nucleotide of RNA, tell one of the nitrogen bases that could be used here. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, or uracil 31. Most enzyme names end in the letters_______. Ase 32. Which part of a phospholipid is polar? Head Tails Head 33. Name the circled organelle and give the chemical equation of the reaction completed in this location. Mitochondria 34.The arrow is pointing to stacks called ________________ that are made up of individual discs called ________________ that contain the pigment ____________________. Grana, thylakoids, chlorophyll 35. Membranes that allow certain substances to pass through, but keep other out are said to be SELECTIVELY_____________ __. Permiable 36. Membrane proteins that pass all the way through the cell membrane are called ____________________ proteins. Integral or channel proteins 37. Any organism with a nuclear membrane and membrane bound organelles is called a _______________________. Eukaryote 38. These circled organelles are called ______ and are used for ______. Centrioles, cell division-> separate chromosome 39. Which organelle acts as the UPS of the cell to sort, modify, and package proteins and other molecules for storage or transport out of the cell? Golgi (ships vesicles) 40. Which organelle synthesizes long chains of this molecule? Ribosomes (synthesize means put together) 41. Name this organelle and write the chemical equation of the reaction completed here. Chloroplast: Photosynthesis 6CO2+6H2O C6H12O6+6O2 42. Define Biology. The study of life 43. Define cell Basic unit of life 44. Define organism An individual animal, plant, or single-celled life form 45. Define metabolism The chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life 46. What is DNA? Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is genetic cell of a cell 47. What is homeostasis? Stable equilibrium between interdependent elements 48. Define evolution Process in which living organisms are thought to have developed and diversified from earlier forms of life 49. Define adaptation The action/process of adapting to the environment around a living thing. 50. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Composed of cells Requires energy Maintains Homeostasis Reproduce Displays heredity Evolve/adapt Responds to stimuli 51. What is the scientific method? A process that is completed where knowledge is obtained 52. Define Independent variable A variable whose variation does not depend on that of another 53. Define dependent variable A variable whose value depends on that of another 54. Define constant Occurs continuously during an experiment 55. Define control Is base of the experiment 56. Define theory Based on facts and is a fact that has not been proven wrong 57. What is spontaneous generation? The supposed production of living organisms coming from non living matter. 58. What did Spallanzani do? Disproved spontaneous generation Experiment- Had 2 flasks had one sealed and one open 59. What did Redi do? Disproved abiogenesis by proving maggots come from flies laying eggs not from rotting meat 60. What did Needham do? Tested spontaneous generation and contradicted spallanzanis work 61. What did Pasteur do? Boiled broth with S curved flask and broke it to disprove spontaneous generation 62. What is a compound light microscope? Light microscope that has 2 lens. The ocular and objective lens 63. What is the total magnification equation? Ocular lens magnification multiplied by the magnification of the objective lens 64. Define resolution The ability of the microscope to differentiate two objects when you view them on a specimen slide 65. What are the parts of a light microscope and their functions? Body Tube Coarse Adjustment Knob Fine Adjustment Knob Arm Base Light Stage Stage clips Nosepiece 66. What is SEM? Scanning electron microscope 67. What is TEM? Transmission Electron Microscope Chapter 2Chemistry of Life 1. Define atoms The basic unit of a chemical element 2. Define element. A substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means and is made up of atoms with identical # of protons 3. What are compounds? A material made up of 2 or more elements 4. What is a chemical reaction? A process that involves rearrangement of the molecular or ionic structure of a substance, opposed to a change in physical form 5. What is a reactant? A substance that undergoes a change 6. What is a product? The result of a reaction 7. What is bond energy? The amount of energy it takes to break a bond 8. What does equilibrium mean? A state in which opposing forces or influences are balanced 9. What is activation energy? The energy it takes to start a reaction 10. What is an exothermic reaction? A reaction that gives off heat 11. What is an endothermic reaction? A reaction that takes in heat 12. What is covalent bonding? A chemical reaction that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule 13. What is ionic bonding? A chemical bond in which one atom loses an electron and another atom gains an electron 14. What is the pH scale? A scale that shows how acidic or basic a material is 0-6 is acidic 7 is neutral and 8-14 is basic. 