Cells & Cellular Processes Exam Study Guide
advertisement

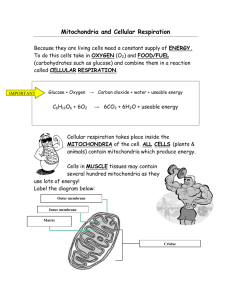
Cells and Cellular Processes Exam Study Guide 1. For each organelle/cell part, describe the function and in what type of cell(s) it can be found: Organelle Animal/Plant/Bacteria Function Cell Wall Plasma/Cell Membrane Plant, bacteria, fungi All Cells Structure, protection Maintains homeostasis by controlling what enters and leaves the cell Vacuoles Lysosomes Large Central in plants, small in animals Animals, plants Stores water, waste, and nutrients for the cell Contains digestive enzymes to break down worn out cell parts and foreign objects within the cell Ribosomes Centrioles All cells Animal Protein synthesis Used in mitosis in the animal cell Chloroplasts Plants Nucleus Animal, plants Mitochondria Animal, plants Golgi body/apparatus Animal, plant Makes glucose through the process of photosynthesis Controls cellular activities and contains chromosomes Produces ATP through the process of cellular respiration; more numerous in active cells such as cardiac and skeletal muscle Sorts, modifies, packages, and transports substances, such as proteins, that it receives from the ER 2. Describe three main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotes have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. 3. Explain the three parts of the Cell Theory. 1. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function for life. 2. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 3. Cells come from preexisting cells. 4. Describe three ways that a plant and animal cell differ from each other. 1. Plant have chloroplast and go through the process of photosynthesis. 2. Plants have a cell wall to give structure to the plant. 3. Plants have a large central vacuole that stores sap. 5. What is the difference between the way plants and animals store glucose? 1. Plants store glucose that they don’t use in the leaves and roots as starch. 2. Animals store glucose in the muscles and liver as glycogen. 6. Why is the nickname for mitochondria “the power house”? Mitochondria produce ATP (cellular energy) through the process of cellular respiration. 7. Write the chemical equation to photosynthesis and cellular respiration and compare the two. Photosynthesis: solar energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Cellular Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP The reactants of photosynthesis are the products of cellular respirations, and the reactants of cellular respiration are the products of photosynthesis. 8. If you don’t eat/ingest any protein or lipids, how do you still end up with proteins and lipids in your body? Proteins and lipids that are not obtained through your diet are synthesized by the ribosomes and ER of the cells. 9. What are reactants in a chemical reaction? Reactants are the molecules on the left side of the equations that are being changed by either putting them together or breaking them apart. 10. What are products of a chemical reaction? Products are on the right side of the equation and are the result of the chemical reaction. 11. Mitochondria, Rough ER, Smooth ER, and Golgi bodies have highly folded membranes. How is this beneficial for the cell? Folded membranes make interconnected compartments that increase the surface area for chemical reactions to take place in. The folding makes the cell more efficient in carrying out its processes. 12. Explain why plants have mitochondria in their cells if they already have chloroplasts. Although plants make glucose through the process of photosynthesis, the glucose does not provide energy for them unless it is broken down through the process of cellular respiration. In order for the plants to grow and carry out cellular processes it needs to produce ATP which is provided by the mitochondria through cellular respiration. 13. For the following, define, describe the movement of water, and what happens to the cell: Isotonic Solution Hypotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution Define: a solution that has an equal amounts of solutes on both sides of the cell membrane Define: a solution that has less solutes in it than the cell which has a higher solute concentration Define: a solution that has more solutes in it than is in the cell Water movement: water will move equally back and forth with no net change in concentration of solutes Water movement: Water will enter the cell Water movement: Water will exit the cell What happens to the cell?: the cell will remain the same size What happens to the cell?: the cell will enlarge; if it is an animal cell it could lyse; if it is a plant cell it will push against the cell wall What happens to the cell?: the cell will shrink; in a plant the membrane will pull away from the cell wall 14. Explain the difference between passive and active transport. Passive transport is movement of molecules across the membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration without energy being used. Active transport is the movement of molecules across the membrane through membrane proteins from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration which requires ATP (cellular energy). 15. Explain cell differentiation. Cell differentiation is the process of stem cells becoming specialized cells that perform specific functions. As cells develop specific genes on the cells chromosomes are turned on or off to allow the cells to develop into specialized cells that express different functions such as: long branching nerve cells that carry messages over great distances; long slender muscle cells that contract for movement; disc shaped blood cells to carry oxygen; flattened compacted epithelial cells to provide protection between the external environment and the internal environment. Other Vocab: Also be familiar with the following words/definitions. ATP chromosomes synthesis epithelial tissue paramecium contractile diffusion regulation excretion osmosis spontaneous generation gene manipulation efficient compartments advantage neurons resistant fatigue organelles TEKS tested: 4: The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells. The student is expected to: A: compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells B: investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules