Cranial nerve examination: CN1: Olfactory Block one nostril at a time
advertisement

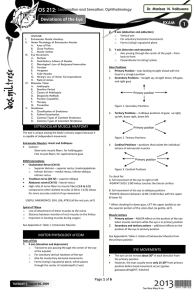
Cranial nerve examination: CN1: Olfactory - Block one nostril at a time, use different smells, eg soap / lemon / nothing / perfume CN2: Ophthalmic - Acuity: Snellen chart - Visual fields – equal distance between patient and examiner, use different numbers of fingers. - Visual acuity – distance is important, one eye at a time. CN3: Oculomotor - PLR. Use bright dazzling light. - Ipsilateral / direct, and contralateral / indirect responses. - Swinging light response, test for RAPD - Accommodation: bring finger towards eyes, check for pupil constriction - Pathologies: DOWN AND OUT Vasculopathic – diabetic, hypertensive. Aneurysm – aneurysm of internal carotid artery, Tumour – will see parasympathetic alterations first. Increased intracranial pressure with herniation / displacement CN3, CN4, CN6: extraocular motor function: - H pattern - Nasal side = left of page Cover-uncover tests for strabismus / tropia / phoria Inferior oblique Medial rectus Superior oblique Superior rectus Lateral rectus Inferior rectus CN4 pathology: CROSSED EYE Vasculopathic, Tumour, Congenital, Trauma CN6 pathology: NASAL UPSHOOT WHEN LOOKING IN Vasculopathic, Tumour, Increased intracranial pressure – long nerve, has a bend, sensitive to increased pressure. CN5: Trigeminal - Motor function: muscles of mastication. Palpate muscles, detect tenderness. Get patient to open mouth. If weakness in one side, jaw will deviate towards affected side. Can also do clench teeth – should feel the same - Touch: divided into crude touch / proprioception vs fine touch / temperature. Also divided into 3 segments of sensation: supra-orbital; between orbit and lips; inferior to lips. Ensure test both components of touch in all three areas, on both sides. Test within mouth, rostral component of hard palate. CN7: Facial - Smile, grimace / show teeth - Close eyes hard, raise eyebrows CN8: Vestibulocochlear - Hearing – finger rub or “sixty-nine” CN9: Glossopharyngeal - Uvula and soft palate should be symmetrical. Will deviate away from weakness CN10: Vagus - Look to side, cough: should see movement of larynx. Ask about change of voice. CN11: Accessory - Head turn strength: trapezius or sternocleidomastoid muscle CN12: Hypoglossal - Tongue protrusion: deviate towards lesion on protrusion, through weakness of affected muscles.