Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Part 1
a. Entrance Ticket
b. Access Prior Knowledge
c. Discuss Answers and misconceptions
Part 2
a. Review Classification and Binomial Nomenclature
b. Review Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
c. Draw and label structures in Plant and Animal Cells
d. Chart organelles and their structure and function
Part 3
a. Examine chloroplast structure and function in more detail
b. Examine mitochondria structure and function in more detail
c. Review the symbols for related elements
d. Discuss Photosynthesis and list main ideas and supporting details
e. Discuss Cellular Respiration and list main ideas and supporting details
Part 4
a. Review categories of producers and consumers
b. Answer media dependent questions on the Carbon Cycle
c. Review extensions and access if re-teaching is necessary
d. Answer any questions, make sure students have completed their activities
listed on the handouts.
Part 5
a. Discuss essay structure, expectations and rubric, and assign essay.
b. Exit ticket assigned for homework
Where do we get our energy?
On your entrance ticket, explain how
organisms get their energy.
Brainstorm and list what organisms
need in order to survive.
Food, water, shelter
Where do we get our food?
From consuming plants and animals!
What types of Organisms need Energy?
Let’s Review
Over time a five kingdom
system developed. At first
things were classified as
being either an animal or a
plant, but some things were
hard to categorize as being a
plant or an animal. Protista
includes plantlike, and animal-like
Organisms, and Monera includes
Bacteria.
All Types of Organisms Need ENERGY!!!
The Six Kingdom System
Over more time, the kingdom Monera which
categorizes bacteria which are also called
PROKARYOTES, got split into two Kingdoms.
MONERA
Eubacteria
Archaea Bacteria
Prokaryotes: are cells where
the DNA is not contained in a
membrane bound nucleus.
Most bacteria consist
of a single cell. Unicellular
organisms consist of one cell.
Introducing the Domain System
Scientists discovered more and more ancient
bacteria so they decided to to give it an entire
domain. The Archaea Bacteria love extreme
environments. All the other bacteria are
considered the Eubacteria.
Three Domain System
1. Archaea Bacteria (extremophiles/Prokaryote)
2. Eubacteria(Common Bacteria/Prokaryote)
3. Eukarya (Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia)
Notice that Eukarya contains all the Eukaryotic
organisms: The DNA is enclosed in a nucleus!!!
Taxonomic Classification/Binomial Nomenclature
Homo sapien
Human
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Chordata
Class
Mammalia
Order
Primates
Family Hominidae
Genus Homo
Species sapien
Panthera pardus
Panther
Animalia
Chordata
Mammalia
Carnivore
Felidae
Panthera
pardus
Did you know that when organisms were classified
according to this Linnaean system, their mode of
nutrition (The way they get energy) was used in
defining different Classes of organisms?
What is inside Plant and Animal Cells?
Plant and animal cells are multicellular organisms meaning
they are composed of two or more cells.
The cells of plants, animals and bacteria have some similar
structures and some different structures.
Inside various cells there are organelles with very specific
functions. Not all cells have the same types of organelles.
Does this plant have anything in common with the raccoon?
An Animal Cell
A video on organelles in an animal cell
A Plant Cell
A look at the organelles inside plant cells...
Let’s take a closer look at the Chloroplast and its
role in Photosynthesis! Chloroplasts look green
because the green pigment chlorophyll is present
in the thylakoid membrane.
The structure and function of the chloroplast
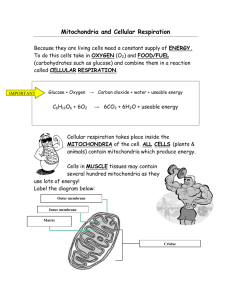
Now let’s take a look at the Mitochondria and its role in Cellular
Respiration!
The Mitochondria Function
So, let’s REVIEW some Main Ideas and Details about Photosynthesis.
Let’s think about what we have learned so far!
In the chloroplast is where photosynthesis occurs
• Sunlight energy powers photosynthesis
• Chlorophyll a green pigment captures the light energy
• Chloroplasts are found in plants and other photosynthetic organisms
but not found in animal and fungal cells
Producers are photosynthetic organisms
• Carbon dioxide, water and sunlight are converted to glucose and
oxygen
• Light energy is converted to chemical energy
• Glucose is formed from the reactants in photosynthesis
The products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen
• Glucose has a chemical formula of C6H12O6 and the oxygen gas
molecule has a chemical formula of O2
• Energy is stored in the carbon bonds of glucose
• Excess glucose not used is stored as starch or glycogen
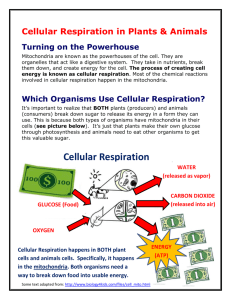
Now let’s REVIEW some Main Ideas and Details about Cellular
Respiration!
Cellular Respiration takes place in the mitochondria
• It is the process of breaking down glucose(sugars/food) into energy
• Mitochondria are in plant and animal cells
• First glucose is broken down to two 3-Carbon molecules in the
cytoplasm
The Mitochondria need the reactants glucose and oxygen
• Oxygen is needed to brake down the two 3-Carbon molecules to make
ATP.
• ATP (Adenosine tri-phosphate) has chemical energy stored in the
phosphate bonds.
• Mitochondria are the power houses of the cell because they get the
energy out of the food and convert it to a form our cells can use to do
work.
The products of cellular respiration are energy (ATP) and carbon
dioxide and water.
• CO2 is carried to the lungs and exhaled
• Some energy is transferred to the surrounding environment as heat
• Cellular respiration is almost the reverse reaction of photosynthesis.
The only difference is in the form of energy (Sunlight/electrical) in
making the glucose and the form of the energy (ATP/chemical) it is
converted to in the mitochondria.
Producers and Consumers
Producers
Autotrophs
Make their own energy
*Chemotrophs
*Phototrophs
Consumers
Heterotrophs
Must consume organisms
*Herbivores
*Carnivores
*Omnivores
*Detritivores
Producers such as phototrophs remove carbon dioxide
from the atmosphere to use in the process of
photosynthesis. Consumers must either consume an
autotroph or another heterotroph in order to get the
energy out of the food in the process of cellular
respiration. When their cells break down the food,
heterotrophs release carbon dioxide back to the
environment.
So, how are photosynthesis and cellular respiration linked?
Watch this 10 minute video if you need to review the processes.
How is Carbon Cycled through Earth’s Ecosystems?
Here watch one more video, this video will show you a more
simple diagram to understand how carbon is recycled
adhering to the laws of the conservation of matter. (Energy
is neither created nor destroyed it is only transformed.) Be
sure to watch and answer the questions on your handout!
The Carbon Cycle
How are Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration linked?
In Photosynthesis the reactants are carbon dioxide, water and sunlight
energy are converted to glucose and oxygen. Plants need more than
just water, and more than just soil. When animals eat plants, the
glucose and oxygen are broken down into chemical energy, water and
carbon dioxide.
The products of photosynthesis are the reactants of cellular respiration.
The products of cellular respiration are just what plants need to make
more food!
Now, you should be well prepared to write an essay explaining
how Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are linked!
Your essay must include an introductory paragraph with a topic
sentence, and a thesis statement. You should have at least two
body paragraphs, one detailing photosynthesis and the other
detailing cellular respiration. A conclusion paragraph explaining
the link between the two processes. You should use key
terminology you have learned, and cite several sources. You
may use your notes, your books or a review of this PowerPoint.
Please review the rubric, and if you have any questions, please
see me.
©Copyright-All rights reserved www.cpalms.org