15. What is an acid? A material that is 0-6 on pH scale 16. What is a base? A material that is 8-14 on pH scale 17. What is the relationship between hydrogen ions and pH? The more H+ added to a substance the more acidic it becomes also the more OH- added to a substance the more basic it becomes 18. What is cohesion? The ability to co exist with the same substance 19. What is adhesion? The ability to stick to a different substance 20. What is capillary action? The ability to draw a liquid due to surface tension upwards against the force of gravity 21. What is a solute? Substance dissolved in the solvent 22. What is a solvent? A substance that dissolves the solute 23. What are the special properties of water? Cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, polar, hydrogen bond and high boiling point 24. What is a catalyst? A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change 25. What is a enzyme? A substance produced by a living thing or organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific reaction 26. What is a substrate? The substance on which an enzyme acts 27. What is the picture below of? Lock-and-Key model 28. What is a monomer? A molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to for a polymer 29. What monomers and types of bonds are in proteins, carbs, lipids, and nucleic acids? Proteins- Amino acids Carbohydrates- Monosaccharides Lipids- Glycerol and fatty acids Nucleic Acids- Nucleotides 30. What is the picture below of? Amino acid 31. What is the picture below of? Fatty acid 32. What is the picture below of? Nucleic acid 33. What is the picture below of? Phospholipid Chapter 3- Cell Structure and Function 1. What is cell theory? Says that all living things are composed of at least one cell 2. What is cytoplasm? The gel like material with in a living cell 3. What is an organelle? Structures within a living cell 4. What is the difference between prokaryote and eukaryote? Eukaryote has a nucleus but prokaryote does not have a nucleus 5. What did Robert Hooke do? Looked at a cork through a microscope and noticed the cells in it 6. What did Anton Van Leeuwenhoek do? Is consider father of microscopy because of his work on microscopes with new methods of grinding and polishing tiny lenses of great curvature 7. What did Matthias Schleidon do? Was co founder of cell theory 8. What did Theodor Schwann do? Identified the cell as the basic structure of plant and animal tissue 9. What did Rudolf Virchow do? Built on the work of Theodor Schwann to prove cell theory 10. Define cytoskeleton? Microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence 11. What is a nucleus? A dense organelle present in most eukaryotic cells, typically a single rounded structure bounded by a double membrane, containing the genetic material 12. What does the endoplasmic Reticulum do? Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it and is involved in protein and lipid synthesis 13. What is a ribosome? A minute particle consisting of RNA and associated proteins, found in large numbers in the cytoplasm of living cells. They bind messenger RNA and transfer RNA to synthesize polypeptides and proteins 14. What is the Golgi Apparatus? A complex of vesicles and folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells, involved in secretion and intracellular transport. Is the UPS of the cell 15. What is a vesicle? Fluid/air filled sac 16. What is a vacuole? Contains fluid 17. What is mitochondria? The place where the process of respiration and energy production occur 18. What is a lysosome? Organelle in the cytoplasm containing enzymes enclosed in a membrane 19. What is a centriole? Involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division 20. What is a cell wall? Rigid layer outside of the membrane in plant cells that consists of cellulose 21. What is chloroplast? Contains chlorophyll and where photosynthesis takes place 22. What is a cell membrane? Semi permeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell 23. What is a phospholipid? Can form a lipid bilayer which is consisted in a cell membrane has a polar head and a non polar tail. Head is hydrophilic and tail is hydrophobic 24. What is the fluid mosaic model? Model of cell membrane composed of lipid bilayer with scattered protiens 25. What is selectively permeable mean? Barrier that lets some material in and out 26. What is a receptor protein? A substance that lets a cell recognize things 27. What is cholesterol? A sterol lipid, plays a central role in many process, and as a lipoprotein that coats the wall of blood vesses 28. What are channel proteins? Trans membrane proteins found in the phospholipid bilayer allow specific molecules to pass through, thus crossing the membrane 29. What are integral proteins? Tran membrane protein that completely spans the hydrophobic interior of the membrane 30. What are peripheral proteins? Protein that is bound to the surface of the membrane not embedded in the phospholipid bilayer 31. What is passive transport? Transport of a substance across a cell membrane by diffusion, use of energy is not required 32. What is diffusion? The intermingling of substances by the natural movement of their particles 33. What is a concentration gradient? The movement of a solute down its concentration gradient is called diffusion 34. What is osmosis? Diffusion of molecules through a semi permeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration of both sides is equal 35. Define Isotonic Having the same or equal osmotic pressure 36. Define Hypertonic Having a higher osmotic pressure than a comparison solution 37. Define Hypotonic Lower osmotic pressure than a comparison solution 38. What is facilitated diffusion? Transport of molecules across a membrane by carrier or channel protein 39. What is active transport? Movement of molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, requires energy 40. What is Endocytosis? The taking in of matter by a living cell by invagination of its membrane to form a vacuole 41. What is phagocytosis? Process where phagocytes engulf and digest microorganisms 42. What is Pinocytosis? The ingestion of liquid into a cell by budding of small vesicles from the cell membrane 43. What is exocytosis? A process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through the fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane Chapter 4Cells and Energy 1. What is ATP? Adenosine triphosphate major source of energy for cellular reactions 2. What is ADP? Adenosine diphosphate can be converted to ATP for energy storage 3. How does ATP and ADP relate? ATP is converted to ADP when a covalent bond is broke 4. What is the difference between heterotrophs and autotrophs? Autotrophs make their own energy heterotrophs have to consume energy 5. What is photosynthesis’ purpose? To make glucose from CO2 and H20 so plants can produce energy 6. What is the overall equation of photosynthesis? 