Quoting
advertisement

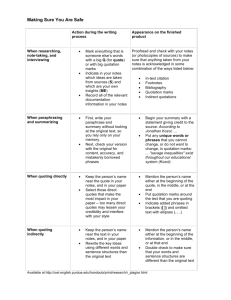
Quoting, Paraphrasing and Summarising In assessments you will be asked to refer to others’ writings and work to help you put together the assignment. Often, it is necessary to include what they say in your work. This can be done in three different ways: Quoting This is when you take a piece of someone else’s writing and insert it in your work. Quotes must be identical to the original author’s words, and must be attributed to the author (see over). For short quotes (eg less than 40 words they have quotation marks around them. Longer quotes (ie more than 40 words) do not have quotation marks but are in a freestanding, indented section of text. Quoting works best when an authors word will lose its meaning and power if paraphrased. Paraphrasing This is when you take someone else’s work and put it in your own words. Again it must be attributed to the author, but you don’t use quotation style. Paraphrasing works best when you want to use ordinary language and use an author’s point in your context. Examples: 1 Quotation: The Community and Voluntary Sector Working Party (2001) identify that ”For Maori, there is no strong sense of ‘other’ within the Whanau, hapu and iwi, and no direct equivalent to the term ‘volunteering’. It has been suggested this is likely to be a significant factor in Maori consistently under-reporting their ‘voluntary’ contribution in census and other research. 2 Paraphrase: When considering the amount of volunteering hours Maori officially report the Community and Voluntary Sector Working Party (2001) suggest that the reality may be a lot higher due to the difference in how Maori perceive the ‘volunteering’. 3 Short quotation and paraphrase together: Paraphrase: Quotation Thompson and Henderson (2006) places more emphasis on why people behave the way they do rather than what they do as a means to define an organisation’s culture. This includes understanding the organisation’s “beliefs, motivation, rituals, values, assumptions, world views, heritage, social system, epistemology, politics and environmental and economic factors”. (P. 98) Summarising This is when you take someone else’s main ideas and put them in your own words. Example: An organisation’s culture is often very difficult to define and describe. Rather than looking at how people behave as a description of an organisations culture, Henderson, Thompson and Henderson (2006) place a much bigger focus on why people behave the way they do, which they say creates an organisation’s culture. Why do we quote, paraphrase and summarise? To provide: An expert’s opinion or research to help you support any claims or arguments you are making Definitions and information to help you explore a topic Evidence of considering other points of view on a topic A poignant and succinct phrase or sentence that highlights what you are saying Your own synthesis of various points of view, building your own case or argument for what you are concluding or recommending Plagiarism Plagiarism is when a writer uses another’s thoughts, ideas or words and presents them as their own. A form of plagiarism is when someone presents thoughts, ideas or words without acknowledging and giving credit to the original author. Although this might not be their intention, without making appropriate acknowledgement, the writer is presenting the thoughts, ideas or words as if they were their own. This is considered a form of misconduct at Unitec as by plagiarising you are taking someone else’s intellectual property and submitting it as your own. To avoid being accused of plagiarism: Always state if you are using other’s facts, ideas and words Correctly reference others’ work Correctly quote, paraphrase and summarise in your work The three step note taking strategy recommended above can help to clearly distinguish from your reading summaries of ideas in your own words, direct quotes (with page references) of quotes you might use and your own thoughts/responses to each reading. Bibliography Paraphrasing and Summarising. Evergreen Writing Center. Dana Lynn Driscoll, Allen Brizee (2010) Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing. Retrieved from http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/563/1/