6CO2+6H20 C6H12O6+6 O2 7. What is a pigment? A molecule that takes in light 8. What is the purpose of the 2 photosystems? Photosystem 1electron transfer Photosystem 2splitting of water molecule and generation of ATP 9. What is chlorophyll? Green pigment present in green plants for the absorption of light to provide energy for photosynthesis 10. What is a thylakoid? Sacs inside a chloroplast bounded by pigmented membranes on which the light reactions of photosynthesis take place and are arranged into stacks called grana 11. What is the equation for light dependent reactions? ADP + light + NADP+ ATP + NADPH+ O2 12. What is the equation for light independent reactions? ATP+ NADPH+ CO2 Glucose+ ADP+ NADPH+ 13. What is stroma? The gel like material surrounding grana 14. What is the difference between grana and granum? Grana is one stack Granum is multiple stacks 15. What is the calvin cycle? Light independent reactions 16. What is the ETC? Electron transport chain and is the end of aerobic respiration 17. What is the purpose of cellular respiration? To produce usable energy from sugars 18. What is the overall equation for cellular respiration? C6H12O6+6O2 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy 19. What is the equation for glycolysis? C6H12O6+2NAD+ +4ADP+2ATP 2 pyruvate+ 2NADH+4ATP+2ADP 20. What is the equation for the Krebs cycle? 2CoA+6NAD+ +2FAD+ +2ADP 4CO2+6NADH+2F ADH2+2ATP 21. What is the equation for ETC? 10 NADH + 2FADH2+ O2 34ATP+H2O+10NAD+ +2FAD+ 22. What is ATP synthase? An enzyme that can synthesize ATP from ADP. It is a axle that spins that turns the ADP and the Inorganic phosphate together to make it ATP 23. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Aerobic needs oxygen to function 24. Describe fermentation Lactic and alcoholic fermentation. The chemical breakdown of a substance by microorganisms Chapter 5- Cell Growth and Division 1. Define cell cycle The series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication. 2. What types of cells undergo mitosis? Eukaryotic cells 3. What is mitosis? A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus 4. What is cytokinesis? The cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, so there is two daughter cells 5. What is a parent cell? The original cell before cell division 6. What is a sister chromatid? 2 identical copies of a chromatin connected by a centromere 7. How is cell sized limited? Surface area to volume ratio limits it 8. What is a chromosome? Threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic info in the form of genes 9. What is a histone? Proteins found in a chromatin that the chromosome wrapped around 10. What is a chromatin? Chromosomes before they wrap around the histone 11. What is a chromatid? Each of the 2 threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division each contains a double helix of DNA 12. What is a centromere? Where the 2 chromatid connect 13. What is a telomere? The ends of the chromatid strands 14. What is interphase and what are the checkpoints of it? G1, S phase, and G2 G1- cell increases in size S phase- DNA instructions are duplicated G2-Continue to grow and produce new proteins 15. What is prophase? First stage before cell division where chromosomes become visible and chromatids disappear 16. What is Metaphase? 2nd stage of cell division where chromosomes line up in the middle of cell 17. What is anaphase? 3rd stage of Cell division where spindle fibers start to separate chromatid 18. What is telophase? The final phase of cell division between anaphase and interphase in which chromatids move to opposite ends of the cell and 2 nuclei are formed 19. What is the difference between cell division in plants and animals? A) Plant cells do not use a mitotic spindle to separate chromosomes. B) Plant cells separate chromosomes by attachment to the plasma membrane. C) In a plant cell, there is no nucleus around the chromosomes. D) There is no DNA replication before cell division in plant cells. E) Plant cells separate by growth of a cell wall and membrane in the middle of the cell. 20. How do parent cells compare to daughter cells? Identical Chapter 8From DNA to Proteins 1. What did Griffith do? Found transforming principle 2. What did Avery do? Continued with Griffiths work 3. What did Hershey and Chase do? Confirmed that DNA is the genetic material 4. What is bacteriophage? A virus at parasitizes a bacterium by infecting it and reproducing inside it 5. What are nucleotides? A compound consisting or a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group. Nucleotides form the basic structural unit of nucleic acids such as DNA 6. Who discovered the DNA structure and what is it? Watson and Crick Double helix 7. What is DNA composed of? 3 primary parts, two long polymers of simple units called nucleotides, with backbones made of (1) five-carbon sugars and (2) phosphate groups joined by ester bonds; (3) attached to each sugar is one of four types of molecules called bases (thymine and cytosine [classified as pyrimidines] and guanine and adenine [classified as purines]). It is the sequence of these four bases along the backbone that encodes information in order to manufacture proteins 8. What is Chargaff’s rule? A=T C=G 9. What did Watson and Crick do? Discovered double helix using xray crystallography 10. What are the types of bonds in DNA? Covalent and hydrogen 11. What is the structure of a nucleotide? 12. What is the structure of DNA? 13. What did Franklin do? Really found out the structure of DNA first but Watson and Crick stole it and were said to be the actual discovers because franklin was a women 14. What is DNA replication and what are its steps? Dna strand unzips and on each side the dna is duplicated with a=t and c=g 15. What is DNA polymerase and what are the 2 functions of it? An enzyme that carries out replication Speeds up the polymerization and assembles the DNA